Image:YiiP Mechanism.png
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
Size of this preview: 800 × 523 pixels
Full resolution (907 × 593 pixel, file size: 328 KB, MIME type: image/png)
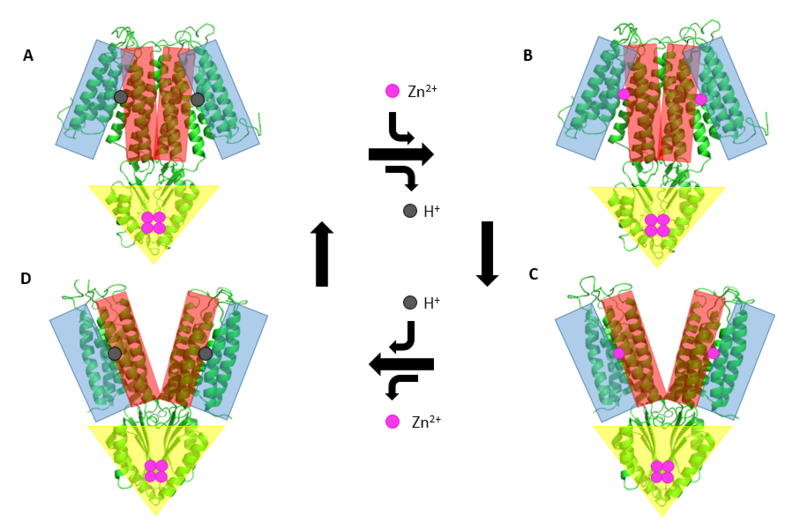
(General mechanism that YiiP uses to transport Zn2+ from the cytoplasm to the periplasm. This mechanism involves 2 major conformations; the inward-facing conformation (A & B) and the outward-facing conformation (C & D).) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | General mechanism that YiiP uses to transport Zn2+ from the cytoplasm to the periplasm. This mechanism involves 2 major conformations; the inward-facing conformation (A & B) and the outward-facing conformation (C & D). | + | General mechanism that YiiP uses to transport Zn2+ from the cytoplasm to the periplasm. This mechanism involves 2 major conformations; the inward-facing conformation (A & B) and the outward-facing conformation (C & D). Helices TM1, TM2, TM4, and TM5 (blue) are shown pivoting relative to helices TM3 & TM6 (blue). The CTD (yellow) does not move during this conformation change as it it held together tightly by binding Zn<sup>2+</sup>. |
Revision as of 18:39, 31 March 2017
General mechanism that YiiP uses to transport Zn2+ from the cytoplasm to the periplasm. This mechanism involves 2 major conformations; the inward-facing conformation (A & B) and the outward-facing conformation (C & D). Helices TM1, TM2, TM4, and TM5 (blue) are shown pivoting relative to helices TM3 & TM6 (blue). The CTD (yellow) does not move during this conformation change as it it held together tightly by binding Zn2+.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | User | Dimensions | File size | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (current) | 18:28, 31 March 2017 | Kyle Colston (Talk | contribs) | 907×593 | 328 KB | General mechanism that YiiP uses to transport Zn2+ from the cytoplasm to the periplasm. This mechanism involves 2 major conformations; the inward-facing conformation (A & B) and the outward-facing conformation (C & D). |
- Edit this file using an external application
See the setup instructions for more information.
Links
The following pages link to this file:
