We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Estelle Metzger/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Humanized Roco4 == | == Humanized Roco4 == | ||
| - | The Roco proteins are serine/threonine specific kinases. This family consists of multidomain Ras-GTPases. Roco4 is 193 kDa and is identified as a key protein for proper stalk cell formation. Between the Dictyostelium roco genes and LRRK genes, there are many structural similarities, which are due to independant acquisitions of distantly related protein kinase domain. | + | The Roco proteins are serine/threonine specific kinases. This family consists of multidomain Ras-GTPases. Roco4 is 193 kDa and is identified as a key protein for proper stalk cell formation. Between the ''Dictyostelium'' roco genes and LRRK genes, there are many structural similarities, which are due to independant acquisitions of distantly related protein kinase domain. |
The characteristics of roco protein family, are a conserved core, consisting of a Ras-like GTPase domain called ROC (Ras of Complex proteins) and a COR domain (C-terminal of ROC), a C-terminal kinase domain and several N-terminal leucine rich repeats (LRR). Roco4 possesses one more domain : a C-terminal WD40 repeats. | The characteristics of roco protein family, are a conserved core, consisting of a Ras-like GTPase domain called ROC (Ras of Complex proteins) and a COR domain (C-terminal of ROC), a C-terminal kinase domain and several N-terminal leucine rich repeats (LRR). Roco4 possesses one more domain : a C-terminal WD40 repeats. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
This involves autophosphorylation of some residues in the activation loop. . Autophosphorylation not only results in the reorientation of the activation loop, but often also alters ATP binding and/or interaction with substrates. (Huse and Kuriyan 2002 kornev). In Roco4 kinase, there are four phosphorylation sites in the activation loop : Ser1181, Ser1184, Ser1187, and Ser1189. | This involves autophosphorylation of some residues in the activation loop. . Autophosphorylation not only results in the reorientation of the activation loop, but often also alters ATP binding and/or interaction with substrates. (Huse and Kuriyan 2002 kornev). In Roco4 kinase, there are four phosphorylation sites in the activation loop : Ser1181, Ser1184, Ser1187, and Ser1189. | ||
| - | The structure of Dictyostelium Roco4 kinase in complex with the LRRK2 inhibitor H1152 allows us to see that Roco4 and other Roco family proteins are essential for the optimization of the current, and identification of new LRRK2 kinase inhibitor. To have a Roco4 protein which have an active site resembling human LRRK2, researchers use a ''Dictyostelium'' Roco4 mutant (F1107L and F1161L) which is called humanized Roco4. | + | The structure of ''Dictyostelium'' Roco4 kinase in complex with the LRRK2 inhibitor H1152 allows us to see that Roco4 and other Roco family proteins are essential for the optimization of the current, and identification of new LRRK2 kinase inhibitor. To have a Roco4 protein which have an active site resembling human LRRK2, researchers use a ''Dictyostelium'' Roco4 mutant (F1107L and F1161L) which is called humanized Roco4<ref>Gilsbach BK, Messias AC, Ito G, Sattler M, Alessi DR, Wittinghofer A, Kortholt A; ''Structural Characterization of LRRK2 Inhibitors''; Journal of medicinal chemistry; 2015 May 14; 58(9):3751-6; PMID: 25897865; doi: 10.1021/jm5018779</ref>. |
== LRRK2-IN-1 == | == LRRK2-IN-1 == | ||
| + | |||
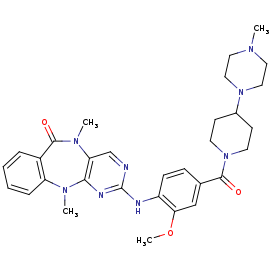
| + | [[Image:4K4-270.png]] | ||
Dire ce que c'est plus image | Dire ce que c'est plus image | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Humanized Roco4 and LRRK2-IN-1 interaction == | == Humanized Roco4 and LRRK2-IN-1 interaction == | ||
Revision as of 10:14, 26 January 2017
Humanized Roco4 bound to LRRK2-IN-1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Gilsbach BK, Messias AC, Ito G, Sattler M, Alessi DR, Wittinghofer A, Kortholt A; Structural Characterization of LRRK2 Inhibitors; Journal of medicinal chemistry; 2015 May 14; 58(9):3751-6; PMID: 25897865; doi: 10.1021/jm5018779
- ↑ Nom autors, titre article, livre, date, pages, PMID et doi à trouver sur pubmed
- ↑ Gilsbach BK, Messias AC, Ito G, Sattler M, Alessi DR, Wittinghofer A, Kortholt A; Structural Characterization of LRRK2 Inhibitors; Journal of medicinal chemistry; 2015 May 14; 58(9):3751-6; PMID: 25897865; doi: 10.1021/jm5018779