User:Jakob Jozwiakowski/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Structural Overview == | == Structural Overview == | ||
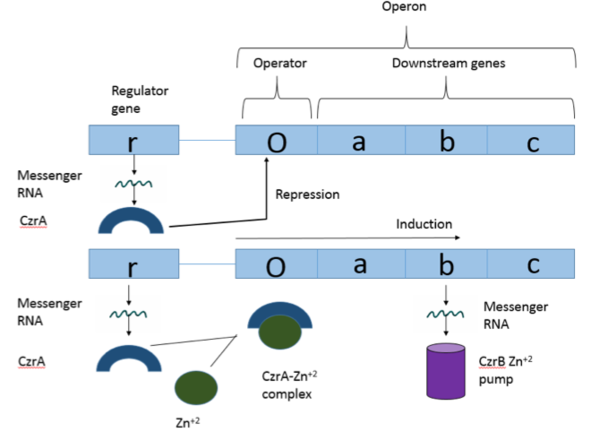
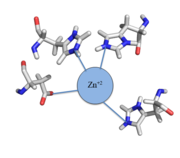
| - | CzrA functions as a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimer_(chemistry) dimer]. The <scene name='69/694218/Monomeric_unit/1'>monomeric units</scene> dimerize at the czr operon, repressing gene transcription. Each monomeric unit contains <scene name='69/694218/Helices/1'>five alpha helices</scene> seen in purple and <scene name='69/694218/B_sheets/1'>two beta sheets</scene> displayed in yellow. While the function of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet beta sheets] are not yet known, key [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix helices] regulate the binding of DNA and Zn<sup> +2 </sup>. The <scene name=' | + | CzrA functions as a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimer_(chemistry) dimer]. The <scene name='69/694218/Monomeric_unit/1'>monomeric units</scene> dimerize at the czr operon, repressing gene transcription. Each monomeric unit contains <scene name='69/694218/Helices/1'>five alpha helices</scene> seen in purple and <scene name='69/694218/B_sheets/1'>two beta sheets</scene> displayed in yellow. While the function of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet beta sheets] are not yet known, key [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix helices] regulate the binding of DNA and Zn<sup> +2 </sup>. The <scene name='75/752349/2kjb_alpha_4_helices/1'>alpha four helices</scene> are the location of DNA binding and the <scene name='75/752349/2kjb_alpha_5_helices/1'>alpha five helices</scene> contain the Zn<sup> +2 </sup> binding site. As Zn<sup> +2 </sup> binds, the alpha 4 helices are <scene name='69/694218/Alpha_4_helices_pushed/1'>pushed out of alignment</scene>, repressing their DNA binding ability. |
| - | + | ||
== Binding of DNA == | == Binding of DNA == | ||
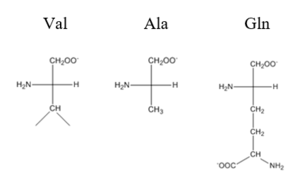
The <scene name='69/694219/Serandhisresidues/2'>main DNA interactions</scene> have been found to occur at the Ser 54 and 57 along with His 58 residues. These residues are likely to interact with the 5'-TGAA sequence found in the half-site of the DNA. These residues are found in the N terminal of the R helix. The residues involved in the <scene name='69/694219/Dna_binding_pocket/1'>DNA binding pocket</scene> are Val 42 and Gln 53. This was experimentally determined by mutating the Gln and Val with Ala residues and measuring the binding capacity; In a previously published article <ref name="critical"/>, the DNA bound state of CzrA was tested by using the known critical residues for DNA interactions. Critical residues, Gln53, Val42, Ser54, Ser57, and His58, were replaced with Ala and then compared to the kinetics of the wild type protein. Replacing only the Q53 and V42 residues resulted in an 11-fold and 160-fold decrease in K<sub>a</sub>, respectively. Other residues such as S54, S57, and H58 were also replaced with Ala residues, and it was found that these mutations caused binding similar to the fully inhibited Zn<sup>2+</sup> bound state. Table 1 in this same article shows the different K<sub>observed</sub>, and the measured decrease in K<sub>observed</sub> for each mutation. The bind between the DNA and the protein can be attributed to losing certain intermolecular forces such as possible hydrogen bonding when changing from Gln and Ala, and a loss of London Dispersion forces in the Val to Ala change. [[Image:Capture01.PNG|300px|center|thumb| Comparison of Val, Ala, and Gln residues]] | The <scene name='69/694219/Serandhisresidues/2'>main DNA interactions</scene> have been found to occur at the Ser 54 and 57 along with His 58 residues. These residues are likely to interact with the 5'-TGAA sequence found in the half-site of the DNA. These residues are found in the N terminal of the R helix. The residues involved in the <scene name='69/694219/Dna_binding_pocket/1'>DNA binding pocket</scene> are Val 42 and Gln 53. This was experimentally determined by mutating the Gln and Val with Ala residues and measuring the binding capacity; In a previously published article <ref name="critical"/>, the DNA bound state of CzrA was tested by using the known critical residues for DNA interactions. Critical residues, Gln53, Val42, Ser54, Ser57, and His58, were replaced with Ala and then compared to the kinetics of the wild type protein. Replacing only the Q53 and V42 residues resulted in an 11-fold and 160-fold decrease in K<sub>a</sub>, respectively. Other residues such as S54, S57, and H58 were also replaced with Ala residues, and it was found that these mutations caused binding similar to the fully inhibited Zn<sup>2+</sup> bound state. Table 1 in this same article shows the different K<sub>observed</sub>, and the measured decrease in K<sub>observed</sub> for each mutation. The bind between the DNA and the protein can be attributed to losing certain intermolecular forces such as possible hydrogen bonding when changing from Gln and Ala, and a loss of London Dispersion forces in the Val to Ala change. [[Image:Capture01.PNG|300px|center|thumb| Comparison of Val, Ala, and Gln residues]] | ||
Revision as of 13:04, 11 April 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
CzrA
| |||||||||||