User:Pierre Rossignol/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
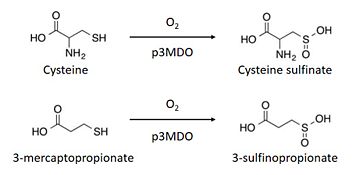
| - | The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thiol thiol] dioxygenation | + | The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thiol thiol] dioxygenation represents the initial [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Redox oxidation] step which allows the incorporation of a thiol to catabolic and biosynthetic pathways. A family of specific non-[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heme heme] mononuclear iron proteins are necessary to catalyse this reaction. During the reaction, each enzyme reacts efficiently with only one substrate. This family of enzymes is made up of cysteine dioxygenase, cysteamine dioxygenase, mercaptosuccinate dioxygenase and 3-mercaptopropionate dioxygenase. <ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617</ref> |
| - | The thiol dioxygenase of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a 3-mercaptopropionate dioxygenase (p3MDO) with a secondary cysteine dioxygenase activity. Therefore it can also be named 3-mercaptopropionate dioxygenase or cysteine dioxygenase. | + | The thiol dioxygenase of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a 3-mercaptopropionate dioxygenase (p3MDO) with a secondary cysteine dioxygenase activity. Therefore, it can also be named 3-mercaptopropionate dioxygenase or cysteine dioxygenase. |
| - | This is the first | + | This is the first example of cysteine dioxygenase homologue which utilizes a second substrate with near stochiometric coupling to dioxygen consumption.<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617</ref> |
The cysteine dioxygenase homologue from ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is expressed in low levels so this metabolic pathway is present in this organism. | The cysteine dioxygenase homologue from ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is expressed in low levels so this metabolic pathway is present in this organism. | ||
Revision as of 16:57, 26 January 2017
Thiol dioxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21450006
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4591825/figure/F1/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.scd-rproxy.u-strasbg.fr/pmc/articles/PMC3136866/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?uid=130072&dps=1
- ↑ http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9I0N5
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/protein/Q9I0N5
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26272617
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4073841