Sandbox Reserved 1063
From Proteopedia
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
=== Binding Site 2 === | === Binding Site 2 === | ||
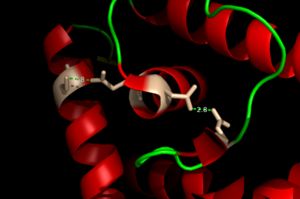
<scene name='69/694230/Binding_site_2/1'>Binding site 2</scene> consists of a highly distorted tetrahedral geometry around the zinc ion. There are three amino acids involved in the binding of the zinc ion (C30, E41, and E107) as well as a water molecule. If a C30A AdcR missense is present in binding site 2, it will have no effect on the ability of the protein to bind DNA <ref>PMID:22085181</ref>. Therefore, binding site 2 has no significant role in DNA binding. | <scene name='69/694230/Binding_site_2/1'>Binding site 2</scene> consists of a highly distorted tetrahedral geometry around the zinc ion. There are three amino acids involved in the binding of the zinc ion (C30, E41, and E107) as well as a water molecule. If a C30A AdcR missense is present in binding site 2, it will have no effect on the ability of the protein to bind DNA <ref>PMID:22085181</ref>. Therefore, binding site 2 has no significant role in DNA binding. | ||
| - | == '''Other Ligands''' == | + | === '''Other Ligands''' === |
The AdcR MarR transcriptional regulator is able to bind Co(II) in binding site 1 in a way that induces similar conformational changes to Zn(II) binding. Co(II) coordination in binding site 1 is able to allosterically activate DNA binding similarly to Zn(II) binding <ref>PMID:22085181</ref>. | The AdcR MarR transcriptional regulator is able to bind Co(II) in binding site 1 in a way that induces similar conformational changes to Zn(II) binding. Co(II) coordination in binding site 1 is able to allosterically activate DNA binding similarly to Zn(II) binding <ref>PMID:22085181</ref>. | ||
== '''DNA Binding''' == | == '''DNA Binding''' == | ||
Revision as of 17:52, 14 April 2017
Adhesin Competence Regulator
Introduction
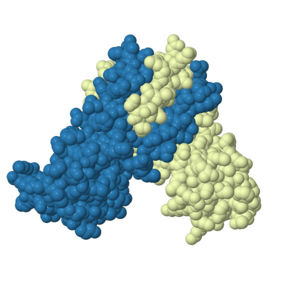
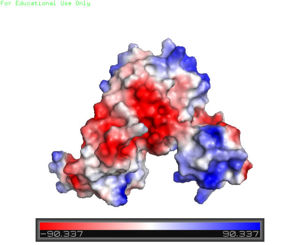
Adhesin Competence Regulator (AdcR) is a transcriptional regulator that controls the activation of over seventy genes within the bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae[1]. Contrasting with other members of the multiple antibiotic resistance regulator (MarR) family, AdcR is metal dependent as the binding of Zinc causes conformational changes that permit AdcR to repress the transcription of high-affinity Zinc specific uptake transporters [2]. Zinc plays a vital role in organism homeostasis acting as a co-factor and a regulator of enzymatic activity, however zinc can lead to cell toxicity and deficiency of other vital metals that are also necessary for protein function[3][4]. Given the many roles zinc plays in general homeostasis the importance of AdcR in Streptococcus pneumoniae can be understood provided its ability to regulate zinc transfer proteins within the bacteria.
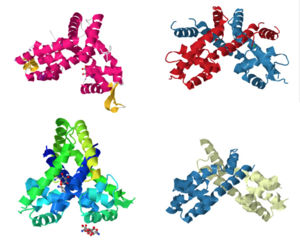
Members of the MarR protein family conserve a number of features including a general triangular shape, a two fold pseudosymmetric homo dimer, and a wingled helix-turn-helix pattern. Consistent with AdcR's identity as a member of the MarR protein family, AdcR exhibits the triangular shape with the (wHTH) binding domain. This structure calls for multiple zinc binding sites that facilitate protein conformational change allowing for DNA binding and regulation through the wHTH domain.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Sanson M, Makthal N, Flores AR, Olsen RJ, Musser JM, Kumaraswami M. Adhesin competence repressor (AdcR) from Streptococcus pyogenes controls adaptive responses to zinc limitation and contributes to virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(1):418-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1304. Epub 2014 Dec, 15. PMID:25510500 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1304
- ↑ Guerra AJ, Dann CE, Giedroc DP. Crystal Structure of the Zinc-Dependent MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator AdcR in the Zn(II)-Bound State. J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Nov 21. PMID:22085181 doi:10.1021/ja2080532
- ↑ Fraústo da Silva J, Williams R. The Biological Chemistry of Elements: The Inorganic Chemistry of Life. Second ed. Oxford University Press; Oxford: 2001.
- ↑ Ma Z, Jacobsen FE, Giedroc DP. Coordination chemistry of bacterial metal transport and sensing. Chem Rev. 2009 Oct;109(10):4644-81. doi: 10.1021/cr900077w. PMID:19788177 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cr900077w
- ↑ Reyes-Caballero H, Guerra AJ, Jacobsen FE, Kazmierczak KM, Cowart D, Koppolu UM, Scott RA, Winkler ME, Giedroc DP. The metalloregulatory zinc site in Streptococcus pneumoniae AdcR, a zinc-activated MarR family repressor. J Mol Biol. 2010 Oct 22;403(2):197-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.030. Epub 2010, Sep 8. PMID:20804771 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.030
- ↑ Reyes-Caballero H, Guerra AJ, Jacobsen FE, Kazmierczak KM, Cowart D, Koppolu UM, Scott RA, Winkler ME, Giedroc DP. The metalloregulatory zinc site in Streptococcus pneumoniae AdcR, a zinc-activated MarR family repressor. J Mol Biol. 2010 Oct 22;403(2):197-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.030. Epub 2010, Sep 8. PMID:20804771 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.030
- ↑ Guerra AJ, Dann CE, Giedroc DP. Crystal Structure of the Zinc-Dependent MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator AdcR in the Zn(II)-Bound State. J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Nov 21. PMID:22085181 doi:10.1021/ja2080532
- ↑ Guerra AJ, Dann CE, Giedroc DP. Crystal Structure of the Zinc-Dependent MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator AdcR in the Zn(II)-Bound State. J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Nov 21. PMID:22085181 doi:10.1021/ja2080532
- ↑ Guerra AJ, Dann CE, Giedroc DP. Crystal Structure of the Zinc-Dependent MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator AdcR in the Zn(II)-Bound State. J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Nov 21. PMID:22085181 doi:10.1021/ja2080532
- ↑ Guerra AJ, Dann CE, Giedroc DP. Crystal Structure of the Zinc-Dependent MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator AdcR in the Zn(II)-Bound State. J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Nov 21. PMID:22085181 doi:10.1021/ja2080532