We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Estelle Metzger/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
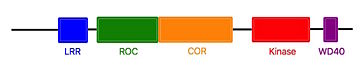
The COR and the ROC domains forms an inseperable tandem, a 300-400 long stretch of amino acids with no significant homology to other described domains. <ref name="Bernd2"/> | The COR and the ROC domains forms an inseperable tandem, a 300-400 long stretch of amino acids with no significant homology to other described domains. <ref name="Bernd2"/> | ||
| - | The Roco4 kinase structure consists of a canonical, two-lobed kinase structure, with an adenine nucleotide bound in the conventional nucleotide-binding pocket. It contains the conserved alphaC-helix and an anti-parallel beta sheets in the smaller N-terminal lobe. Other Alpha-helices and the activation loop with the conserved N-terminal DFG motif are localized in the bigger C-terminal lobe. | + | The Roco4 kinase structure consists of a canonical, two-lobed kinase structure, with an adenine nucleotide bound in the conventional nucleotide-binding pocket. It contains the conserved alphaC-helix and an anti-parallel beta sheets in the smaller N-terminal lobe. Other Alpha-helices and the activation loop with the conserved N-terminal DFG motif are localized in the bigger C-terminal lobe.<ref name="Bernd2"/> |
The activation loop and alphaC-helix together form the catalytic site of the kinase, an ATP binding site formed by a cleft between the two lobes. | The activation loop and alphaC-helix together form the catalytic site of the kinase, an ATP binding site formed by a cleft between the two lobes. | ||
For catalysis, the formation of a polar contact is essential. This polar contact takes place between Roco4 Lys1055 from the beta3-strand and the Glu1078 from the alphaC-helix. The amino acids Asp makes contact with all three ATP phosphates either directly or via coordination of a magnesium ion. Moreover, the amino acid Phe makes hydrophobic contacts to the alphaC-helix and the HxD motif, and leads for the correct positioning of the DFG motif. <ref name="Bernd2"/> | For catalysis, the formation of a polar contact is essential. This polar contact takes place between Roco4 Lys1055 from the beta3-strand and the Glu1078 from the alphaC-helix. The amino acids Asp makes contact with all three ATP phosphates either directly or via coordination of a magnesium ion. Moreover, the amino acid Phe makes hydrophobic contacts to the alphaC-helix and the HxD motif, and leads for the correct positioning of the DFG motif. <ref name="Bernd2"/> | ||
Revision as of 18:19, 26 January 2017
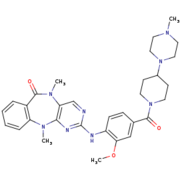
Humanized Roco4 bound to LRRK2-IN-1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Gilsbach BK, Messias AC, Ito G, Sattler M, Alessi DR, Wittinghofer A, Kortholt A. Structural Characterization of LRRK2 Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2015 May 1. PMID:25897865 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm5018779
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Gilsbach BK, Kortholt A. Structural biology of the LRRK2 GTPase and kinase domains: implications for regulation. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014 May 5;7:32. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032. eCollection, 2014. PMID:24847205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00741-9
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Taylor SS, Kornev AP. Protein kinases: evolution of dynamic regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011 Feb;36(2):65-77. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.006. Epub, 2010 Oct 23. PMID:20971646 doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.006