Some studies to find a treatment for the Parkinson's disease are focused on LRRK2. Indeed, mutations in LRRK2, which increases its kinase activity, are found in case of Parkinson’s disease. Thus, a kinase inhibitor for LRRK2 would be an interesting thetapeutic target.
Thanks to the similarity between LRRK2 and Roco4 from the Dictyostelium, Roco4 is used in studies with a view to finding that inhibitor. One of the candidates to inhibit this activity is .[1]
Humanized Roco4
Roco proteins are serine/threonine specific kinases. This family consists of multidomain Ras-GTPases. Roco4 is 193 kDa and is identified as a key protein for proper stalk cell formation. Between the Dictyostelium Roco genes and LRRK genes, there are many structural similarities, which are due to independant acquisitions of distantly related protein kinase domain.
The characteristics of roco protein family, are a conserved core, consisting of a Ras-like GTPase domain called ROC (Ras of Complex proteins) and a COR domain (C-terminal of ROC), a C-terminal and several N-terminal leucine rich repeats (LRR). Roco4 possesses one more domain : a C-terminal WD40 repeats.[2]
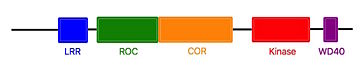
Linear structure of Roco4
[2]The ROC domain possesses five G motifs that are required for guanine nucleotid binding. This domain presents some similarities with the proteins of the ras family. The COR and the ROC domains forms an inseperable tandem, a 300-400 long stretch of amino acids with no significant homology to other described domains. [2]
The Roco4 kinase structure consists of a canonical, two-lobed kinase structure, with an adenine nucleotide bound in the conventional . It contains the conserved alphaC-helix and an anti-parallel beta sheets in the smaller N-terminal lobe. Other Alpha-helices and the activation loop with the conserved N-terminal DFG motif are localized in the bigger C-terminal lobe.[2]
The activation loop and alphaC-helix together form the catalytic site of the kinase, an formed by a cleft between the two lobes.
For catalysis, the formation of a polar contact is essential. This polar contact takes place between Roco4 from the beta3-strand and the from the alphaC-helix. The amino acids Asp makes contact with all three ATP phosphates either directly or via coordination of a . Moreover, the amino acid Phe makes hydrophobic contacts to the alphaC-helix and the HxD motif, and leads for the correct positioning of the DFG motif. [2]
Roco4 has two conformation, an active conformation and an inactive conformation. These conformations depend of the conformation of the DFG motif : a DFG-in (active) and a DFG-out (inactive) conformation. Therefore, in the structure of active Roco4 kinase, the activation loop is visible and ordered. In contrast, in the structure of inactive Roco4 kinase, the activation loop is not visible.[3] [4]
In most kinases, there is a mechanism to switch from an inactive to an active state.
This involves autophosphorylation of some residues in the activation loop. . Autophosphorylation not only results in the reorientation of the activation loop, but often also alters ATP binding and/or interaction with substrates.[3][4] In Roco4 kinase, there are four phosphorylation sites in the activation loop : Ser1181, Ser1184, Ser1187, and Ser1189.[1]
The structure of Dictyostelium Roco4 kinase in complex with the LRRK2 inhibitor H1152 allows us to see that Roco4 and other Roco family proteins are essential for the optimization of the current, and identification of new LRRK2 kinase inhibitor. To have a Roco4 protein which have an active site resembling human LRRK2, researchers use a Dictyostelium Roco4 mutant ( and ) which is called humanized Roco4.[1]
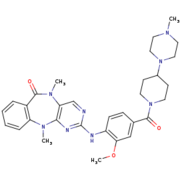
LRRK2-IN-1
is the first identified LRRK2-specific inhibitor, which is now a common tool compound for the LRRK2 research community. has a 2-amino-5,11- dimethyl-5H-benzo[e]pyrimido[5,4-b][1,4]diazepine-6(11H)-one scaffold.
The function is of is to dephosphorylate LRRK2 residues Ser910 and Ser935 in the kidney, but not in the brain. This compound is not capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier.
The structure of does not stabilize the active conformation. Indeed, the activation loop is poorly resolved indicating that it is flexible. Moreover, it presents a closure of the glycine-rich loop in the inhibitor structure.[1]
Humanized Roco4 and LRRK2-IN-1 interaction
makes 2 hydrogen bounds and 24 vander Walls contacts with Roco4. The first hydrogen bound is formed between the backbone carbonyl of and the N24 of the with a distance of 2.8 Å. The second is formed between the Nz of and O40 of LRRK2-IN-1 with a
distance of 3.2 Å. This interaction takes place in the [1].
is predicted to be a type 1 inhibitor. That mean that it should only bind the active form of its target and stabilize it. However, a study showed that it can also bind the inactive form of Roco4[1].
Relevance
LRRK2, for leucine-rich repeat serin/thereonin kinase 2, is a protein from the Roco family of G-proteins. It takes part in divers pathway such as synaptic vesicule trafficking, retrograde trafficking pathway for recycling protein or the CaMKK/AMPK pathway. Its importance comes from the fact that its susspetced to have a role in the phosphorylation of a central protein in the Parkinson’s disease.[6] Indeed, mutation associated with Parkinson Disease can be found in asmost every domains of LRRK2. For techrapeutic research Rocco4 from the Dictyostelium was mutated, especially in the active site, in order to mime LRRK2.[1]
Disease
The Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that is associated with resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity and postural instability.[6] This is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, which is affecting 2% of the population above 65 years[1].
Two types of Parkinson’s disease existe, the heditary or the sporadic also called idiopathic. LRRK2 mutations can be found in almost its every domains for both types. The most important mutation is the G2019S, which is located on the kinase domain. It stabilise the domains, thus leading to an indresed kinase activity of 2 to 4 fold. That’s why a treatment stategy would be to develop a kinase inhibitor in order to counter it.[1]
The use of roco4, permited to learn that the G2019S mutation is the results of an additional hydrogen bound between Ser2019 (Ser1179 in Roco4) and Gln1918 (Arg1077 in Roco4).[1]
However, , like many LRRK2 inhibitors, presents a lack of selectivity or difficulties to pass the blood-brain barrier. Kinase inhibitors can lead also to kidney and lung abnormality. Without working on these points, couldn’t be used as a treatment for the Parkinson’s disease.
In the main time, they are used as tools for characterization of the function and activation mechanism of LRRK2 in order to find new therapeutic target. [1]