Background
Operon Overview
Operons are a critical genetic component of most prokaryotic cells. There are many different operons that are responsible for the production of proteins with a wide range of functions, the most well-known of which are the Lac and Trp operons, responsible for producing enzymes which metabolize lactose and tryptophan respectively. Despite many differences in each operon and the proteins that they encode, operons all function in the same general manner. Structurally, each operon contains a regulator, an operator, and one or more structural genes. The regulator protein is responsible for managing the expression level of the structural genes, the operator is similar to a promoter in a regular gene and is where transcription begins, and the structural genes code for proteins. The regulator protein (produced as a result of expression of the regulator gene) most often acts in a repressive manner, though this is not always the case. That is, the regulator protein will bind to the operator of the operon, inhibiting the binding and/or progression of RNA polymerase to the structural genes, thus inhibiting transcription of the genes into mRNA. If the regulator protein were to consistently be active, there could never be adequate expression of the structural genes, so there must be a way to inactive the regulator protein, thus enabling expression of the structural genes. This is achieved through the binding of an inhibitor to the regulator protein. Since regulator proteins are DNA binding proteins, often this inhibition is allosteric rather than competitive, that is the inhibitor is not something that mimics DNA and binds to the active site physically blocking DNA from binding. Rather, the inhibitor of the regulator binds to somewhere other than the active site of the protein, changing it in some way which decreases the proteins affinity or ability to bind DNA.
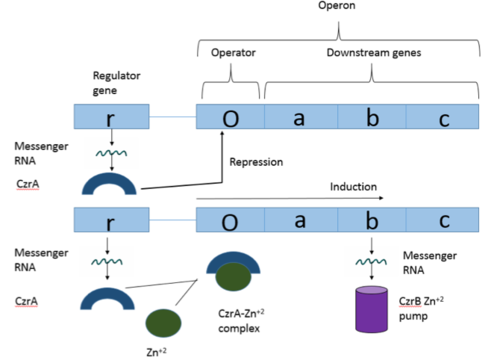
Figure 1:Overview of Operon Structure
Czr Operon
The Chromosome Determined Zinc Responsible (Czr) operon acts as described above, with Czr A acting as the regulator protein. As such, Czr A is responsible for controlling the transcription of the rest of the operon and by extension, the transport of Zn 2+ out of the cell; the role of Czr A in the Czr operon is described in further detail as part of the explanation of biological function. In addition to being a component of an operon, Czr A is also considered to be a metal sensor protein. While the immediate function of Czr A is gene regulation, this serves the larger purpose of acting to maintain an appropriate concentration of Zn 2+ in the cell.
Biological Function
Czr A is a transcriptional repressor protein responsible for the regulation of the Czr operon[1]. The Czr operon contains genes for the proteins Czr A and Czr B. Czr B is a Zinc transport protein which moves Zn2+ out of a cell while Czr A regulates this process by controlling expression level of Czr B. When relatively low amounts of zinc are present in the cell Czr A will bind to DNA, preventing the progression of RNA polymerase and thus inhibiting expression of Czr B. Decreased expression of Czr B results in the ability of the cell to retain Zn2+ more readily. Because Czr A and Czr B are transcribed as part of the same operon, an inhibitor of Czr A must be readily available to allow full transcription of Czr B when necessary. Czr A is noncompetitively inhibited by the binding of two Zn2+ ions, which is ideal in that this allows for expression of Czr B, a Zn2+ transporter to be dependent on the relative amount of Zn2+ in the cell. Czr A displays two different conformations; the first typically binds DNA and has relatively low affinity for Zn2+, in this conformation the . The to achieve the other conformation which binds two Zn2+ ions and has relatively low affinity for DNA.
DNA Binding
Czr A performs it's primary function when bound to DNA[1]. Each monomeric subunit of the protein binds DNA individually, coming together once attached to the DNA. While bound, Czr A prevents the transcription of the DNA in the Czr operon, acting as a repressor protein and effectively turning off the operon. As was briefly mentioned above, the Czr operon contains the gene responsible for producing Czr B, a metal transport protein which regulates the concentration of zinc in the cell. So, by extension, Czr A is responsible for retaining Zn2+ inside the cell by inhibiting the production of the protein responsible for transporting zinc out of the cell.
Zinc Binding
Zinc acts as an inhibitor to Czr A[1], thus preventing transcriptional repression of Czr B and allowing Zn2+ transport out of the cell. This allows for zinc transport to essentially be self regulated. That is, when zinc concentration in the cell is relatively high, zinc ions bind to Czr A, causing a conformational change which releases the bound DNA. DNA without Czr A bound is free to be transcribed and Czr B is again expressed, allowing for Zn2+ transport out of the cell.
Structural Overview
CzrA functions as a dimer. The dimerize at the czr operon, repressing gene transcription. Each monomeric unit contains seen in purple and displayed in yellow. While the function of the beta sheets are not yet known, key helices regulate the binding of DNA and Zn +2 . The are the location of DNA binding and the contain the Zn +2 binding site. As Zn +2 binds, the alpha 4 helices are , repressing their DNA binding ability (Figure 2).
