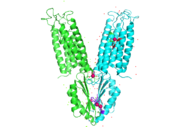
Structure
YiiP is a homodimer, with each monomer consisting of 238 residues (protein dimer) with a TransMembrane () and C-Terminal () domain that are connected via a charge interlocking mechanism located on a flexible loop. The TMD, where Zn2+ binding site A resides, consists of a total of six helices in each . Four of these helices are bundled together while the remaining two are oriented antiparallel to the . Movement of these helices play a role in the function of YiiP. A large portion of the protein containing binding site C, the CTD, approximately 30 Å in length[1], protrudes into the cytoplasm functioning as a zinc sensor within the cell.
Site A is located in both TMDs of the protein, while site C is located in the CTD, and site B is located at the junction of the domains join. Both TMD are composed of 6 helices, 4 of which (TM1, TM2, TM4, TM5) pivot about the ion binding site A. Zn2+ binding at site C helps hold the CTD together and is thought to stabilize conformational changes in YiiP. YiiP has two different functional conformations which dictates whether or not YiiP is open to the periplasm or the cytoplasm. An interlocked salt bridge connects the two domains with the Lys77 and the Asp207 from each monomer. This salt bridge acts as the hinge for the conformational changes that YiiP undergoes.
Interlocking Salt Bridge
The formation between Lys77 and Asp207 of each domain of YiiP form an interlocking interaction that acts as the pivot point of the conformational change that drives the function of YiiP. The salt bridge is disrupted when Zinc is bound, due to movement of the antiparallel helices. This disrupts the ion-ion attractions that established the salt bridge- causing a conformational shift in YiiP. This salt bridge also aids in holding the two monomers together.
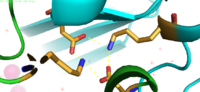
Lys77 and Asp207 Salt Bridges
residues around the salt bridge further stabilize the two domains in the v-shaped void where the domains connect. This prevents degradation of the protein's interlock via interactions with the environment.
Zn2+ Binding Sites
Each zinc promoter contains three zinc binding sites. There is an active site (Site A), and two cytoplasmic binding sites (Site B and C). It was found that only site A and C are conserved, while the function of Site B not well defined, though it seems to play a role in subunit dimerization.
Binding Site A
Binding site A is in the center of the transmembrane domain, attached and confined via residues from the TM2 and TM5 helices. The TM2 domain has and Asp49, and the TM5 has His153 and Asp157. The TM5 helix is significantly shorter than the other 5 helices around it, and this length forms a cavity in the membrane. In turn, this cavity is able to bind a Zn2+ ion. This site is the protein's active site, meaning that this is where the zinc is able to attach and eventually exit the cell via proton transport. This particular site has an ideal tetrahedron among its residues which is preferred for Zn2+, thus making it the perfect active site for Zn2+ to bind.
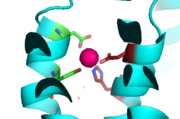
Binding Site A showing TM2 domain (left) and TM5 domain (right). The Asp45 and Asp49 as well as the His153 and Asp157 are the coordination residues in the acitve site.
It is important to note that the structure of this binding site is rigid because of the coordination of the Zn2+ between the four residues. This rigidity is indicative that any slight shift on either of the helices will cause a drastic readjustment of the coordination of Zn2+. In addition, there are no outer-shell constraints to hold the residues in place, which means that with a readjustment of the molecule, there is no energy being expended to bind or release another Zn2+ molecule. Therefore, the Zn2+ is able to rapidly release and a new Zn2+ can bind again with a simple reorientation or shift of the molecule. This rapid on off bind and release mechanism is the regulator of homeostatic levels of Zn2+ in the cell. This regulation is so rapid in fact, it is significantly faster than other Zn2+ exchange rate proteins- by several orders of magnitude.
Binding Site C
has vastly opposite properties from what is seen in binding site A. It is located on the TM2-TM3 loop on the cytoplasmic membrane and between the two C-terminus domain interfaces. Here, there is a binuclear coordination of Zn2+ between the residue that bridges the Zn2+ ions together and the four coordinating residues (His232, His248, His283 and His261). The Asp285 residue is conserved, meaning it does not have outer shell constraints. However, the four histidine residues all have outer shell constraints. These constraints consist of hydrogen bonds to the residues surrounding the binding site. These hydrogen bonds can form bidentate bonds, which means that the hydrogen bond attaches to a metal in two places. These bonds in turn create an extensive network of interactions at the CTD interface, and it is these interactions that allow for stability and strengthening of the CTD-CTD association.
