Sandbox Reserved 1063
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== '''Zn(II) Binding''' == | == '''Zn(II) Binding''' == | ||
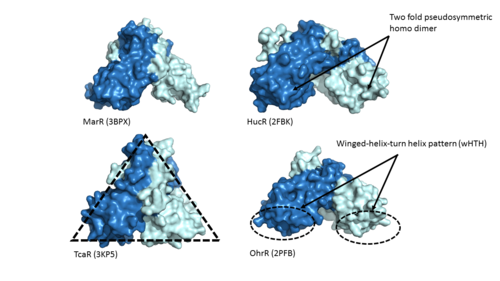
| - | Zinc-Dependent Transcriptional Regulator AdcR has <scene name='69/694230/2_binding_sites/1'>two binding sites</scene> on each of its two protomers and can bind a total of four Zn(II). One of the two functional domains of AdcR is <scene name='69/694230/Dimerization_domain/2'>dimerization domain</scene>. This domain is made up of the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_1/1'>α1 helix</scene>, the C-terminus of the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_five/1'>α5 helix</scene> , and the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_6/1'>α6 helix</scene>. This domain is connected to the wHTH domain by the long α5 helix. The <scene name='69/694230/Alpha1-alpha2_loop/1'>α1-α2 loop</scene> combined with the α5 and <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_2/1'>α2 helix</scene> make up the <scene name='69/694230/2_binding_sites/1'>metal binding sites</scene>. Each protomer has one high affinity site (Binding site 1; KZn1 = 10^12 M; pH 8) and one low affinity binding site (Binding Site 2; KZn2 = 10^7 M; pH 8) <ref name="Reyes">PMID:20804771</ref>. The metal binding pockets of the AdcR MarR transcriptional regulator are made up of the DNA binding domain with the extended α1-α2 loop. The two different Zn(II) binding sites are connected via <scene name='69/694230/Hydrogen_bonding/4'>hydrogen bonding</scene> of H108 and E41. | + | Zinc-Dependent Transcriptional Regulator AdcR has <scene name='69/694230/2_binding_sites/1'>two binding sites</scene> on each of its two protomers and can bind a total of four Zn(II). One of the two functional domains of AdcR is <scene name='69/694230/Dimerization_domain/2'>dimerization domain</scene>. This domain is made up of the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_1/1'>α1 helix</scene>, the C-terminus of the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_five/1'>α5 helix</scene> , and the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_6/1'>α6 helix</scene>. This domain is connected to the wHTH domain by the long α5 helix. The <scene name='69/694230/Alpha1-alpha2_loop/1'>α1-α2 loop</scene> combined with the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_five/1'>α5 helix</scene> and <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_2/1'>α2 helix</scene> make up the <scene name='69/694230/2_binding_sites/1'>metal binding sites</scene>. Each protomer has one high affinity site (Binding site 1; KZn1 = 10^12 M; pH 8) and one low affinity binding site (Binding Site 2; KZn2 = 10^7 M; pH 8) <ref name="Reyes">PMID:20804771</ref>. The metal binding pockets of the AdcR MarR transcriptional regulator are made up of the DNA binding domain with the extended α1-α2 loop. The two different Zn(II) binding sites are connected via <scene name='69/694230/Hydrogen_bonding/4'>hydrogen bonding</scene> of H108 and E41. |
=== Binding Site 1 === | === Binding Site 1 === | ||
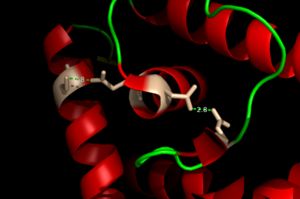
<scene name='69/694230/Binding_site_1/4'>Binding site 1</scene> consists of a distorted tetrahedral geometry around Zn(II). The four amino acids involved in zinc binding are E24, H42, H108, and H112. Binding site 1 is the only binding site that plays a significant role in the protein's regulatory function. The ability of binding site 1 to coordinate to the Zn(II) ion is pH dependent. At pH 6 the binding affinity for the Zn(II) ion is 10^9 - 10^10 M^-1, but at pH 8 the binding affinity increases to 10^12 M^-1 <ref name="Reyes" />. This is due to the charges on the histidines of the binding site. At pH 6, the histidines are positively charged and can interact with the negatively charged Zn(II) ion. However, at pH 8 the histidines are neutrally charged and will not coordinate as well with Zn(II). | <scene name='69/694230/Binding_site_1/4'>Binding site 1</scene> consists of a distorted tetrahedral geometry around Zn(II). The four amino acids involved in zinc binding are E24, H42, H108, and H112. Binding site 1 is the only binding site that plays a significant role in the protein's regulatory function. The ability of binding site 1 to coordinate to the Zn(II) ion is pH dependent. At pH 6 the binding affinity for the Zn(II) ion is 10^9 - 10^10 M^-1, but at pH 8 the binding affinity increases to 10^12 M^-1 <ref name="Reyes" />. This is due to the charges on the histidines of the binding site. At pH 6, the histidines are positively charged and can interact with the negatively charged Zn(II) ion. However, at pH 8 the histidines are neutrally charged and will not coordinate as well with Zn(II). | ||
Revision as of 20:16, 19 April 2017
Adhesin Competence Regulator
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Sanson M, Makthal N, Flores AR, Olsen RJ, Musser JM, Kumaraswami M. Adhesin competence repressor (AdcR) from Streptococcus pyogenes controls adaptive responses to zinc limitation and contributes to virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(1):418-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1304. Epub 2014 Dec, 15. PMID:25510500 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1304
- ↑ Fraústo da Silva J, Williams R. The Biological Chemistry of Elements: The Inorganic Chemistry of Life. Second ed. Oxford University Press; Oxford: 2001.
- ↑ Ma Z, Jacobsen FE, Giedroc DP. Coordination chemistry of bacterial metal transport and sensing. Chem Rev. 2009 Oct;109(10):4644-81. doi: 10.1021/cr900077w. PMID:19788177 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cr900077w
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Guerra AJ, Dann CE, Giedroc DP. Crystal Structure of the Zinc-Dependent MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator AdcR in the Zn(II)-Bound State. J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Nov 21. PMID:22085181 doi:10.1021/ja2080532
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Reyes-Caballero H, Guerra AJ, Jacobsen FE, Kazmierczak KM, Cowart D, Koppolu UM, Scott RA, Winkler ME, Giedroc DP. The metalloregulatory zinc site in Streptococcus pneumoniae AdcR, a zinc-activated MarR family repressor. J Mol Biol. 2010 Oct 22;403(2):197-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.030. Epub 2010, Sep 8. PMID:20804771 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.030