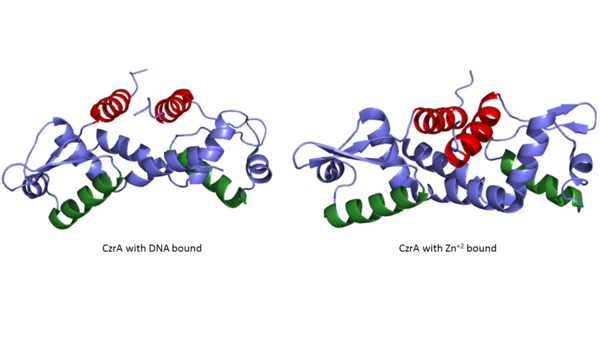
Figure 2:Comparison of CzrA with Zn
+2 bound and CzrA with DNA bound with the alpha five helices shown in red and the alpha four helices shown in green
Binding of DNA
The have been found to occur at the Ser 54 and 57 along with His 58 residues. These residues are likely to interact with the 5'-TGAA sequence found in the half-site of the DNA. These residues are found in the N terminal of the alpha 4 helix. The residues involved in the are Val 42 and Gln 53. This was experimentally determined by mutating the Gln and Val with Ala residues and measuring the binding capacity; In a previously published article [1], the DNA bound state of CzrA was tested by using the known critical residues for DNA interactions. Critical residues, Gln53, Val42, Ser54, Ser57, and His58, were replaced with Ala and then compared to the kinetics of the wild type protein. Replacing only the Q53 and V42 residues resulted in an 11-fold and 160-fold decrease in Ka, respectively. Other residues such as S54, S57, and H58 were also replaced with Ala residues, and it was found that these mutations caused binding similar to the fully inhibited Zn2+ bound state. Table 1 in this same article shows the different Kobserved, and the measured decrease in Kobserved for each mutation. The bind between the DNA and the protein can be attributed to losing certain intermolecular forces such as possible hydrogen bonding when changing from Gln and Ala, and a loss of London Dispersion forces in the Val to Ala change.
The differences in binding favorability can also be seen when comparing the ΔG for the Apo-state vs. the DNA bound state and the Zinc vs. the Zinc and DNA bound state. These ΔGs were found to be -15.2kcal/mol and -9kcal/mol respectively[2]. This agrees with previously published data showing the Zinc binding inhibits the affinity the protein has to DNA.
Zinc Binding
Many zinc-dependent proteins are transcriptional regulators[3]. CzrA fits into this category as an allosteric inhibitor of the czr operon. Two Zn +2 ions may bind to the dimer[1], at the location of the helix from each monomer. As zinc binds, the alpha 5 helices to inhibit the DNA binding residues. Furthermore, CzrA must be in its dimer form for zinc to bind. The is formed by two residues from each monomer, so Zn+2 cannot bind to the monomer. The is formed by Asp84 and His86 from one monomer, and His97 and His100 from the other monomer. Zinc ions were not present in the solution NMR crystal structure, so a representation of a zinc ion in the binding pocket can be seen in figure 3. Histidines are a repetitive and commonly found residue in zinc-binding proteins [4].
Zinc+2 binding is driven by a large entropic gain [5]. Water molecules around the metal ion and CzrA protein are displaced, and gain greater freedom. This gain in entropy allows Zn+2 to bind to CzrA with reasonable affinity and speed in vivo. The zinc+2 ion forms a tetrahedral complex with the four residues (Figure 3). This allows other metal ions to act as allosteric inhibitors to CzrA. Any metal that may form a tetrahedral complex will have some affinity for CzrA, assuming it is not too large to fit into the pocket. However, the metal binding pocket of CzrA has been optimized to bind Zn+2 with the highest affinity. As CzrA is a transcriptional repressor, binding of Zn+2 to the dimer will activate the czr operon. Zn+2 is preferred as CzrB opens a Zn+2 channel, allowing the excess zinc ions to export the cell.
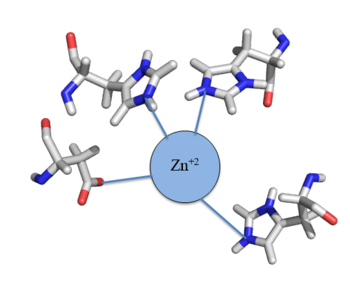
Figure 3:Zn
+2 tetrahedral binding complex
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Arunkumar A., Campanello G., Giedroc D. (2009). Solution Structure of a
paradigm ArsR family zinc sensor in the DNA-bound state. PNAS 106:43
18177-18182.
- ↑ Chakravorty DK, Wang B, Lee CW, Giedroc DP, Merz KM Jr. Simulations of allosteric motions in the zinc sensor CzrA. J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Feb 22;134(7):3367-76. doi: 10.1021/ja208047b. Epub 2011 Nov , 14. PMID:22007899 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja208047b
- ↑ MacPherson S, Larochelle M, Turcotte B. A fungal family of transcriptional regulators: the zinc cluster proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Sep;70(3):583-604. PMID:16959962 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00015-06
- ↑ Miller J, McLachlan AD, Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun 4;4(6):1609-1614.
- ↑ Grossoehme NE, Giedroc DP. Energetics of allosteric negative coupling in the zinc sensor S. aureus CzrA. J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Dec 16;131(49):17860-70. doi: 10.1021/ja906131b. PMID:19995076 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja906131b