Mechanism of Transport
YiiP's ability to export Zn2+ from the cytoplasm is best described as an alternating access mechanism with Zn2+/H+ antiport. YiiP has 2 major structural conformations as shown by the crystallized structures 3H90 and 3J1Z [1] (a YiiP homolog derived from Shewanella oneidensis). 3H90 shows YiiP in its outward-facing conformation and 3J1Z shows the YiiP homolog in an inward-facing conformation.
When YiiP is saturated with Zn2+ it seems to favor the whereas when active sites are either empty or bound to H+ the is favored. This drives the export of Zn2+ from the cytoplasm and enhances the coupling of the proton-motive force. Although YiiP exists as a homodimer both monomers can undergo conformation change independent of one other to
produce the alternating access mechanism.
Zn2+ Induced Conformation Change
Conformation changes occur in the TMD and CTD, both of which are heavily influenced by the presence of Zn2+. The conformation change directly involved with Zn2+/H+ antiport occurs in the TMD as helix pivoting controls what environment site A is available to. Conformation change occurs when the transmembrane helix pairs TM1, TM2, TM4, and TM5 pivot around cation binding site.[2] It is believed that the energy for TMD conformation change comes from energy of binding each substrate. Changing to the outward from the inward-facing conformation causes a shift in which disrupts the tetrahedral geometry of active site A. This in turn decreases binding affinity site A has for Zn2+ making export to the periplasm possible. After Zn2+ is exported and site A is either empty or bound to hydrogen change back to the inward-facing conformation is favored.
In contrast the main purpose of conformation change in the CTD is to stabilize the YiiP dimer and to act as a Zn2+ sensor. This is possible because of the flexible loop that links the TMD and the CTD. This loop harbors the charge interlock which serves as a hinge that allows movement of the CTD. Using FRET to measure the distance between the CTD of each monomer fluorescence quenching was observed as the concentration Zn2+ increased, which supports that idea that Zn2+ induces a stabilizing conformation change in the CTD.[3]
Electrostatic Interactions
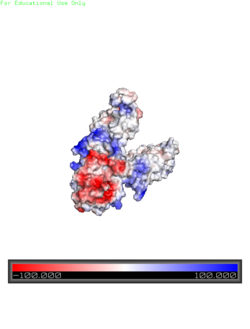
Electrostatic Charge Distribution
along the exterior surface of the protein is primarily neutral for the TMDs, but transitions to positive near the location of the charge interlock and interior side of the cell membrane. This positive section is characteristic of trans-membrane proteins as a means of achieving proper orientation within the cell membrane. Binding sites A, B, and C, as well as the CTDs of both monomers, all possess a high negative charge relative to the other charges present, facilitating the binding and releasing of Zn
2+ ions. The two CTDs are held together by the charge interlock and hydrophobic interactions of the TMDs, despite their electrostatic repulsion. Upon the release of Zn
2+ ions, the CTDs undergo alterations to electronegativity, which enables domain separation.
References
- ↑ Coudray N, Valvo S, Hu M, Lasala R, Kim C, Vink M, Zhou M, Provasi D, Filizola M, Tao J, Fang J, Penczek PA, Ubarretxena-Belandia I, Stokes DL. Inward-facing conformation of the zinc transporter YiiP revealed by cryoelectron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 22. PMID:23341604 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1215455110
- ↑ Coudray N, Valvo S, Hu M, Lasala R, Kim C, Vink M, Zhou M, Provasi D, Filizola M, Tao J, Fang J, Penczek PA, Ubarretxena-Belandia I, Stokes DL. Inward-facing conformation of the zinc transporter YiiP revealed by cryoelectron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 22. PMID:23341604 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1215455110
- ↑ Lu M, Chai J, Fu D. Structural basis for autoregulation of the zinc transporter YiiP. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Oct;16(10):1063-7. Epub 2009 Sep 13. PMID:19749753 doi:10.1038/nsmb.1662