User:Luke Edward Severinac/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
=='''Structure'''== | =='''Structure'''== | ||
===Active Site=== | ===Active Site=== | ||
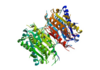
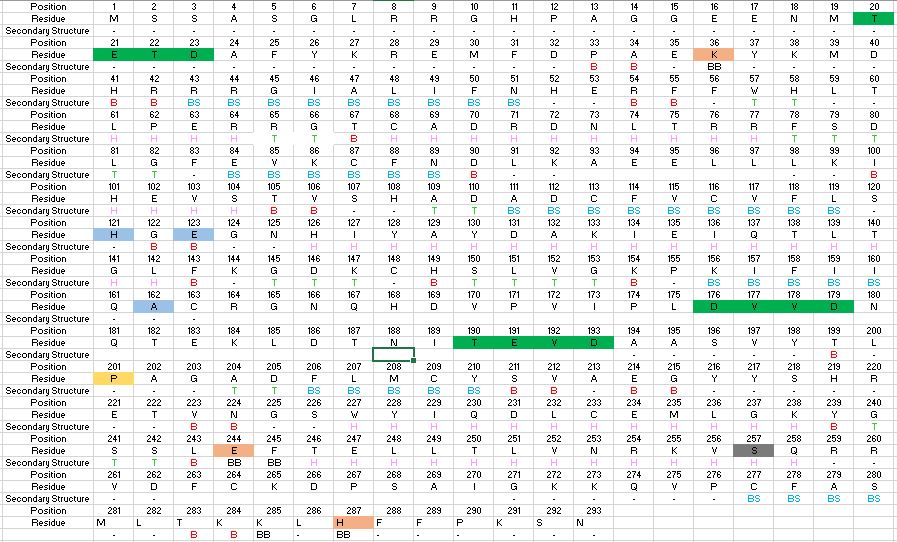
| - | In order to function as an endoprotease, Caspase-6 binds a <scene name='75/752344/Protein_ligand_real/1'>ligand</scene>, which can include neuronal proteins and tubulins [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tubulin], in its active site | + | In order to function as an endoprotease, Caspase-6 binds a <scene name='75/752344/Protein_ligand_real/1'>ligand</scene>, which can include neuronal proteins and tubulins [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tubulin], in its active site. This binding groove contains three critical amino acid residues necessary to perform cleavage of the peptide bonds. Together,<scene name='75/752344/His121_real/1'>His-121</scene>, <scene name='75/752344/Glu123_real/1'>Glu-123</scene>, and <scene name='75/752344/Cys163_real/1'>Cys-163</scene> form a <scene name='75/752344/Catalytic_triad_real/1'>catalytic triad</scene>[[Image:The real caspase mechanism.jpg|100 px|left|thumb|Cystine Aspartase mechanism]]. In the theorized mechanism, His-121 acts as an acid catalyst, Glu-123 acts as a base catalyst to deprotonate Cys-163, which then acts as covalent catalyst. |
===Zinc Exosite=== | ===Zinc Exosite=== | ||
| - | Caspase-6 function is inhibited by the binding of a <scene name='75/752344/Zinc_caspase-6/1'>Zinc</scene> ion, which binds to an <scene name='75/752344/Caspase6_allosteric_site/1'>allosteric site</scene> instead of the active site. This allosteric site is located on the outside of the protein and it is distal to the active site. The Zinc ion is bound to three amino acid residues, Lys-36, Glu-244, and His-287, once the ion is bound to the protein it is then stabilized by a single water molecule. The binding of Zinc at the exosite is suggested to cause a conformational change to the protein, which then causes a change in the active site, which inhibits Caspase-6's ability to bind to substrate. Zinc binding to the exosite is tightly regulated, because it inhibits Caspase-6's ability to inititate apoptosis. | + | Caspase-6 function is inhibited by the binding of a <scene name='75/752344/Zinc_caspase-6/1'>Zinc</scene> ion, which binds to an <scene name='75/752344/Caspase6_allosteric_site/1'>allosteric site</scene> instead of the <scene name='75/752344/Caspase6_allostericactiv_site/1'>active site</scene>. This allosteric site is located on the outside of the protein and it is distal to the active site. The Zinc ion is bound to three amino acid residues, Lys-36, Glu-244, and His-287, once the ion is bound to the protein it is then stabilized by a single water molecule. The binding of Zinc at the exosite is suggested to cause a conformational change to the protein, which then causes a change in the active site, which inhibits Caspase-6's ability to bind to substrate. Zinc binding to the exosite is tightly regulated, because it inhibits Caspase-6's ability to inititate apoptosis. |
=='''Activation of Caspase-6'''== | =='''Activation of Caspase-6'''== | ||
Revision as of 03:10, 3 April 2017
Caspase-6 in Homo sapiens
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wang XJ, Cao Q, Zhang Y, Su XD. Activation and regulation of caspase-6 and its role in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:553-72. doi:, 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124414. Epub 2014 Oct 17. PMID:25340928 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124414
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Velazquez-Delgado EM, Hardy JA. Zinc-Mediated Allosteric Inhibition of Caspase-6. J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 13. PMID:22891250 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.397752
Wang, Xiao-Jun, Qin Cao, Yan Zhang, and Xiao-Dong Su. "Activation and Regulation of Caspase-6 and Its Role in Neurodegenerative Diseases." Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 55.1 (2015): 553-72. Web.
Wang XJ, Cao Q, Liu X, Wang KT, Mi W, et al. 2010. Crystal structures of human caspase 6 reveal a new mechanism for intramolecular cleavage self-activation. EMBO Rep. 11: 841–47
(self cleavage article)
http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2WDP (this is the non-self cleaved protien)