We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1072
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Structural Overview == | == Structural Overview == | ||
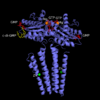
| - | Diguanylate Cyclase is a homodimer that exhibits <scene name='69/694239/C2_symmetry/ | + | Diguanylate Cyclase is a homodimer that exhibits <scene name='69/694239/C2_symmetry/6'>C2</scene> symmetry down its vertical axis. |
===GGEEF Domain=== | ===GGEEF Domain=== | ||
The <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_dgcz/2'>GGEEF</scene> Domain of Diguanylate Cyclase is the active site of the protein and has two amino acid sequences of GGEEF which allows for binding of two GTP molecules. The Active site can be divided up into two enzymatic <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_half_site_dgcz/1'>half-sites</scene>, each with a GGEEF domain for binding a single GTP molecule. DgcZ binds the guanine base of GTP through hydrogen bonds to <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_guanine_bonds_asn_asp_dgcz/4'>Asn173 and Asp 182</scene>. The ribose portion of GTP is bound loosely and the alpha phosphate is not bound at all so that it is available for attack by the 3 prime hydroxyl group on another GTP. A <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_magnesium_cofactors_dgcz/1'>Magnesium ion</scene> acts as a cofactor for each half-site, helping to stabilize the negative charges on the phosphates of GTP. | The <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_dgcz/2'>GGEEF</scene> Domain of Diguanylate Cyclase is the active site of the protein and has two amino acid sequences of GGEEF which allows for binding of two GTP molecules. The Active site can be divided up into two enzymatic <scene name='69/694239/Ggeef_domain_half_site_dgcz/1'>half-sites</scene>, each with a GGEEF domain for binding a single GTP molecule. DgcZ binds the guanine base of GTP through hydrogen bonds to <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_guanine_bonds_asn_asp_dgcz/4'>Asn173 and Asp 182</scene>. The ribose portion of GTP is bound loosely and the alpha phosphate is not bound at all so that it is available for attack by the 3 prime hydroxyl group on another GTP. A <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_magnesium_cofactors_dgcz/1'>Magnesium ion</scene> acts as a cofactor for each half-site, helping to stabilize the negative charges on the phosphates of GTP. | ||
Revision as of 17:13, 31 March 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Diguanylate Cyclase DgcZ from Escherichia coli
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644