We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1053
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
== Structural Overview == | == Structural Overview == | ||
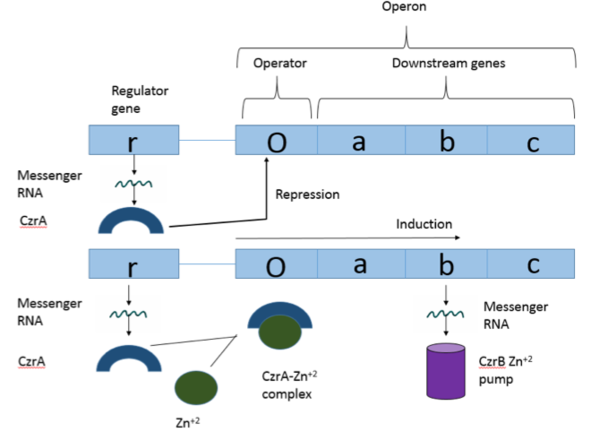
CzrA functions as a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimer_(chemistry) dimer]. The <scene name='69/694218/Monomeric_unit/1'>monomeric units</scene> dimerize at the czr operon, repressing gene transcription. Each monomeric unit contains <scene name='69/694218/Helices/1'>five alpha helices</scene> seen in purple and <scene name='69/694218/B_sheets/1'>two beta sheets</scene> displayed in yellow. While the function of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet beta sheets] are not yet known, key [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix helices] regulate the binding of DNA and Zn<sup> +2 </sup>. The <scene name='69/694218/Alpha_4_helix/1'>alpha 4 helix</scene> is the location of DNA binding and the <scene name='69/694218/Alpha_5_helix/1'>alpha 5 helix</scene> contains the Zn<sup> +2 </sup> binding site. As Zn<sup> +2 </sup> binds, the alpha 4 helices are <scene name='69/694218/Alpha_4_helices_pushed/1'>pushed out of alignment</scene>, repressing their DNA binding ability. | CzrA functions as a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimer_(chemistry) dimer]. The <scene name='69/694218/Monomeric_unit/1'>monomeric units</scene> dimerize at the czr operon, repressing gene transcription. Each monomeric unit contains <scene name='69/694218/Helices/1'>five alpha helices</scene> seen in purple and <scene name='69/694218/B_sheets/1'>two beta sheets</scene> displayed in yellow. While the function of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet beta sheets] are not yet known, key [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix helices] regulate the binding of DNA and Zn<sup> +2 </sup>. The <scene name='69/694218/Alpha_4_helix/1'>alpha 4 helix</scene> is the location of DNA binding and the <scene name='69/694218/Alpha_5_helix/1'>alpha 5 helix</scene> contains the Zn<sup> +2 </sup> binding site. As Zn<sup> +2 </sup> binds, the alpha 4 helices are <scene name='69/694218/Alpha_4_helices_pushed/1'>pushed out of alignment</scene>, repressing their DNA binding ability. | ||
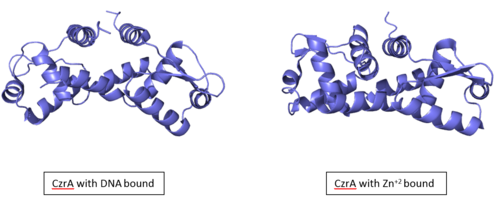
| - | [[Image:2KJB + 2KJC compared.fw.png|center|thumb| Figure :Comparison of CzrA with Zn<sup>+2</sup> bound and CzrA with DNA bound]] | + | [[Image:2KJB + 2KJC compared.fw.png|500px|center|thumb| Figure :Comparison of CzrA with Zn<sup>+2</sup> bound and CzrA with DNA bound]] |
== Binding of DNA == | == Binding of DNA == | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
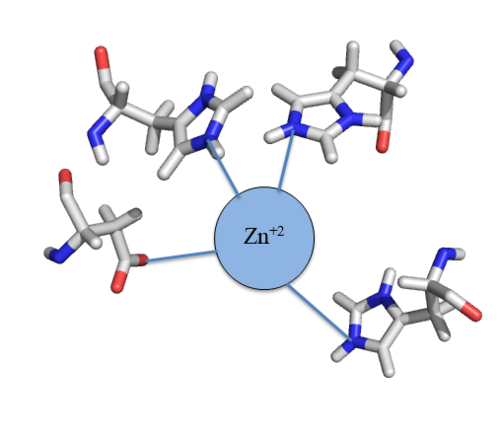
Zinc<sup>+2</sup> binding is driven by a large [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Entropy entropic] gain <ref>DOI:10.1021/ja906131b</ref>. Water molecules around the metal ion and CzrA protein are displaced, and gain greater freedom. This gain in entropy allows Zn<sup>+2</sup> to bind to CzrA with reasonable affinity and speed in vivo. The zinc<sup>+2</sup> ion forms a tetrahedral complex with the four residues (Figure 1). This allows other metal ions to act as allosteric inhibitors to CzrA. Any metal that may form a tetrahedral complex will have some affinity for CzrA, assuming it is not too large to fit into the pocket. However, the metal binding pocket of CzrA has been optimized to bind Zn<sup>+2</sup> with the highest affinity. As CzrA is a transcriptional repressor, binding of Zn<sup>+2</sup> to the dimer will activate the czr operon. Zn<sup>+2</sup> is preferred as CzrB opens a Zn<sup>+2</sup> channel, allowing the excess zinc ions to export the cell. | Zinc<sup>+2</sup> binding is driven by a large [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Entropy entropic] gain <ref>DOI:10.1021/ja906131b</ref>. Water molecules around the metal ion and CzrA protein are displaced, and gain greater freedom. This gain in entropy allows Zn<sup>+2</sup> to bind to CzrA with reasonable affinity and speed in vivo. The zinc<sup>+2</sup> ion forms a tetrahedral complex with the four residues (Figure 1). This allows other metal ions to act as allosteric inhibitors to CzrA. Any metal that may form a tetrahedral complex will have some affinity for CzrA, assuming it is not too large to fit into the pocket. However, the metal binding pocket of CzrA has been optimized to bind Zn<sup>+2</sup> with the highest affinity. As CzrA is a transcriptional repressor, binding of Zn<sup>+2</sup> to the dimer will activate the czr operon. Zn<sup>+2</sup> is preferred as CzrB opens a Zn<sup>+2</sup> channel, allowing the excess zinc ions to export the cell. | ||
| - | [[Image:Zinc tetrahedral complex.PNG|thumb|center| Figure 1:Zn<sup>+2</sup> tetrahedral binding complex]] | + | [[Image:Zinc tetrahedral complex.PNG|500px|thumb|center| Figure 1:Zn<sup>+2</sup> tetrahedral binding complex]] |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 12:52, 11 April 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
CzrA: A Zinc dependent Transcriptional Regulator
| |||||||||||