User:Charli Barbet/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Grb2 (1gri)''' | '''Grb2 (1gri)''' | ||
<StructureSection load='1gri' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1gri' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
| - | This is a default text for your page '''Charli Barbet/Sandbox'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
| - | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
| - | Grb2 protein: Growth Factor Receptor Bound Protein is a cytosolic protein made of 217 amino acids and weighing 25,206 Da. Ubiquitously present in the cell, this protein is involved in signal transduction and especially in the MAP kinase pathway. | + | Grb2 protein: Growth Factor Receptor Bound Protein is a cytosolic protein made of 217 amino acids and weighing 25,206 Da. Ubiquitously present in the cell, this protein is involved in signal transduction and especially in the MAP kinase pathway. Grb2 interacts mainly with tyrosine kinase such as EGFR once it’s been activated by ligand binding. This specific binding leads to the recruitment of GEF (like SOS1), stimulating the activation of other pathways. Several others interactions have been elucidated like the capacity of the protein to dimerise thus implicated in the growth of malignant cells. |
| - | Grb2 interacts mainly with tyrosine kinase such as EGFR once it’s been activated by ligand binding. This specific binding leads to the recruitment of GEF (like SOS1), stimulating the activation of other pathways. | + | |
| - | Several others interactions have been elucidated like the capacity of the protein to dimerise thus implicated in the growth of malignant cells. | + | |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 14: | ||
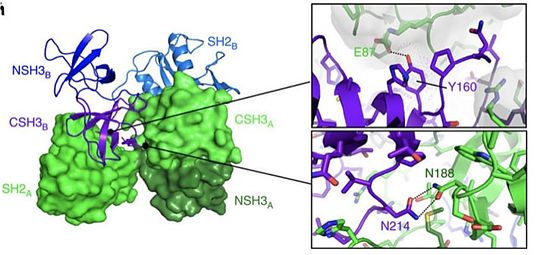
<scene name='75/750264/Sh2/1'>SH2 DOMAIN</scene>: | <scene name='75/750264/Sh2/1'>SH2 DOMAIN</scene>: | ||
| - | SH2 domain is a domain that is approximately 100 amino acids long and with a very conserved structure. Identified in in several human and rodent proteins such as phosphatases, TF, or adaptor like protein such as Grb2 for instance. | + | SH2 domain is a domain that is approximately 100 amino acids long and with a very conserved structure. Identified in in several human and rodent proteins such as phosphatases, TF, or adaptor like protein such as Grb2 for instance. This domain is therefore ubiquitous in several cellular signaling pathways.Typically, SH2 domain specifically recognize sites with phosphorylated tyrosine in different types of proteins. SH2 can for instance bind to the intracellular region of EGF leading in turn, to the formation of protein signalization complexes. This binding and the role of SH2 is thus, very important in the conversion of an extra-cellular signal in an intra-cellular signal able to give rise to diversified cellular responses or the expression of specific genes.It is also important to note that the SH2 domain can bind to other SH2 domains.However, a mutation in the specific binding site of SH2 can impede the interaction of two proteins and thus the formation of a protein complex. Therefore, mutations in SH2 can give rise to cellular dysfunction and lead to several diseases. |
| - | This domain is therefore ubiquitous in several cellular signaling pathways. | + | |
| - | Typically, SH2 domain specifically recognize sites with phosphorylated tyrosine in different types of proteins. | + | |
| - | SH2 can for instance bind to the intracellular region of EGF leading in turn, to the formation of protein signalization complexes. | + | |
| - | This binding and the role of SH2 is thus, very important in the conversion of an extra-cellular signal in an intra-cellular signal able to give rise to diversified cellular responses or the expression of specific genes. | + | |
| - | It is also important to note that the SH2 domain can bind to other SH2 domains. | + | |
| - | However, a mutation in the specific binding site of SH2 can impede the interaction of two proteins and thus the formation of a protein complex. Therefore, mutations in SH2 can give rise to cellular dysfunction and lead to several diseases. | + | |
<scene name='75/750264/Sh3/1'>SH3 DOMAIN</scene>: | <scene name='75/750264/Sh3/1'>SH3 DOMAIN</scene>: | ||
| - | The SH3 domain is a region of a protein that is approximately 50 amino acid long. Largely present in proteins associated to the membrane. | + | The SH3 domain is a region of a protein that is approximately 50 amino acid long. Largely present in proteins associated to the membrane. The domain is made of 5 to 6 Beta-sheets arranged in two antiparallel Beta-sheets. The linking region between the two Beta-sheets can contain alpha helices. This special conformation allows the arrangement of a hydrophobic pocket in which the ligand can bind. Typically, the binding region has a motif rich in Prolines: PXXP. This binding allows the formation of multi-proteins complexes involved in the translation of an extra-cellular signal and its conversion. The binding can thus be largely involved in gene expression and protein concentration. |
| - | The domain is made of 5 to 6 Beta-sheets arranged in two antiparallel Beta-sheets. The linking region between the two Beta-sheets can contain alpha helices. This special conformation allows the arrangement of a hydrophobic pocket in which the ligand can bind. Typically, the binding region has a motif rich in Prolines: PXXP | + | |
| - | This binding allows the formation of multi-proteins complexes involved in the translation of an extra-cellular signal and its conversion. The binding can thus be largely involved in gene expression and protein concentration. | + | |
ISOFORM: | ISOFORM: | ||
| - | |||
Nevertheless, Grb2’s isoform (Grb3.3) is also present in the cell and induces apoptosis. This isoform has a very similar structure to Grb2 but is truncated from an SH3 domain (from the 60th amino acid to the 100th ) resulting in a degradation of its SH2 domain and therefore in a loss of functionality. | Nevertheless, Grb2’s isoform (Grb3.3) is also present in the cell and induces apoptosis. This isoform has a very similar structure to Grb2 but is truncated from an SH3 domain (from the 60th amino acid to the 100th ) resulting in a degradation of its SH2 domain and therefore in a loss of functionality. | ||
| Line 92: | Line 79: | ||
By its essential role in the MAPK pathway, Grb3 can have effects on HIV-1 infections. Indeed, the replication of the virus is activated by Lymphocytes T replication. Yet lymphocytes T’s activation depend on the activation of the MAPK pathway dictated by the presence or not of grb3 in the cell. This pathway finally activates NFAT TF, a TF enhancing the LTR promotor of HIV-1 leading to its replication. | By its essential role in the MAPK pathway, Grb3 can have effects on HIV-1 infections. Indeed, the replication of the virus is activated by Lymphocytes T replication. Yet lymphocytes T’s activation depend on the activation of the MAPK pathway dictated by the presence or not of grb3 in the cell. This pathway finally activates NFAT TF, a TF enhancing the LTR promotor of HIV-1 leading to its replication. | ||
| - | == | + | == Relevance == |
[[Image:Y160.jpg|thumb|upright=3|test]] | [[Image:Y160.jpg|thumb|upright=3|test]] | ||
| Line 102: | Line 89: | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | == Relevance == | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
| - | |||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | == References == | ||
| - | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 19:10, 12 January 2017
Grb2 (1gri)
| |||||||||||