User:Pierre Rossignol/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='4tlf' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of one subunit of thiol dioxygenase from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudomonas_aeruginosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa] (PDB code [[4tlf]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4tlf' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of one subunit of thiol dioxygenase from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudomonas_aeruginosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa] (PDB code [[4tlf]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudomonas_aeruginosa ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''] is Gram-negative bacteria. It | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudomonas_aeruginosa ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''] is classified as a Gram-negative bacteria. It can be described as an opportunistic microorganism since it possesses the ability to colonize bodies of vulnerable patients, especially critically ill ones or those suffering from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cystic_fibrosis cystic fibrosis]. ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is one of the major causes of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hospital-acquired_infection Hospital-acquired infection] worldwide and a represents a serious threat to Public Health. <ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21450006</ref> |
| - | ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' can colonize many natural environments like soil, water and skin, because of its | + | ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' can colonize many natural environments like soil, water and skin, because of its faculty to utilize a wide range of organic matter and cope with different environmental conditions. ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' colonizes human hosts, therefore it can use [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cysteine cysteine] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methionine methionine] as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sulfur sulfur] a source of energy. <ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617</ref> |
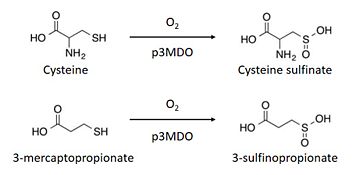
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 26 January 2017
Thiol dioxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21450006
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4591825/figure/F1/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.scd-rproxy.u-strasbg.fr/pmc/articles/PMC3136866/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?uid=130072&dps=1
- ↑ http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9I0N5
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/protein/Q9I0N5
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4073841