This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
IGF1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Insulin is a very important endocrine protein. Indeed, it is the only hypoglycemic hormone of the human body. This protein is secreted in the beta cells of the Langerhans’ islet in the pancreas and takes part in the glycogenesis. This molecule helps the transportation of glucose into the cells, thus reducing the blood sugar rate, contrary to glucagon. | Insulin is a very important endocrine protein. Indeed, it is the only hypoglycemic hormone of the human body. This protein is secreted in the beta cells of the Langerhans’ islet in the pancreas and takes part in the glycogenesis. This molecule helps the transportation of glucose into the cells, thus reducing the blood sugar rate, contrary to glucagon. | ||
| - | Insulin also has a huge effect on growth and thereby has a lot of structural similarities with its main associated growth factor: | + | Insulin also has a huge effect on growth and thereby has a lot of structural similarities with its main associated growth factor: IGF1, aka somatomedin. Both share lots of properties thanks to their 60% similarity. |
| - | + | IGF1 is a peptidic hormone of 69 amino acids which is secreted by the liver. | |
This protein deals with a large scale of regulations, from growth to nutrition and it is even implied in stress response, breeding and longevity.<ref>Patrick Jouandin. Rôle de la voie de signalisation Insuline dans le couplage des informations nutritionnelles et développementales au cours de l'ovogenèse chez la drosophile. Sciences agricoles.Université Nice Sophia Antipolis, 2013. Français.<NNT : 2013NICE4102>.<tel-00932409></ref>. | This protein deals with a large scale of regulations, from growth to nutrition and it is even implied in stress response, breeding and longevity.<ref>Patrick Jouandin. Rôle de la voie de signalisation Insuline dans le couplage des informations nutritionnelles et développementales au cours de l'ovogenèse chez la drosophile. Sciences agricoles.Université Nice Sophia Antipolis, 2013. Français.<NNT : 2013NICE4102>.<tel-00932409></ref>. | ||
It is the main actor in primary growth cell control. | It is the main actor in primary growth cell control. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Biological structures and interactions == | == Biological structures and interactions == | ||
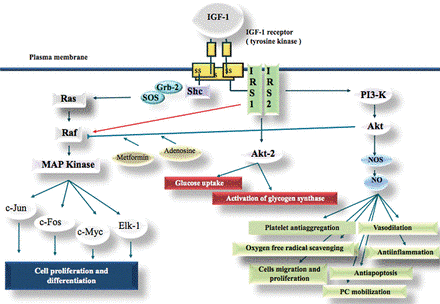
| - | In the pituitary gland inside the brain, Growth Hormone (GH) is secreted and its release enable transcription of IGF-1 in liver and depending on the nutritional state, a paracrine or autocrine activation | + | In the pituitary gland inside the brain, Growth Hormone (GH) is secreted and its release enable transcription of IGF-1 in liver and depending on the nutritional state, a paracrine or autocrine activation IGF1 occurs. IGF1 then acts as a ligand and can interact with Insulin Receptor protein and Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein. |
=== Structures === | === Structures === | ||
| - | + | IGF1 is a 8.28 kDa protein consisting of 69 amino acids. | |
The coding RNA of this protein creates 4 isoforms differing from each other due to RNA splicing. | The coding RNA of this protein creates 4 isoforms differing from each other due to RNA splicing. | ||
