We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Camille Zumstein/Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Rat Calcineurin== | ==Rat Calcineurin== | ||
<StructureSection load='4il1' size='340' side='right' caption='' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4il1' size='340' side='right' caption='' scene=''> | ||
| - | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
<scene name='75/750223/Picture_intro/1'> Calcineurin </scene> is a serine/threonine [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatase phosphatase] that is activated by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin calmodulin](CaM) in a calcium-dependant manner. | <scene name='75/750223/Picture_intro/1'> Calcineurin </scene> is a serine/threonine [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphatase phosphatase] that is activated by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin calmodulin](CaM) in a calcium-dependant manner. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 30: | ||
'''Secondary structure:''' | '''Secondary structure:''' | ||
| - | |||
[[Image:170106 Uniprot SecundaryStructure.png|thumb|upright=4|The secondary structure mostly includes helical structures [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63100 Uniprot]]] | [[Image:170106 Uniprot SecundaryStructure.png|thumb|upright=4|The secondary structure mostly includes helical structures [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63100 Uniprot]]] | ||
| - | |||
Besides, there are six turns reported in the structure of one chain. | Besides, there are six turns reported in the structure of one chain. | ||
| - | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| - | |||
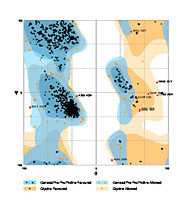
The Ramachandran blot of Calcineurin [[Image:Ramachandran 4il1.jpg|thumb|left|Ramachandran Plot of 4il1]] has been obtained by [http://mordred.bioc.cam.ac.uk/~rapper/rampage2.php MolProbity of the DUke University]. It plots the torsional angles phi (φ)and psi (ψ)of the molecule and thereby represents the secondary structure. Further information about the Interpretation of this plot can be found at [[Ramachandran Plot]]. | The Ramachandran blot of Calcineurin [[Image:Ramachandran 4il1.jpg|thumb|left|Ramachandran Plot of 4il1]] has been obtained by [http://mordred.bioc.cam.ac.uk/~rapper/rampage2.php MolProbity of the DUke University]. It plots the torsional angles phi (φ)and psi (ψ)of the molecule and thereby represents the secondary structure. Further information about the Interpretation of this plot can be found at [[Ramachandran Plot]]. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== Principle of action == | == Principle of action == | ||
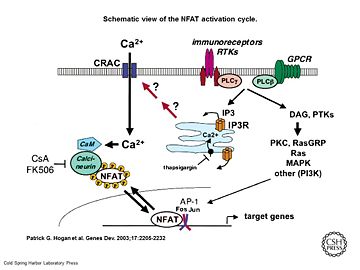
[[Image:Genes Dev. 2003 Sep 17(18) 2205-32, Figure 1.jpg|thumb|upright=2|Schematic view of the NFAT activation cycle <ref>PMID:12975316</ref>]] | [[Image:Genes Dev. 2003 Sep 17(18) 2205-32, Figure 1.jpg|thumb|upright=2|Schematic view of the NFAT activation cycle <ref>PMID:12975316</ref>]] | ||
| Line 51: | Line 42: | ||
It has been reported that Calcineurin activates the transcription factor [https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/NF-AT NFAT] by forming a complex and dephosporylation <ref>PMID:17502104</ref>. Following, the factor enters the nucleus and activates the expression of Interleukin-2. | It has been reported that Calcineurin activates the transcription factor [https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/NF-AT NFAT] by forming a complex and dephosporylation <ref>PMID:17502104</ref>. Following, the factor enters the nucleus and activates the expression of Interleukin-2. | ||
| - | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| - | |||
== Binding Partners == | == Binding Partners == | ||
| - | |||
The main partners of interaction are [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin Calmodulin],NFATc1, NFATc2 and NFATc3. | The main partners of interaction are [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calmodulin Calmodulin],NFATc1, NFATc2 and NFATc3. | ||
Many of the calcineurin substrates’ contain a PxIxIT motif. Among them, beside the phosphorylated forms of NFAT we can also mentioned; cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), PP1, microtubule-associated protein tau and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK- 3)<ref>PMID: 17666045</ref><ref>PMID: 22676853</ref><ref>PMID:14701880</ref><ref>PMID: 7515479</ref>. | Many of the calcineurin substrates’ contain a PxIxIT motif. Among them, beside the phosphorylated forms of NFAT we can also mentioned; cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), PP1, microtubule-associated protein tau and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK- 3)<ref>PMID: 17666045</ref><ref>PMID: 22676853</ref><ref>PMID:14701880</ref><ref>PMID: 7515479</ref>. | ||
