User:Estelle Metzger/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
== LRRK2-IN-1 == | == LRRK2-IN-1 == | ||
[[Image:4K4-270.png|thumb|LRRK2-IN-1 structure (4K4 on PDB website)|upright=1,5]] | [[Image:4K4-270.png|thumb|LRRK2-IN-1 structure (4K4 on PDB website)|upright=1,5]] | ||
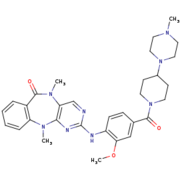
| - | <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene> is the first identified LRRK2-specific inhibitor, which is now a common tool compound for the LRRK2 research community. LRRK2-IN-1 has a 2-amino-5,11- dimethyl-5H-benzo[e]pyrimido[5,4-b][1,4]diazepine-6(11H)-one scaffold. | + | <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene> is the first identified LRRK2-specific inhibitor, which is now a common tool compound for the LRRK2 research community. <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene> has a 2-amino-5,11- dimethyl-5H-benzo[e]pyrimido[5,4-b][1,4]diazepine-6(11H)-one scaffold. |
| - | The function is of LRRK2- | + | The function is of <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene> is to dephosphorylate LRRK2 residues Ser910 and Ser935 in the kidney, but not in the brain. This compound is not capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. |
| - | The structure of LRRK2- | + | The structure of <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene> does not stabilize the active conformation. Indeed, the activation loop is poorly resolved indicating that it is flexible. Moreover, it presents a closure of the glycine-rich loop in the inhibitor structure.<ref name="Bernd"/> |
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
== Humanized Roco4 and LRRK2-IN-1 interaction == | == Humanized Roco4 and LRRK2-IN-1 interaction == | ||
| - | LRRK2-IN-1 makes 2 hydrogen bounds and 24 vander Walls contacts with Roco4. The first hydrogen bound is formed between the backbone carbonyl of <scene name='75/751216/1108/1'>Val1108</scene> and the N24 of the LRRK2-IN-1 with a distance of 2.8 Å. The second is formed between the Nz of <scene name='75/751216/1055/2'>Lys1055</scene> and O40 of LRRK2-IN-1 with a | + | <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene> makes 2 hydrogen bounds and 24 vander Walls contacts with Roco4. The first hydrogen bound is formed between the backbone carbonyl of <scene name='75/751216/1108/1'>Val1108</scene> and the N24 of the <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene> with a distance of 2.8 Å. The second is formed between the Nz of <scene name='75/751216/1055/2'>Lys1055</scene> and O40 of LRRK2-IN-1 with a |
distance of 3.2 Å. This interaction takes place in the <scene name='75/751216/Atp_binding_pocket/1'>ATP-binding pocket</scene><ref name="Bernd"/>. | distance of 3.2 Å. This interaction takes place in the <scene name='75/751216/Atp_binding_pocket/1'>ATP-binding pocket</scene><ref name="Bernd"/>. | ||
| - | LRRK2-IN-1 is predicted to be a type 1 inhibitor. That mean that it should only bind the active form of its target and stabilize it. However, a study showed that it can also bind the inactive form of Roco4<ref name="Bernd"/>. | + | <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene> is predicted to be a type 1 inhibitor. That mean that it should only bind the active form of its target and stabilize it. However, a study showed that it can also bind the inactive form of Roco4<ref name="Bernd"/>. |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
The use of roco4, permited to learn that the G2019S mutation is the results of an additional hydrogen bound between Ser2019 (Ser1179 in Roco4) and Gln1918 (Arg1077 in Roco4).<ref name="Bernd"/> | The use of roco4, permited to learn that the G2019S mutation is the results of an additional hydrogen bound between Ser2019 (Ser1179 in Roco4) and Gln1918 (Arg1077 in Roco4).<ref name="Bernd"/> | ||
| - | However, LRRK2-IN-1, like many LRRK2 inhibitors, presents a lack of selectivity or difficulties to pass the blood-brain barrier. Kinase inhibitors can lead also to kidney and lung abnormality. Without working on these points,LRRK2-IN-1 couldn’t be used as a treatment for the Parkinson’s disease. | + | However, <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene>, like many LRRK2 inhibitors, presents a lack of selectivity or difficulties to pass the blood-brain barrier. Kinase inhibitors can lead also to kidney and lung abnormality. Without working on these points,<scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene> couldn’t be used as a treatment for the Parkinson’s disease. |
In the main time, they are used as tools for characterization of the function and activation mechanism of LRRK2 in order to find new therapeutic target. <ref name="Bernd"/> | In the main time, they are used as tools for characterization of the function and activation mechanism of LRRK2 in order to find new therapeutic target. <ref name="Bernd"/> | ||
Revision as of 23:33, 26 January 2017
Humanized Roco4 bound to LRRK2-IN-1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 Gilsbach BK, Messias AC, Ito G, Sattler M, Alessi DR, Wittinghofer A, Kortholt A. Structural Characterization of LRRK2 Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2015 May 1. PMID:25897865 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm5018779
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Gilsbach BK, Kortholt A. Structural biology of the LRRK2 GTPase and kinase domains: implications for regulation. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014 May 5;7:32. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032. eCollection, 2014. PMID:24847205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00741-9
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Taylor SS, Kornev AP. Protein kinases: evolution of dynamic regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011 Feb;36(2):65-77. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.006. Epub, 2010 Oct 23. PMID:20971646 doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.006