| - | Nevertheless, all 4 of them have cysteine residues that are able to make disulfide bond. This enable them to link to | + | Nevertheless, all 4 of them have cysteine residues that are able to make disulfide bond. This enable them to link to IGF1 receptor. |
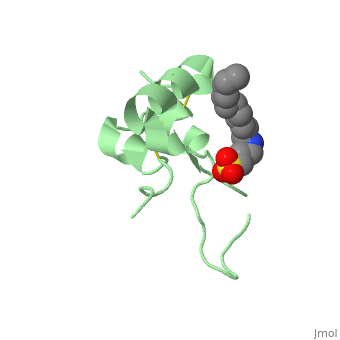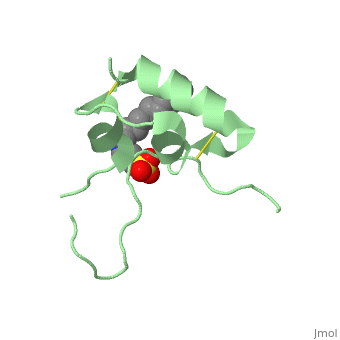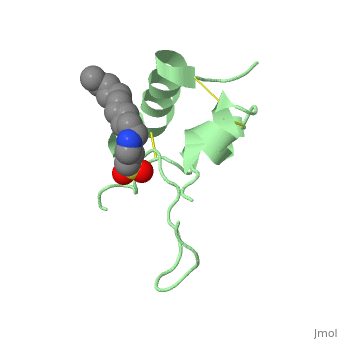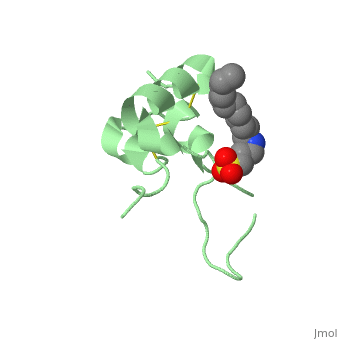
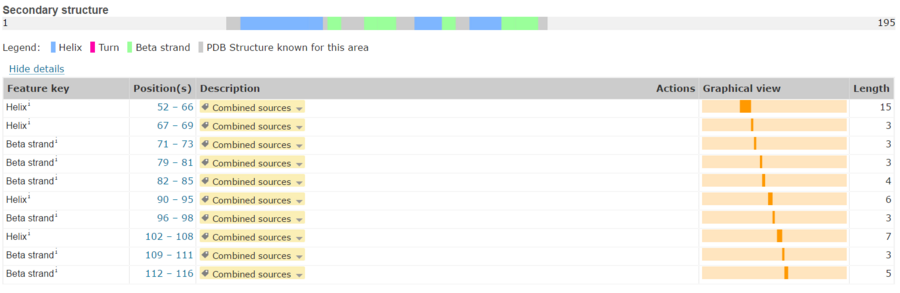
Its secondary structure as shown here is composed of alpha helix and beta strand. | Its secondary structure as shown here is composed of alpha helix and beta strand. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
=== Inhibiting interaction : IGF1 - IGFBP === | === Inhibiting interaction : IGF1 - IGFBP === | ||
| - | IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) weight 24 to 45 kDa. All six IGFBPs share 50% homology with each other and have binding affinities at the same order of magnitude for | + | IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) weight 24 to 45 kDa. All six IGFBPs share 50% homology with each other and have binding affinities at the same order of magnitude for IGF1 and IGF2 but have greater affinities then IGF1 for its receptor. Once IGF1 is bound to Insulin-like Growth Binding Protein (IGFBP), IGF1 cannot be linked to IGF1R any longer. Therefore, increases in serum levels of this IGFBP result in a decrease of IGF1 activity thus inhibiting the cellular pathways. |
| - | The IGFBPs help to lengthen the half-life of circulating IGFs in all tissues. That is why approximately 98% of | + | The IGFBPs help to lengthen the half-life of circulating IGFs in all tissues. That is why approximately 98% of IGF1 exists as complexed form with one of the six different IGFBP. IGFBP3, the most abundant protein, accounts for 80% of all IGF binding. Inside the liver, this mechanism is responsible for positive feedback, more precisely it allows growth hormone to continuously act upon the liver to produce more IGF1. |
Revision as of 19:53, 26 January 2017
Insulin-like growth factor 1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Patrick Jouandin. Rôle de la voie de signalisation Insuline dans le couplage des informations nutritionnelles et développementales au cours de l'ovogenèse chez la drosophile. Sciences agricoles.Université Nice Sophia Antipolis, 2013. Français.<NNT : 2013NICE4102>.<tel-00932409>
- ↑ http://www.hal.inserm.fr/tel-00932409/, 26/01/2017
- ↑ Elena Conti, Maria Beatrice Musumeci, et all, IGF-1 and atherothrombosis: relevance to pathophysiology and therapy,Clinical Science, May 01, 2011, 120 (9) 377-402
- ↑ R. Kaaks, Médecine Nucléaire - Imagerie fonctionnelle et métabolique, 2003, vol.27, n°1
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laron_syndrome, 26/01/2017
- ↑ Richard Holt, Diabetes Voice, Septembre 2003, Volume 48, Numéro 2
- ↑ Srinivas Teppala, Anoop Shankar, Diabetes Care, Octobre 2010, Volume 33, Number 10
- ↑ Westwood AJ, Beiser A, et all, Neurology, 2014 May, 6;82(18):1613-9
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Maxime Julliot, Alexia Kindler, Virginie Nakad, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky