Sandbox Reserved 1240
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
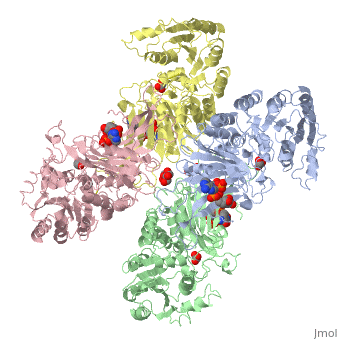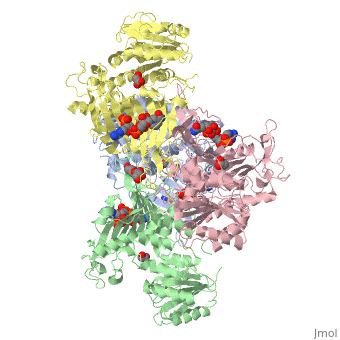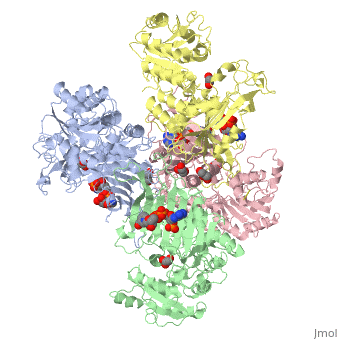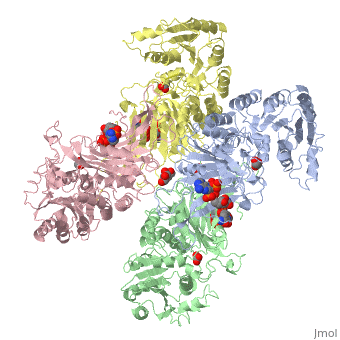
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis. Not only does it catalyze the rate limiting step of the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway, it maintains the shape of red blood cells by protecting against potential deadly reactive oxygen species. Glucose-6-Phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency is the most common enzyme deficiency in humans, affecting over 400 million people worldwide. G6PD deficiency resulted in 4100 deaths worldwide in 2013. | Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis. Not only does it catalyze the rate limiting step of the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway, it maintains the shape of red blood cells by protecting against potential deadly reactive oxygen species. Glucose-6-Phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency is the most common enzyme deficiency in humans, affecting over 400 million people worldwide. G6PD deficiency resulted in 4100 deaths worldwide in 2013. | ||
== <b>Structural highlights </b> == | == <b>Structural highlights </b> == | ||
| - | The two dimers are held together by charge-charge interactions. | + | The two dimers are held together in a tetramer by charge-charge interactions. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 20 April 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 17 through June 31, 2017 for use in the course Biochemistry II taught by Jason Telford at the Maryville University, St. Louis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1225 through Sandbox Reserved 1244. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Structure
| |||||||||||