We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Estelle Metzger/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Some studies to find a treatment for the Parkinson's disease are focused on LRRK2. Indeed, mutations in LRRK2, which increases its kinase activity, are found in case of Parkinson’s disease. Thus, a kinase inhibitor for LRRK2 would be an interesting thetapeutic target.<ref name="pnas">doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203223109</ref> | Some studies to find a treatment for the Parkinson's disease are focused on LRRK2. Indeed, mutations in LRRK2, which increases its kinase activity, are found in case of Parkinson’s disease. Thus, a kinase inhibitor for LRRK2 would be an interesting thetapeutic target.<ref name="pnas">doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203223109</ref> | ||
| - | Thanks to the similarity between LRRK2 and Roco4 from the ''Dictyostelium'', Roco4 is used in studies with a view to finding that inhibitor. One of the candidates to inhibit this activity is <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene>.<ref name="Bernd">doi: 10.1021/jm5018779</ref><ref name="pnas"/> | + | Thanks to the similarity between LRRK2 and Roco4 from the ''Dictyostelium'', Roco4 is used in studies with a view to finding that inhibitor. One of the candidates to inhibit this activity is <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene>.<ref name="Bernd">doi: 10.1021/jm5018779</ref><ref name="pnas"/><ref name="Wouter">doi: 10.1128/EC.00366-09</ref> |
== Humanized Roco4 == | == Humanized Roco4 == | ||
| - | Roco proteins are serine/threonine specific kinases. This family consists of multidomain Ras-GTPases. Roco4 is 193 kDa and is identified as a key protein for proper stalk cell formation. Between the ''Dictyostelium'' Roco genes and LRRK genes, there are many structural similarities, which are due to independant acquisitions of distantly related protein kinase domain. | + | Roco proteins are serine/threonine specific kinases. This family consists of multidomain Ras-GTPases. Roco4 is 193 kDa and is identified as a key protein for proper stalk cell formation. Between the ''Dictyostelium'' Roco genes and LRRK genes, there are many structural similarities, which are due to independant acquisitions of distantly related protein kinase domain.<ref name="Wouter"/> |
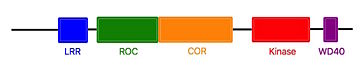
| - | The characteristics of roco protein family, are a conserved core, consisting of a Ras-like GTPase domain called ROC (Ras of Complex proteins) and a COR domain (C-terminal of ROC), a C-terminal <scene name='75/751216/Kinase_domain/1'>kinase domain</scene> and several N-terminal leucine rich repeats (LRR). Roco4 possesses one more domain : a C-terminal WD40 repeats.<ref name="Bernd2"/><ref name="Mills">doi: 10.1002/humu.22515</ref> | + | The characteristics of roco protein family, are a conserved core, consisting of a Ras-like GTPase domain called ROC (Ras of Complex proteins) and a COR domain (C-terminal of ROC), a C-terminal <scene name='75/751216/Kinase_domain/1'>kinase domain</scene> and several N-terminal leucine rich repeats (LRR). Roco4 possesses one more domain : a C-terminal WD40 repeats.<ref name="Bernd2"/><ref name="Mills">doi: 10.1002/humu.22515</ref><ref name="Wouter"/> |
| - | [[Image:Roco4.jpg|thumb| Linear structure of Roco4 <ref name="Bernd2">doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032</ref>|center|upright=2,5]] | + | [[Image:Roco4.jpg|thumb| Linear structure of Roco4 <ref name="Bernd2">doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032</ref><ref name="Wouter"/>|center|upright=2,5]] |
| - | The ROC domain possesses five G motifs that are required for guanine nucleotid binding. This domain presents some similarities with the proteins of the ras family. The COR and the ROC domains forms an inseperable tandem, a 300-400 long stretch of amino acids with no significant homology to other described domains. <ref name="Bernd2"/> | + | The ROC domain possesses five G motifs that are required for guanine nucleotid binding. This domain presents some similarities with the proteins of the ras family. The COR and the ROC domains forms an inseperable tandem, a 300-400 long stretch of amino acids with no significant homology to other described domains. <ref name="Bernd2"/><ref name="Wouter"/> |
| - | The Roco4 kinase structure consists of a canonical, two-lobed kinase structure, with an adenine nucleotide bound in the conventional <scene name='75/751216/Atp_binding_pocket/1'>ATP-binding pocket</scene>. It contains the conserved alphaC-helix and an anti-parallel beta sheets in the smaller N-terminal lobe. Other Alpha-helices and the activation loop with the conserved N-terminal DFG motif are localized in the bigger C-terminal lobe.<ref name="Bernd2"/> | + | The Roco4 kinase structure consists of a canonical, two-lobed kinase structure, with an adenine nucleotide bound in the conventional <scene name='75/751216/Atp_binding_pocket/1'>ATP-binding pocket</scene>. It contains the conserved alphaC-helix and an anti-parallel beta sheets in the smaller N-terminal lobe. Other Alpha-helices and the activation loop with the conserved N-terminal DFG motif are localized in the bigger C-terminal lobe.<ref name="Bernd2"/><ref name="Wouter"/> |
