User:Morgane Crausaz/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Lipid oxidation products and in particular '''oxidized phospholipids (OxPL)''' are increasingly recognized as inducers of chronic inflammation characteristic of '''atherosclerosis'''. Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by accumulation of monocytes and T-cells due to lipid abnormalities. Increased levels of phospholipids’ oxidation products have been detected in different organs and pathological states, including atherosclerotic vessels. They can integrate the lipid membranes of cells and lipoproteins, act as ligands and may cause local membrane disruption. Indeed, they stimulate production of chemokines and adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells. | Lipid oxidation products and in particular '''oxidized phospholipids (OxPL)''' are increasingly recognized as inducers of chronic inflammation characteristic of '''atherosclerosis'''. Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by accumulation of monocytes and T-cells due to lipid abnormalities. Increased levels of phospholipids’ oxidation products have been detected in different organs and pathological states, including atherosclerotic vessels. They can integrate the lipid membranes of cells and lipoproteins, act as ligands and may cause local membrane disruption. Indeed, they stimulate production of chemokines and adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells. | ||
| - | Truncated oxidized-glycerophospholipids (ox-PLs) are bioactive lipids resulting from '''oxidative stress'''. They are generated by the oxidation of polyunsaturated '''fatty acid residues''', which are usually present in the phospholipids at the sn-2 position (cleave position of lysosomal phospholipase A2). Since the ox-PLs are transferred to lysosomes, the lysosomal phosphatase A2 plays an important role in the '''degradation''' of them. | + | Truncated oxidized-glycerophospholipids (ox-PLs) are bioactive lipids resulting from '''oxidative stress'''. They are generated by the oxidation of polyunsaturated '''fatty acid residues''', which are usually present in the phospholipids at the sn-2 position (cleave position of lysosomal phospholipase A2). |
| + | Since the ox-PLs are transferred to lysosomes, the lysosomal phosphatase A2 plays an important role in the '''degradation''' of them. In fact, lysosomal phosphatase A2 preferentially hydrolyzes truncated ox-PCs compared to non-oxidized phospholipids with two long acyl chains (like DOPC) under acidic conditions | ||
This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
Revision as of 12:01, 24 January 2017
|
This is a default text for your page Morgane Crausaz/Sandbox. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Contents |
Introduction
The lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in animal cells. Those are acidic vesicles and contain more than fifty digestive enzymes such as proteases, nucleases, glycosidases, sulfatases, lipases, phosphatases phospholipases and esterases. The lumen’s pH of 4,5 is optimal for the hydrolytic enzymes. Indeed, acidic pH is important for the degradation of intracellular and extracellular compounds.
Particularly, there are enzymes able to cleave phospholipids on a specific site: those enzymes are named: phospholipases. These phospholipases are classified into four types, phospholipase A1, A2, C and D depending on the specific cleavage site of the substrate. Phospholipase A2 cleave the acyl-ester bonds of sn-2 position of glycerophospholipids and they produce free fatty acids.
Substrate specificity depending on the phospholipase family :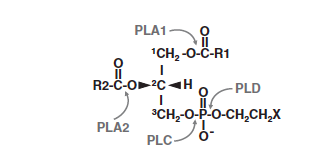
Structure
Function
Disease's treatment
Implication of the lysosomal phosphatase A2 in the detoxification :
Lipid oxidation products and in particular oxidized phospholipids (OxPL) are increasingly recognized as inducers of chronic inflammation characteristic of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by accumulation of monocytes and T-cells due to lipid abnormalities. Increased levels of phospholipids’ oxidation products have been detected in different organs and pathological states, including atherosclerotic vessels. They can integrate the lipid membranes of cells and lipoproteins, act as ligands and may cause local membrane disruption. Indeed, they stimulate production of chemokines and adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells. Truncated oxidized-glycerophospholipids (ox-PLs) are bioactive lipids resulting from oxidative stress. They are generated by the oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acid residues, which are usually present in the phospholipids at the sn-2 position (cleave position of lysosomal phospholipase A2). Since the ox-PLs are transferred to lysosomes, the lysosomal phosphatase A2 plays an important role in the degradation of them. In fact, lysosomal phosphatase A2 preferentially hydrolyzes truncated ox-PCs compared to non-oxidized phospholipids with two long acyl chains (like DOPC) under acidic conditions
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
</StructureSection>
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
