We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
IntronA (Interferon alpha 2b)
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<StructureSection load='1rh2' size='340' side='right' caption='The IntronA (Interferon-alpha 2b) human recombinant' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1rh2' size='340' side='right' caption='The IntronA (Interferon-alpha 2b) human recombinant' scene=''> | ||
| - | This is a default text for your page '''IntronA (Interferon alpha 2b)'''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
| - | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 25: | Line 23: | ||
'''Hepatitis Virus''' | '''Hepatitis Virus''' | ||
| - | ''Hepatitis | + | ''Hepatitis B'' |
| - | Hepatitis | + | IFNα2b treats chronic Hepatitis B (HBV) by interfering with viral DNA synthesis and enhancing the cellular immune response <ref name="seven"> doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2007.08.010</ref>. The cytokine enhances T-cell and natural killer cell activity by interacting with the infected cell’s surface <ref name="seven"> doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2007.08.010</ref>. IFNα2b also activates antiviral enzymes to inhibit proliferation of HBV <ref name="seven"> doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2007.08.010</ref>. |
| - | ''Hepatitis | + | ''Hepatitis C'' |
| - | + | Hepatitis C (HCV) can range from acute to chronic conditions and progression occurs in more than half of these cases <ref name="five"> doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011232</ref>. HCV attacks the liver tissues causing inflammation and cirrhosis, which can lead to chronic liver disease <ref name="five"> doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011232</ref>. IFNα2b is used to treat the acute stage of HVC to prevent progression into the chronic disease <ref name="five"> doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011232</ref>. IFNα2b overall reduces the viral amplification and allows T-cells to effectively respond to the infection <ref name="six"> Doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.04.031</ref>. | |
'''Cancer''' | '''Cancer''' | ||
Revision as of 06:34, 30 March 2017
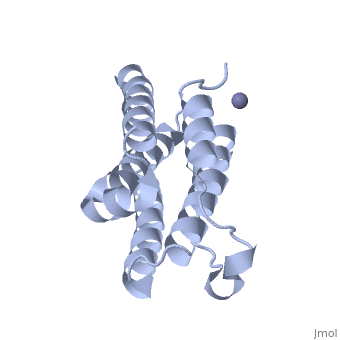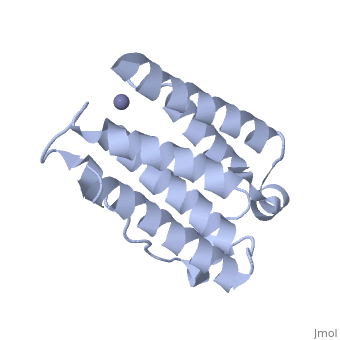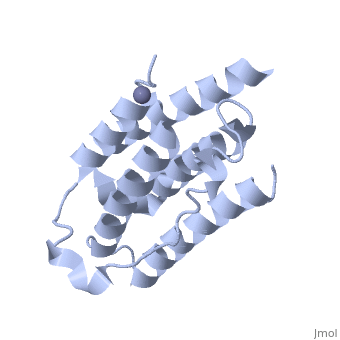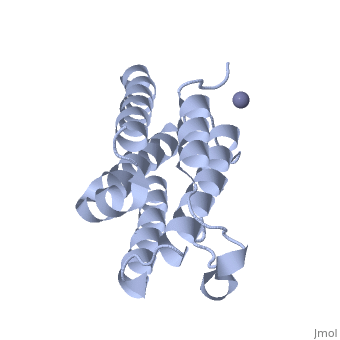
An overview of IntronA (Interferon alpha 2b)
IntronA, also known as interferon alpha-2b (IFNα2b), is a drug used in antiviral and anti-tumor therapeutic treatments [1]. IFNα2b is classified as a cytokine, a secreted protein that stimulates the immune system, and is produced by T-cells in order to hinder viral infections, cancer, bacteria, or other pathogens in humans [1].
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 Asmana Ningrum R. Human interferon alpha-2b: a therapeutic protein for cancer treatment. Scientifica (Cairo). 2014;2014:970315. doi: 10.1155/2014/970315. Epub 2014 Mar, 10. PMID:24741445 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/970315
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Tompkins WA. Immunomodulation and therapeutic effects of the oral use of interferon-alpha: mechanism of action. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1999 Aug;19(8):817-28. PMID:10476925 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/107999099313325
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/i/intron_a/intron_a_pi.pdf
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Radhakrishnan R, Walter LJ, Hruza A, Reichert P, Trotta PP, Nagabhushan TL, Walter MR. Zinc mediated dimer of human interferon-alpha 2b revealed by X-ray crystallography. Structure. 1996 Dec 15;4(12):1453-63. PMID:8994971
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Asselah T, Lada O, Moucari R, Martinot M, Boyer N, Marcellin P. Interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis B. Clin Liver Dis. 2007 Nov;11(4):839-49, viii. PMID:17981231 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2007.08.010
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Jaeckel E, Cornberg M, Wedemeyer H, Santantonio T, Mayer J, Zankel M, Pastore G, Dietrich M, Trautwein C, Manns MP. Treatment of acute hepatitis C with interferon alfa-2b. N Engl J Med. 2001 Nov 15;345(20):1452-7. PMID:11794193 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa011232
- ↑ Guo JT, Sohn JA, Zhu Q, Seeger C. Mechanism of the interferon alpha response against hepatitis C virus replicons. Virology. 2004 Jul 20;325(1):71-81. PMID:15231387 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2004.04.031
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Blade J, San Miguel JF, Escudero ML, Fontanillas M, Besalduch J, Gardella S, Arias J, Garcia-Conde J, Carnero M, Marti JM, Rozman C, Estape J, Montserrat E. Maintenance treatment with interferon alpha-2b in multiple myeloma: a prospective randomized study from PETHEMA (Program for the Study and Treatment of Hematological Malignancies, Spanish Society of Hematology). Leukemia. 1998 Jul;12(7):1144-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401039. PMID:9665202 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401039
- ↑ Quesada JR, Reuben J, Manning JT, Hersh EM, Gutterman JU. Alpha interferon for induction of remission in hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 5;310(1):15-8. PMID:6689734 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM198401053100104