We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Estelle Metzger/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='4yzm' size='340' side='right' caption='Cocrystal 3D structure of Roco4 kinase and LRRK2-IN-1' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4yzm' size='340' side='right' caption='Cocrystal 3D structure of Roco4 kinase and LRRK2-IN-1' scene=''> | ||
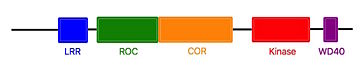
| - | Some | + | Some treatment targets for the Parkinson's disease are focused around LRRK2. Indeed, mutations increasing its kinase activity, are found in both case of the Parkinson’s disease. Thus, a kinase inhibitor for LRRK2 would be an interesting thetapeutic target.<ref name="pnas">doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203223109</ref> |
Thanks to the similarity between LRRK2 and Roco4 from the ''Dictyostelium'', Roco4 is used in studies with a view to finding that inhibitor. One of the candidates to inhibit this activity is <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene>.<ref name="Bernd">doi: 10.1021/jm5018779</ref><ref name="pnas"/><ref name="Wouter">doi: 10.1128/EC.00366-09</ref> | Thanks to the similarity between LRRK2 and Roco4 from the ''Dictyostelium'', Roco4 is used in studies with a view to finding that inhibitor. One of the candidates to inhibit this activity is <scene name='75/751216/Lrrk2-in-1/3'>LRRK2-IN-1</scene>.<ref name="Bernd">doi: 10.1021/jm5018779</ref><ref name="pnas"/><ref name="Wouter">doi: 10.1128/EC.00366-09</ref> | ||
Revision as of 09:16, 27 January 2017
Humanized Roco4 bound to LRRK2-IN-1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Gilsbach BK, Ho FY, Vetter IR, van Haastert PJ, Wittinghofer A, Kortholt A. Roco kinase structures give insights into the mechanism of Parkinson disease-related leucine-rich-repeat kinase 2 mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 11. PMID:22689969 doi:10.1073/pnas.1203223109
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Gilsbach BK, Messias AC, Ito G, Sattler M, Alessi DR, Wittinghofer A, Kortholt A. Structural Characterization of LRRK2 Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2015 May 1. PMID:25897865 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm5018779
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 van Egmond WN, van Haastert PJ. Characterization of the Roco protein family in Dictyostelium discoideum. Eukaryot Cell. 2010 May;9(5):751-61. doi: 10.1128/EC.00366-09. Epub 2010 Mar 26. PMID:20348387 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/EC.00366-09
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Gilsbach BK, Kortholt A. Structural biology of the LRRK2 GTPase and kinase domains: implications for regulation. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014 May 5;7:32. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032. eCollection, 2014. PMID:24847205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2014.00032
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Mills RD, Mulhern TD, Liu F, Culvenor JG, Cheng HC. Prediction of the repeat domain structures and impact of parkinsonism-associated variations on structure and function of all functional domains of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2). Hum Mutat. 2014 Apr;35(4):395-412. doi: 10.1002/humu.22515. Epub 2014 Feb 24. PMID:24470158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/humu.22515
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Liu Z, West AB. The dual enzyme LRRK2 hydrolyzes GTP in both its GTPase and kinase domains in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Dec 8;1865(3):274-280. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.12.001. PMID:27939437 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.12.001
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00741-9
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Taylor SS, Kornev AP. Protein kinases: evolution of dynamic regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011 Feb;36(2):65-77. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.006. Epub, 2010 Oct 23. PMID:20971646 doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2010.09.006
- ↑ [1], Retrieved on January 27th 2017.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 UniProtKB - Q5S007 (LRRK2_HUMAN), Retrieved on January 27th 2017.