Sandbox Reserved 1269
From Proteopedia
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
1YSA is a transcription factor that activates over 30 genes necessary for amino acid or <scene name='75/751162/Purine/1'>purine</scene> biosynthesis. 1YSA binds to the DNA sequence: 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3' (1). | 1YSA is a transcription factor that activates over 30 genes necessary for amino acid or <scene name='75/751162/Purine/1'>purine</scene> biosynthesis. 1YSA binds to the DNA sequence: 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3' (1). | ||
==Structure, Interactions, and Location== | ==Structure, Interactions, and Location== | ||
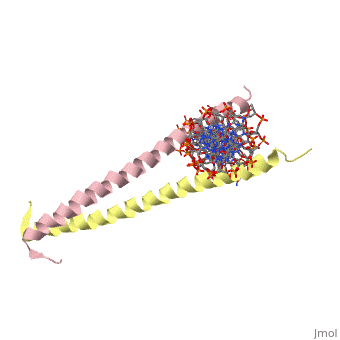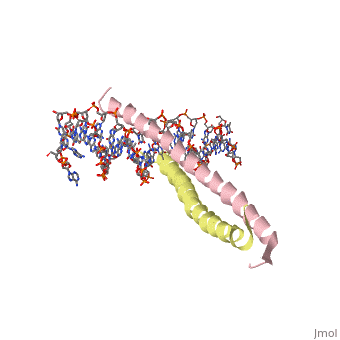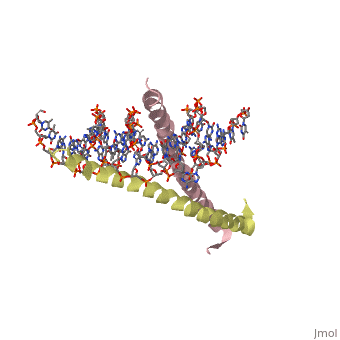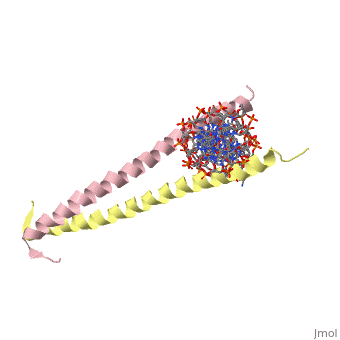
| - | 1YSA is a four chain, <scene name='75/751162/Four-chain_structure/1'>two-stranded</scene> transcription factor. There are both polar and <scene name='75/751162/Nonpolar/1'>nonpolar</scene> regions within 1YSA. It interacts with DNA and binds DNA as a dimer. 1YSA interacts in several locations within the DNA | + | 1YSA is a four chain, <scene name='75/751162/Four-chain_structure/1'>two-stranded</scene> transcription factor. There are both polar and <scene name='75/751162/Nonpolar/1'>nonpolar</scene> regions within 1YSA. |
| + | |||
| + | It interacts with DNA and binds DNA as a dimer. 1YSA interacts in several locations within the DNA. Within DNA, 1YSA binds to DNA (5'-3 D(*tp*tp*cp*cp*tp*ap*tp*gp*ap*cp*tp*cp*ap*tp*cp*cp*a4 P*gp*tp*t)-3') and DNA (5'-9 D(*ap*ap*ap*cp*tp*gp*gp*ap*tp*gp*ap*gp*tp*cp*ap*tp*a10 P*gp*gp*a)-3') (2). The bZIP interacts with the major groove of the DNA (7). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The location of 1YSA within a cell is in nucleus P03069 (3). | ||
==Origin== | ==Origin== | ||
Revision as of 21:10, 8 February 2017
|
Contents |
1YSA
1YSA is the PDB of GCN4 leucine zipper. Leucine zippers are a class of eukaryotic transcription factors that belongs to the domain basic-region leucine zipper (BZIP) (6). The zipper has "leucine" in its name because leucines can be found every seven amino acids within the domain. The location of the leucines is critical for the dimerization of DNA. The zipper is coil of alpha helices which interact through ion pairs and hydrogen bonding. The leucines make side-to-side interactions in every other layer of the dimer structure that is formed with the DNA (5). Leucine zipper regulatory proteins are crucial to development. When the proteins are overproduced, they can be carcinogenic (7).
Function of 1YSA
1YSA is a transcription factor that activates over 30 genes necessary for amino acid or biosynthesis. 1YSA binds to the DNA sequence: 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3' (1).
Structure, Interactions, and Location
1YSA is a four chain, transcription factor. There are both polar and regions within 1YSA.
It interacts with DNA and binds DNA as a dimer. 1YSA interacts in several locations within the DNA. Within DNA, 1YSA binds to DNA (5'-3 D(*tp*tp*cp*cp*tp*ap*tp*gp*ap*cp*tp*cp*ap*tp*cp*cp*a4 P*gp*tp*t)-3') and DNA (5'-9 D(*ap*ap*ap*cp*tp*gp*gp*ap*tp*gp*ap*gp*tp*cp*ap*tp*a10 P*gp*gp*a)-3') (2). The bZIP interacts with the major groove of the DNA (7).
The location of 1YSA within a cell is in nucleus P03069 (3).
Origin
1YSA originates from the organism Saccharomyces cerevisiae, or commonly known as baker's yeast (4).
References
(1) www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/1ysa
(2) www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?uid=1ysa
(3) www.pdbj.org/mine/summary/1ysa
(4) www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P03069
(5) www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1948029
(6) www.science.sciencemag.org/content/246/4932/911
(7) www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2245831/