User:Luke Edward Severinac/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
===Phosphorylation=== | ===Phosphorylation=== | ||
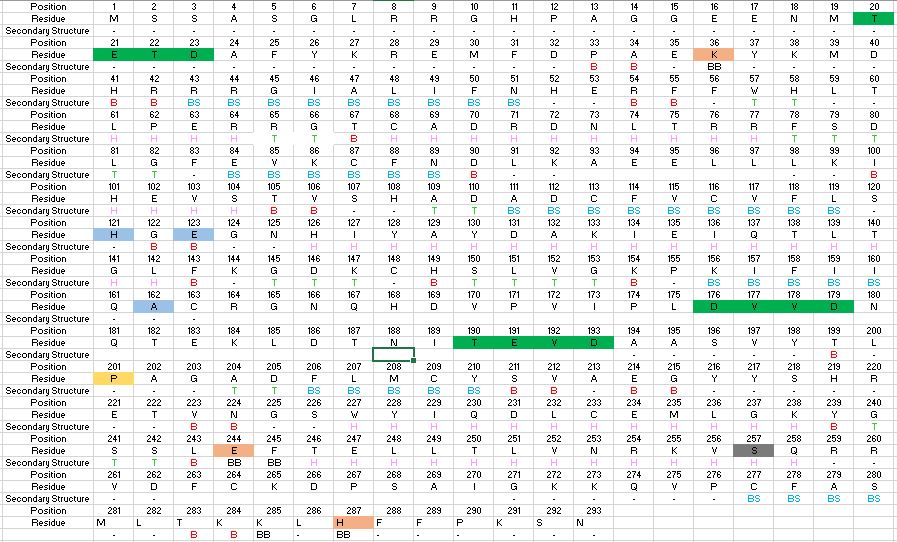
| - | The function of Caspase-6 can be inhibited by phosphorylation of Ser-257. The exact mechanism of this reaction remains unidentified at the time of publication, but proceeds when ARK5 kinase is present. This modification can occur before and after zymogen activation or auto-processing. The phosphoryl group inhibits Caspase-6 through steric interference. When Ser-257 is phosphorylated, the amino acid residue interacts with <scene name='75/752344/Caspase-6_his-208/1'>Pro-201</scene>, causing a shift in the helices of Caspase-6. This is shown in the <scene name='75/752344/Caspase-6_s257d_mutant/1'>S257D Caspase-6 mutant</scene> mutant, whose mutation mimics phosphorylation. The shift misaligns and disrupts residues found in the active site. This conformational difference prevents the inter-subunit loop from entering during zymogen activation and the self-cleaved active dimer cannot be formed. Additionally, no new substrate is able to enter the active site. | + | The function of Caspase-6 can be inhibited by phosphorylation of Ser-257. The exact mechanism of this reaction remains unidentified at the time of publication, but proceeds when ARK5 kinase is present. This modification can occur before and after zymogen activation or auto-processing. The phosphoryl group inhibits Caspase-6 through steric interference. When Ser-257 is phosphorylated, the amino acid residue interacts with <scene name='75/752344/Caspase-6_his-208/1'>Pro-201</scene>, causing a shift in the helices of Caspase-6. This is shown in the <scene name='75/752344/Caspase-6_s257d_mutant/1'>S257D Caspase-6 mutant</scene> mutant, whose mutation mimics phosphorylation.[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3S8E]<ref name="Phosphorylation regulates assembly of the caspase-6 substrate-binding groove.">PMID: 25340928 </ref> The shift misaligns and disrupts residues found in the active site. This conformational difference prevents the inter-subunit loop from entering during zymogen activation and the self-cleaved active dimer cannot be formed. Additionally, no new substrate is able to enter the active site. |
Revision as of 00:20, 4 April 2017
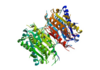
Caspase-6 in Homo sapiens
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wang XJ, Cao Q, Zhang Y, Su XD. Activation and regulation of caspase-6 and its role in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:553-72. doi:, 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124414. Epub 2014 Oct 17. PMID:25340928 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124414
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Velazquez-Delgado EM, Hardy JA. Zinc-Mediated Allosteric Inhibition of Caspase-6. J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 13. PMID:22891250 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.397752
- ↑ Wang XJ, Cao Q, Zhang Y, Su XD. Activation and regulation of caspase-6 and its role in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:553-72. doi:, 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124414. Epub 2014 Oct 17. PMID:25340928 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124414
Wang, Xiao-Jun, Qin Cao, Yan Zhang, and Xiao-Dong Su. "Activation and Regulation of Caspase-6 and Its Role in Neurodegenerative Diseases." Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 55.1 (2015): 553-72. Web.
Wang XJ, Cao Q, Liu X, Wang KT, Mi W, et al. 2010. Crystal structures of human caspase 6 reveal a new mechanism for intramolecular cleavage self-activation. EMBO Rep. 11: 841–47
(self cleavage article)
http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2WDP (this is the non-self cleaved protien)