We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1067
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | < | + | ==Zinc Transporter Yiip== |
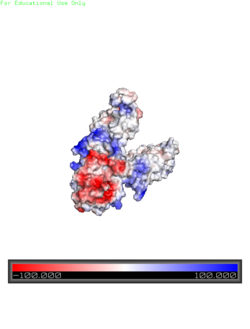
| + | <StructureSection load='3h90' size='350' side='right' caption='Escherichia coli reca protein-bound DNA (PDB entry [[3h90]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | == Zinc Transporter Yiip == | ||
<scene name='69/694234/3h90/1'>3h90</scene> is an integral membrane protein of the E. coli bacteria that regulates the import and export of Zn<sup>2+</sup>. | <scene name='69/694234/3h90/1'>3h90</scene> is an integral membrane protein of the E. coli bacteria that regulates the import and export of Zn<sup>2+</sup>. | ||
| - | + | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
Yiip's monomer structure is classified into two different domains, the Trans-Membrane Domain (TMD) and C-terminus Domain (CTD). The TMD consists of six helices, forming binding site A, four of which are oriented in a parallel manner, with respect to each other, while the remaining two are anti parallel to this four helix cluster. A "salt bridge" or "charge interlock" consisting of four amino acid residues, two Lysines and two Aspartates, forms a junction that both monomers of Yiip converge at, forming a pivot point for conformational changes. | Yiip's monomer structure is classified into two different domains, the Trans-Membrane Domain (TMD) and C-terminus Domain (CTD). The TMD consists of six helices, forming binding site A, four of which are oriented in a parallel manner, with respect to each other, while the remaining two are anti parallel to this four helix cluster. A "salt bridge" or "charge interlock" consisting of four amino acid residues, two Lysines and two Aspartates, forms a junction that both monomers of Yiip converge at, forming a pivot point for conformational changes. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 17:33, 24 March 2017
Zinc Transporter Yiip
| |||||||||||