<scene name='75/750223/Can_fk506/1'>Calcineurin , here shown in complex with FK506 and FKPB (in pink on the model)</scene> is inhibited by the immunosuppressive drugs tacrolismus (<scene name='75/750223/Tacrolimus/1'>FK506</scene>) or cyclosporine A (CsA). CsA and conduct their therapeutic role thought binding to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunophilins immunophilins] cyclophilin and FK506 binding protein (FK506BP) respectively. The complexes CsA-cyclophilin and FK506-FK506BP bind then to calcineurin in a calcium-dependent manner thus inhibiting its phosphatase activity. Therefore the addition of these drugs to lymphocytes T prevent NFAT translocation to the nucleus and the subsequent activation its target gene.That's why FK506 and CsA are use in the treatment of various immune-mediated diseases. However since calcineurin is is widely expressed in non-haemopoietic tissues like the kidney and the hearth, both drugs present a long term toxicity and can lead to deleterious effect to these Organs <ref>PMID: 8811062</ref>, (http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus). | <scene name='75/750223/Can_fk506/1'>Calcineurin , here shown in complex with FK506 and FKPB (in pink on the model)</scene> is inhibited by the immunosuppressive drugs tacrolismus (<scene name='75/750223/Tacrolimus/1'>FK506</scene>) or cyclosporine A (CsA). CsA and conduct their therapeutic role thought binding to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immunophilins immunophilins] cyclophilin and FK506 binding protein (FK506BP) respectively. The complexes CsA-cyclophilin and FK506-FK506BP bind then to calcineurin in a calcium-dependent manner thus inhibiting its phosphatase activity. Therefore the addition of these drugs to lymphocytes T prevent NFAT translocation to the nucleus and the subsequent activation its target gene.That's why FK506 and CsA are use in the treatment of various immune-mediated diseases. However since calcineurin is is widely expressed in non-haemopoietic tissues like the kidney and the hearth, both drugs present a long term toxicity and can lead to deleterious effect to these Organs <ref>PMID: 8811062</ref>, (http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus). | ||
| - | |||
'''Cofactors''': | '''Cofactors''': | ||
Calcineurin belong to the family of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metalloprotein metalloprotein]. To conduct its activity it requires the presence of Fe3+ and Zn2+ ions in the active site (one per subunit).Superoxide dismutase has been shown to protect calcineurin from inactivation by preventing Fe3+ from oxidation. Thus after activation of calcineurin by calmodulin, the AID is displaced from the <scene name='75/750223/Catalytic_core/1'> catalytic core,with phosphate and Fe and Zn ions bound </scene> exposing Fe3+ to oxidation <ref>PMID: 8837775</ref>(Calmodulin and Signal Transduction (p184), Linda J. Van Eldik,D. Martin Watterson (1998)). | Calcineurin belong to the family of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metalloprotein metalloprotein]. To conduct its activity it requires the presence of Fe3+ and Zn2+ ions in the active site (one per subunit).Superoxide dismutase has been shown to protect calcineurin from inactivation by preventing Fe3+ from oxidation. Thus after activation of calcineurin by calmodulin, the AID is displaced from the <scene name='75/750223/Catalytic_core/1'> catalytic core,with phosphate and Fe and Zn ions bound </scene> exposing Fe3+ to oxidation <ref>PMID: 8837775</ref>(Calmodulin and Signal Transduction (p184), Linda J. Van Eldik,D. Martin Watterson (1998)). | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== Related health defects == | == Related health defects == | ||
| - | |||
Calcineurin hyperactivation thought dysregulation of the Ca2+ dynamic have been show to play a critical role in several diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Schizophrenia ,Diabetes, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus as well as Alzheimer diseases(AD) (http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus)<ref>PMID: 12851457</ref><ref>PMID: 16988714</ref><ref>PMID:20421909</ref>. | Calcineurin hyperactivation thought dysregulation of the Ca2+ dynamic have been show to play a critical role in several diseases like Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Schizophrenia ,Diabetes, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus as well as Alzheimer diseases(AD) (http://www.uptodate.com/contents/pharmacology-of-cyclosporine-and-tacrolimus)<ref>PMID: 12851457</ref><ref>PMID: 16988714</ref><ref>PMID:20421909</ref>. | ||
Taking the example of AD which is a age-related memory dysfunction ; it it know that in older organism the brain is less plastic due to a dysregulation of Ca2+ dynamic. This in addition to the presence of oligomeric Aß is sufficient to explain an enhancement of CaN activity leading to severals symptoms like decreased neurotransmission , synaptic loss , neuroinflammation ...<ref>PMID: 22654726</ref>Therefore calmodulin inhibitors are potential alternatives against Alzheimer diseases. | Taking the example of AD which is a age-related memory dysfunction ; it it know that in older organism the brain is less plastic due to a dysregulation of Ca2+ dynamic. This in addition to the presence of oligomeric Aß is sufficient to explain an enhancement of CaN activity leading to severals symptoms like decreased neurotransmission , synaptic loss , neuroinflammation ...<ref>PMID: 22654726</ref>Therefore calmodulin inhibitors are potential alternatives against Alzheimer diseases. | ||
| - | |||
== Human/Rat calcineurin comparison == | == Human/Rat calcineurin comparison == | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
