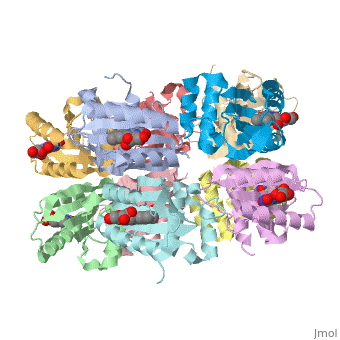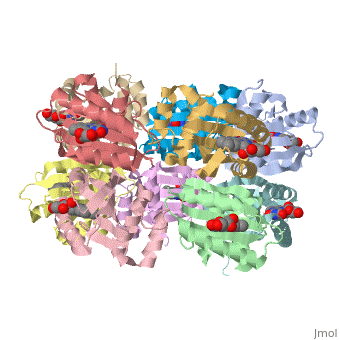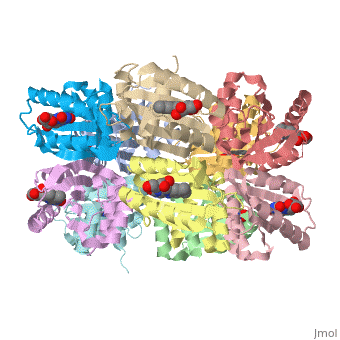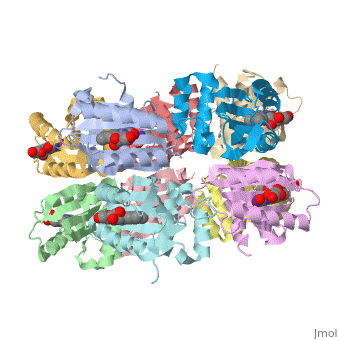
AppA protein BLUF domain
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m (BLUF domain moved to BLUF domain protein: requested by Editor) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='1x0p' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of BLUF domain protein (PDB code [[1x0p]]).' scene=''> | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
The proteins containing sensors for '''blue light using''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flavin_adenine_dinucleotide FAD] '''(BLUF) domains''' are one class of photoreceptor family that utilizes a flavin [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromophore chromophore]<ref name ="one">PMID: 15876364</ref>. The other two classes include [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phototropin phototropins] (LOV) and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptochrome cryptochromes]<ref name="two">PMID: 14730990</ref>. The BLUF domain was first discovered in [http://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Rhodobacter ''Rhodobacter sphaeroides''] as the blue light photoreceptor involved in the repression of photosynthesis genes in AppA protein<ref name="one" /><ref name ="three">PMID: 12230978</ref>. The BLUF domain is known to exist in many bacteria, including cyanobacteria. | The proteins containing sensors for '''blue light using''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flavin_adenine_dinucleotide FAD] '''(BLUF) domains''' are one class of photoreceptor family that utilizes a flavin [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chromophore chromophore]<ref name ="one">PMID: 15876364</ref>. The other two classes include [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phototropin phototropins] (LOV) and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptochrome cryptochromes]<ref name="two">PMID: 14730990</ref>. The BLUF domain was first discovered in [http://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Rhodobacter ''Rhodobacter sphaeroides''] as the blue light photoreceptor involved in the repression of photosynthesis genes in AppA protein<ref name="one" /><ref name ="three">PMID: 12230978</ref>. The BLUF domain is known to exist in many bacteria, including cyanobacteria. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
=Function= | =Function= | ||
Overall, the main function of the BLUF domain is to detect and respond to blue light. More specifically, in ''R. sphaeroides'', the BLUF domain is a blue light photo receptor involved in repressing the photosynthesis genes at the N-terminal region of the AppA protein<ref name="three" />. In ''E. gracilis'', the BLUF domain of PAC complexes serves as a blue light receptor in photophobic responses<ref name="six" />. | Overall, the main function of the BLUF domain is to detect and respond to blue light. More specifically, in ''R. sphaeroides'', the BLUF domain is a blue light photo receptor involved in repressing the photosynthesis genes at the N-terminal region of the AppA protein<ref name="three" />. In ''E. gracilis'', the BLUF domain of PAC complexes serves as a blue light receptor in photophobic responses<ref name="six" />. | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
=3D structures of BLUF domain protein= | =3D structures of BLUF domain protein= | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
Revision as of 09:35, 22 March 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of BLUF domain protein
Updated on 22-March-2017
2byc - RsBLUF dark structure - Rhodobacter sphaeroides
2iyg, 2iyi - RsBLUF dark structure BLUF domain (mutant)
1x0p - BLUF - Thermosynechococcus elongatus
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 Kita A, Okajima K, Morimoto Y, Ikeuchi M, Miki K. Structure of a cyanobacterial BLUF protein, Tll0078, containing a novel FAD-binding blue light sensor domain. J Mol Biol. 2005 May 27;349(1):1-9. Epub 2005 Apr 9. PMID:15876364 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.067
- ↑ van der Horst MA, Hellingwerf KJ. Photoreceptor proteins, "star actors of modern times": a review of the functional dynamics in the structure of representative members of six different photoreceptor families. Acc Chem Res. 2004 Jan;37(1):13-20. PMID:14730990 doi:10.1021/ar020219d
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Masuda S, Bauer CE. AppA is a blue light photoreceptor that antirepresses photosynthesis gene expression in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Cell. 2002 Sep 6;110(5):613-23. PMID:12230978
- ↑ Laan W, van der Horst MA, van Stokkum IH, Hellingwerf KJ. Initial characterization of the primary photochemistry of AppA, a blue-light-using flavin adenine dinucleotide-domain containing transcriptional antirepressor protein from Rhodobacter sphaeroides: a key role for reversible intramolecular proton transfer from the flavin adenine dinucleotide chromophore to a conserved tyrosine? Photochem Photobiol. 2003 Sep;78(3):290-7. PMID:14556317
- ↑ Hasegawa K, Masuda S, Ono TA. Spectroscopic analysis of the dark relaxation process of a photocycle in a sensor of blue light using FAD (BLUF) protein Slr1694 of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005 Jan;46(1):136-46. Epub 2005 Jan 19. PMID:15659451 doi:10.1093/pcp/pci003
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Iseki M, Matsunaga S, Murakami A, Ohno K, Shiga K, Yoshida K, Sugai M, Takahashi T, Hori T, Watanabe M. A blue-light-activated adenylyl cyclase mediates photoavoidance in Euglena gracilis. Nature. 2002 Feb 28;415(6875):1047-51. PMID:11875575 doi:10.1038/4151047a
- ↑ Yuan H, Anderson S, Masuda S, Dragnea V, Moffat K, Bauer C. Crystal structures of the Synechocystis photoreceptor Slr1694 reveal distinct structural states related to signaling. Biochemistry. 2006 Oct 24;45(42):12687-94. PMID:17042486 doi:10.1021/bi061435n
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Amanda Cookhouse, Jaime Prilusky