The activation loop and alphaC-helix together form the catalytic site of the kinase, an <scene name='75/751216/Atp_binding_pocket/1'>ATP binding site</scene> formed by a cleft between the two lobes. | The activation loop and alphaC-helix together form the catalytic site of the kinase, an <scene name='75/751216/Atp_binding_pocket/1'>ATP binding site</scene> formed by a cleft between the two lobes. | ||
For catalysis, the formation of a polar contact is essential. This polar contact takes place between Roco4 <scene name='75/751216/1055/2'>Lys1055</scene> from the beta3-strand and the <scene name='75/751216/1078/1'>Glu1078</scene> from the alphaC-helix. The amino acids Asp makes contact with all three ATP phosphates either directly or via coordination of a <scene name='75/751216/Mg/1'>magnesium ion</scene>. Moreover, the amino acid Phe makes hydrophobic contacts to the alphaC-helix and the HxD motif, and leads for the correct positioning of the DFG motif. <ref name="Bernd2"/><ref name="bba">doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.12.001</ref> | For catalysis, the formation of a polar contact is essential. This polar contact takes place between Roco4 <scene name='75/751216/1055/2'>Lys1055</scene> from the beta3-strand and the <scene name='75/751216/1078/1'>Glu1078</scene> from the alphaC-helix. The amino acids Asp makes contact with all three ATP phosphates either directly or via coordination of a <scene name='75/751216/Mg/1'>magnesium ion</scene>. Moreover, the amino acid Phe makes hydrophobic contacts to the alphaC-helix and the HxD motif, and leads for the correct positioning of the DFG motif. <ref name="Bernd2"/><ref name="bba">doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.12.001</ref> | ||
Revision as of 09:11, 27 January 2017
Humanized Roco4 bound to LRRK2-IN-1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Gilsbach BK, Ho FY, Vetter IR, van Haastert PJ, Wittinghofer A, Kortholt A. Roco kinase structures give insights into the mechanism of Parkinson disease-related leucine-rich-repeat kinase 2 mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 11. PMID:22689969 doi:10.1073/pnas.1203223109
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Gilsbach BK, Messias AC, Ito G, Sattler M, Alessi DR, Wittinghofer A, Kortholt A. Structural Characterization of LRRK2 Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2015 May 1. PMID:25897865 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm5018779
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 van Egmond WN, van Haastert PJ. Characterization of the Roco protein family in Dictyostelium discoideum. Eukaryot Cell. 2010 May;9(5):751-61. doi: 10.1128/EC.00366-09. Epub 2010 Mar 26. PMID:20348387 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/EC.00366-09
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Gilsbach BK, Kortholt A. Structural biology of the LRRK2 GTPase and kinase domains: implications for regulation. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014 May 5;7:32. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032. eCollection, 2014. PMID:24847205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Mills RD, Mulhern TD, Liu F, Culvenor JG, Cheng HC. Prediction of the repeat domain structures and impact of parkinsonism-associated variations on structure and function of all functional domains of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2). Hum Mutat. 2014 Apr;35(4):395-412. doi: 10.1002/humu.22515. Epub 2014 Feb 24. PMID:24470158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/humu.22515
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Liu Z, West AB. The dual enzyme LRRK2 hydrolyzes GTP in both its GTPase and kinase domains in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Dec 8;1865(3):274-280. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.12.001. PMID:27939437 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.12.001
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00741-9
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Taylor SS, Kornev AP. Protein kinases: evolution of dynamic regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011 Feb;36(2):65-77. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.006. Epub, 2010 Oct 23. PMID:20971646 doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.006
- ↑ [1], Retrieved on January 27th 2017.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 UniProtKB - Q5S007 (LRRK2_HUMAN), Retrieved on January 27th 2017.