Introduction
Noxafil, also known as posaconazole, was developed by Schering-Plough in the mid-2000s [1]. It is a broad spectrum antifungal drug mainly used to treat fungal infections caused by Candida and Aspergillus species and derived from a similar triazole antifungal agent, Itraconazole. It is especially effective against filamentous fungi. Noxafil is also often used when other antifungal medicines are not able to be tolerated or if the patient is immunocompromised. Noxafil falls under the triazole class of antifungal drugs and thus works through inhibiting the biosynthesis of ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane, an essential factor that if inhibited, will lead to prevention of cell growth and ultimately death [2]. It was seen that in a group of patients undergoing chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation, posaconazole was the most effective at the prevention and elimination of invasive fungal infections when compared to alternative treatment options [3].
Function/Structure
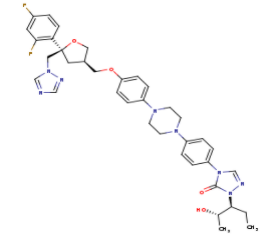 (Posaconazole 2D Structure)[2]
(Posaconazole 2D Structure)[2]
- Chemical Formula: C37H42F2N8O4
- Molecular Weight: 700.792 g/mol
- IUPAC name: 4-[4-[4-[4-[[(3R,5R)-5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)oxolan-3-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-2-[(2S,3S)-2-hydroxypentan-3-yl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
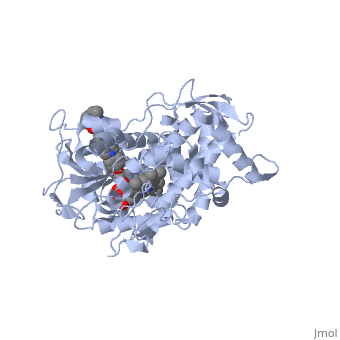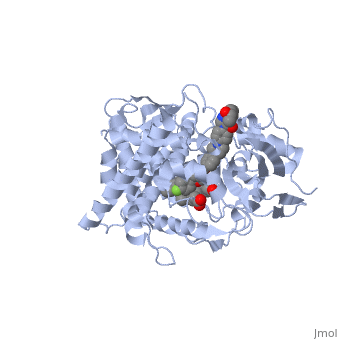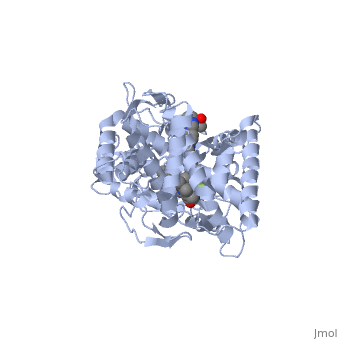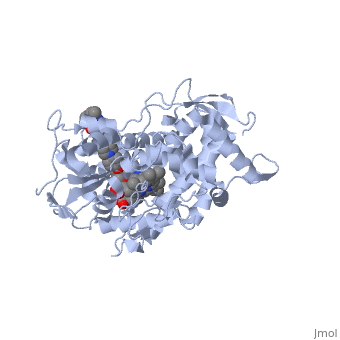
The primary component of Noxafil, is a potent, broad-spectrum antifungal drug. It was derived from a similar triazole antifungal agent, itraconazole. The differences in structure are that the chlorine substituents in the aromatic ring on the left-hand side of the images are replaced with fluorines and that the triazolone sidechain is hydroxylated in the posaconazole structure[4]. The extended side chain residues enhance antifungal activity by allowing tighter binding affinities to the in the active site of the fungal cytochrome P450-dependent enzyme 14-alpha-demthylase () [5][6]. The tighter binding affinity of posaconazole makes it less susceptible to be affected by mutations in the enzyme resulting in resistance of fungi [7]. The entirety of the scene shows the crystal of sterol 14-alpha demethylase (CYP51) from a pathogenic yeast, Candida albicans, in complex with the antifungal drug posaconazole (PDB ID: 5FSA).
Mechanism
When administered, posaconazole acts as a potent and broad-spectrum antifungal drug by binding to the through an ionic bond between a neutral nitrogen atom, on , and an iron atom, on heme, located in the active site of . This prevents biosynthesis of ergosterol and causes accumulation of toxic methylated sterol precursor, 14-alpha-methylsterol [5]. Ergosterol is essential and performs in fungal cells how cholesterol does in animal cells, making the cell membrane less permeable. Without it, the cells can no longer proliferate and eventually die because the cell membranes become “leaky”, releasing essential organic components from the cell’s interior and preventing it from performing normal cellular functions. In this way, posaconazole acts as a fungistatic against Candida species, and a fungicidal against Aspergillus species [7].
