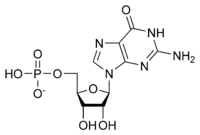
Structure
GMP synthetase is a homodimer enzyme, in which each monomer is composed of 693 amino acids and weights 76,2 kDa. Each monomer is composed of , encoded by a single gene: a N-terminal glutaminase domain (GATase domain), and a C-terminal synthetase domain.

Secondary structure of GMP synthetase
GTase domain:
The GATase domain, stretched from residue 27 to residue 216, is composed of a single structural domain. It is constituted of a central β-sheet surrounded by several α-helices. It contains composed of residues Cys104, His190, and Glu192.
Synthetase domain:
, stretched from residue 217 to residue 693, can be divided into three different sub-domains: an ATP pyrophosphatase domain (ATPPase domain) and two dimerization domains D1 and D2.
The ATPPase sub domain (residues 217-435) is composed of a 5-stranded parallele β-sheet-sandwiched between 9 α-helices.
The D1 sub-domain (residues 450-578), absent in bacteria and archaea, is involved in dimerization and substrate binding. It is constituted of an anti-parallel three-stranded β-sheet surrounded by five α-helices. The middle β-strand stretches out to form (Ile514–Tyr528) which interacts with the XMP binding site of the other subunit of the dimer.
The second dimerization sub-domain, D2 (residues 579-693) is similar to D1 sub-domain and they are superposed. This leads also to the D2 sub-domain to be superposed on the ATPPase sub-domain allowing the formation of the XMP active site in the synthetase domain.
Indeed, is located between the ATPPase sub-domain and the D2 sub-domain. When XMP is bound to it, it is allostericly regulated and covered by a lid motif (residues 368-408). Moreover, the XMP is wedged between a Pro-rich region (residues 438–441) and a loop (residues 383–385).
The synthetase domain binds several cofactors. Indeed, are bound to the ATPPase and D2 sub-domains. There are also Mg2+ and ATP which can bind.
Function
GMP synthetase is a cytosolic enzyme belonging to the glutamine amidotransferases family. These amidotransferases catalyse the amination of a wide range of molecules using the amide nitrogen of the side chain of glutamine. GMP synthetase is one of the three glutamine amidotransferases that plays a role in the de novo purine biosynthesis. Indeed, thanks to its bifunctional two domains, GMP synthetase catalyses the final step in the de novo synthesis of GMP from XMP in the presence of other cofactors including ATP, glutamine and water. The global reaction is summarized below:
ATP + XMP + L-glutamine + H2O --> AMP + diphosphate + GMP + L-glutamate.
Actually, the enzyme operates in two successive steps:
1) L-glutamine + H2O --> L-glutamate + NH3
2) ATP + XMP + NH3 --> AMP + pyrophosphate + GMP
First, the glutaminase domain generates ammonia from glutamine-hydrolysis when L-glutamine binds to the catalytic triad. Then, an activation step prepares the XMP for amination. Indeed, GPM synthetase activates its XMP substrate by adenylylation on the xanthine C2 oxygen, which can then be primed for attack by a nitrogen nucleophile. In order to perform the second reaction, the glutamine-derived ammonia needs to be transferred to the . This one is located in the active site of the synthetase domain, situated no far away from the catalytic triad. The ammonia translocation is enabled by a channel between the two active sites. This channel is formed thanks to a conformational change of the catalytic triad, further to its production. Thus, the activated XMP is aminated to produce GMP. Then, the GMP is released and will be used as a monomer in RNA.
Activation and inhibition
The presence of free Mg2+ is essential for activation of the GMP synthetase and a complex between ATP and Mg2+ can be formed but MgATP2− alone is not sufficient for catalysis. Moreover, the total chelation of free Mg2+ by ATP results of inactivation of the enzyme.
Inhibitor:
-Decoyinine is an uncompetitive inhibitor
-Inorganic pyrophosphate is the most effective inhibitor and it is competitive toward ATP.
-Psicofuranin is known to inhibit this enzyme.
-6-Diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine (DON) is a glutamine antagonist
Disease
Relevance