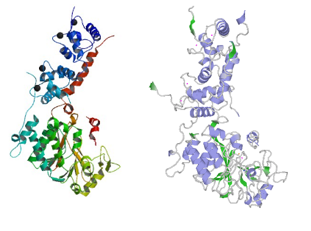
[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q08209 Human] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63329 Rat] calcineurin have the same function and global structure [[Image:Human rat comparison.PNG|thumb|upright=2|right| Structure of rat calcineurin and human calcineurin ]]. | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q08209 Human] and [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P63329 Rat] calcineurin have the same function and global structure [[Image:Human rat comparison.PNG|thumb|upright=2|right| Structure of rat calcineurin and human calcineurin ]]. | ||
The size (521 amino acids) and subunits of the linear structure are the same, as well as the 3D structure. | The size (521 amino acids) and subunits of the linear structure are the same, as well as the 3D structure. | ||
| - | |||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| - | |||
However, there are a few differences, such as the secondary structures. [[Image:Proteopedia.PNG|thumb|upright=2|right|size=4| Structure of human calcineurin (up) and rat calcineurin (down) ]] | However, there are a few differences, such as the secondary structures. [[Image:Proteopedia.PNG|thumb|upright=2|right|size=4| Structure of human calcineurin (up) and rat calcineurin (down) ]] | ||
For instance, Human Calcineurin has one Beta strand at <scene name='75/750223/Residues_11-13_beta_strand/1'>residues 11-13</scene> whereas Rat Calcineurin has not. | For instance, Human Calcineurin has one Beta strand at <scene name='75/750223/Residues_11-13_beta_strand/1'>residues 11-13</scene> whereas Rat Calcineurin has not. | ||
| - | |||
Indeed, Calcineurin is a highly conserved protein from yeast to mammals. | Indeed, Calcineurin is a highly conserved protein from yeast to mammals. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== Evolutionary conservation == | == Evolutionary conservation == | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
'''Calcineurin A''' | '''Calcineurin A''' | ||
| - | |||
This catalytic subunit is highly conserved. Nevertheless it can be up to 20% larger in lower eukaryotic species. | This catalytic subunit is highly conserved. Nevertheless it can be up to 20% larger in lower eukaryotic species. | ||
| - | |||
In addition, the NH2 and COOH terminals are variable among species, as well as between calcineurin A genes within the same organism. | In addition, the NH2 and COOH terminals are variable among species, as well as between calcineurin A genes within the same organism. | ||
The function of these variable domains is unknown.<ref name="paper">PMID: 11015619</ref> | The function of these variable domains is unknown.<ref name="paper">PMID: 11015619</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
'''Calcineurin B''' | '''Calcineurin B''' | ||
| - | |||
[[Image:Ih.jpg|thumb|upright=2|right|size=4| Evolutionary conservation within eukaryotes ]] | [[Image:Ih.jpg|thumb|upright=2|right|size=4| Evolutionary conservation within eukaryotes ]] | ||
This regulatory subunit is also highly conserved throughout evolution. For instance, the sequence of the rat calcineurin B brain isoform is exactly the same as the human calcineurin B. | This regulatory subunit is also highly conserved throughout evolution. For instance, the sequence of the rat calcineurin B brain isoform is exactly the same as the human calcineurin B. | ||
This high degree of conservation allows functional interchange of calcineurin B subunits between eukaryotic species. <ref name="paper" /> | This high degree of conservation allows functional interchange of calcineurin B subunits between eukaryotic species. <ref name="paper" /> | ||
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| - | |||
== Calcineurin history == | == Calcineurin history == | ||
| - | |||
Calcineurin was first detected by Wang and Desai in 1976 as a column fraction that inhibited the calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. | Calcineurin was first detected by Wang and Desai in 1976 as a column fraction that inhibited the calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. | ||
| - | |||
Klee and Krinks did the first purification of calcineurin in 1978 and hypothesized that it might be a regulatory subunit of phosphodiesterase since it was demonstrated to inhibit phosphodiesterase activity. | Klee and Krinks did the first purification of calcineurin in 1978 and hypothesized that it might be a regulatory subunit of phosphodiesterase since it was demonstrated to inhibit phosphodiesterase activity. | ||
Klee et al. named it “calcineurin” on the basis of its Ca2+-binding properties (calci) and localization to neuronal tissue (neurin). | Klee et al. named it “calcineurin” on the basis of its Ca2+-binding properties (calci) and localization to neuronal tissue (neurin). | ||
| - | |||
From this time, functions and structure of Calcineurin have been discovered as well as medical applications (e.g. calcineurin inhibitors). <ref name="paper" /> | From this time, functions and structure of Calcineurin have been discovered as well as medical applications (e.g. calcineurin inhibitors). <ref name="paper" /> | ||
| - | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 11:59, 27 January 2017
Rat Calcineurin
Rat Calcineurin
| |||||||||||