Pharmaceutical Information
Noxafil is available in several forms, such as an oral suspension, gastro resistant tablets, and a concentrate (EMA). The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Noxafil, specifically posaconazole, have been studied extensively and continue to be studied today to further improve the overall effectivenes of the drug [8].
Some of the most commonly reported side effects include nausea, diarrhea, headaches, fever, vomiting, tiredness, and dizziness.
Posaconazole has not been found to be have significant dose-limiting toxicity and has more reduced drug-drug interactions than many other antifungals (formularyjournal).
It should be taken with food to help absorption and is generally taken 3 times a day in 200 mg doses. For fungi that have been unmanageable through other treatments, 800 mg are given 2 or 4 times a day to treat infection [9]
Relevance
Invasive fungal infections, commonly caused by Candida or Aspergillus species affect patients that are immunocompromised such as those with different pre-existing infections or more seriously for those with immunologically suppressing diseases like HIV/AIDS. Candida (thrush/Candidiasis) is the most common yeast pathogen that typically grows in human mucosal surfaces like the intestinal tract and causes pathology when it becomes overgrown. Aspergillus is the most common mold pathogen leading to invasive fungal infections, termed Aspergillosis, when it is acquired from the surrounding environment [10]. Fungal resistance among these pathogens are becoming more frequent, requiring the development of new, more effective antifungal drugs. Noxafil oral suspension is the most effective form of treatment for invasive Candida and Aspergillus infections in patients 13 years and older who are severely immunocompromised. Noxafil is also more effective at preventing invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients when compared to other antifungal treatments (fluconazole and itraconazole)[8] . Overall, Noxafil displays fewer cases of invasive fungal infections and is also a more affordable treatment for immunocompromised patients. There has been a noticeable increase in the incidence of invasive fungal infections, particularly within patients receiving chemotherapy and transplant recipients. These patients are extremely susceptible because of their compromised immune system and the pressures from antibiotic usage, which is why invasive fungal infections are on the rise with these medical advances [8].
References
- ↑ Posaconazole. (2011, December 12). Retrieved from https://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/molecule-of-the-week/archive/p/molecule-of-the-week-posaconazole.html?_ga=1.240614083.1136742914.1490798730
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database; CID=468595, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/468595
- ↑ Cornely OA, Maertens J, Winston DJ, Perfect J, Ullmann AJ, Walsh TJ, Helfgott D, Holowiecki J, Stockelberg D, Goh YT, Petrini M, Hardalo C, Suresh R, Angulo-Gonzalez D. Posaconazole vs. fluconazole or itraconazole prophylaxis in patients with neutropenia. N Engl J Med. 2007 Jan 25;356(4):348-59. PMID:17251531 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa061094
- ↑ Posaconazole. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01263
Accession Number: DB01263
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Groll AH, Walsh TJ. Posaconazole: clinical pharmacology and potential for management of fungal infections. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2005 Aug;3(4):467-87. PMID:16107193 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1586/14787210.3.4.467
- ↑ Nagappan V, Deresinski S. Reviews of anti-infective agents: posaconazole: a broad-spectrum triazole antifungal agent. Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Dec 15;45(12):1610-7. doi: 10.1086/523576. PMID:18190324 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/523576
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Sircar-Ramsewak,, F., Nicolau, D. P., & Kuti, J. L. (2005). Focus on posaconazole: A novel triazole antifungal for the treatment of invasive fungal infections. Formulary Journal - Modern Medicine Network
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Dekkers BG, Bakker M, van der Elst KC, Sturkenboom MG, Veringa A, Span LF, Alffenaar JC. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Posaconazole: an Update. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2016;10:51-61. Epub 2016 May 7. PMID:27358662 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12281-016-0255-4
- ↑ Greer ND. Posaconazole (Noxafil): a new triazole antifungal agent. Proceedings (Baylor University Medical Center). 2007;20(2):188-196. PMID: PMC1849883
- ↑ Soysal A. Prevention of invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients: the role of delayed-release posaconazole. Infect Drug Resist. 2015 Sep 9;8:321-31. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S65592. eCollection, 2015. PMID:26392781 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S65592