User:Morgane Crausaz/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | The lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in animal cells. Those are acidic vesicles and contain more than fifty digestive enzymes as proteases, nucleases, glycosidases, sulfatases, lipases, phosphatases phospholipases and esterases. The lumen’s pH of 4,5 is optimal for the hydrolytic enzymes. Indeed, acidic pH is important for the degradation of intracellular and extracellular compounds. | + | The lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in animal cells. Those are acidic vesicles and contain more than fifty digestive enzymes such as proteases, nucleases, glycosidases, sulfatases, lipases, phosphatases phospholipases and esterases. The lumen’s pH of 4,5 is optimal for the hydrolytic enzymes. Indeed, acidic pH is important for the degradation of intracellular and extracellular compounds. |
Particularly, there are enzymes able to cleave phospholipids on a specific site: those enzymes are named: '''phospholipases'''. These phospholipases are classified into four types, ''phospholipase A1, A2, C and D'' depending on the specific cleavage site of the substrate. Phospholipase A2 cleave the acyl-ester bonds of '''sn-2 position of glycerophospholipid'''s and they produce''' free fatty acids'''. | Particularly, there are enzymes able to cleave phospholipids on a specific site: those enzymes are named: '''phospholipases'''. These phospholipases are classified into four types, ''phospholipase A1, A2, C and D'' depending on the specific cleavage site of the substrate. Phospholipase A2 cleave the acyl-ester bonds of '''sn-2 position of glycerophospholipid'''s and they produce''' free fatty acids'''. | ||
Revision as of 12:35, 23 January 2017
|
This is a default text for your page Morgane Crausaz/Sandbox. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Contents |
Introduction
The lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in animal cells. Those are acidic vesicles and contain more than fifty digestive enzymes such as proteases, nucleases, glycosidases, sulfatases, lipases, phosphatases phospholipases and esterases. The lumen’s pH of 4,5 is optimal for the hydrolytic enzymes. Indeed, acidic pH is important for the degradation of intracellular and extracellular compounds.
Particularly, there are enzymes able to cleave phospholipids on a specific site: those enzymes are named: phospholipases. These phospholipases are classified into four types, phospholipase A1, A2, C and D depending on the specific cleavage site of the substrate. Phospholipase A2 cleave the acyl-ester bonds of sn-2 position of glycerophospholipids and they produce free fatty acids.
Substrate specificity depending on the phospholipase family :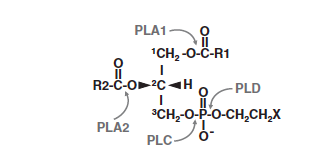
Function
Structure
Disease
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
</StructureSection>
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
