Sandbox Reserved 1072
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Structural Overview == | == Structural Overview == | ||
| - | [[Image:DgcZ all domains sites labeled.png|250 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 4: Diguanylate cyclase DgcZ from ''E. Coli''.''' The | + | [[Image:DgcZ all domains sites labeled.png|250 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 4: Diguanylate cyclase DgcZ from ''E. Coli''.''' The domains of the enzyme are labeled, as well as the allosteric binding sites and the Zn<sup>+2</sup> binding sites on the CZB domains.]] |
DgcZ is a dimeric protein with <scene name='69/694239/Dgcz_ggeef_dom_and_czb_dom/3'>two domains</scene> per monomer<sup>[4]</sup>. The DgcZ protein has <scene name='69/694239/C2_symmetry/6'>C2</scene> symmetry down its central axis. The catalytic glycine-glycine-glutamate-glutamate-phenylalanine (GGEEF) domains are responsible for synthesizing c-di-GMP. The regulatory chemoreceptor Zinc binding (CZB) domains house the two zinc binding sites, one site located on each monomer. DgcZ binds Zinc in the CZB domains with sub-femtomolar (10<sup>-16</sup>M) affinity. When Zinc is bound, the CZB and GGEEF domains adopt conformations that inhibit DgcZ function, as illustrated in Figure 3<sup>[3]</sup>. Enzyme DgcZ was co-crystallized with Zinc, fixing the structure in its inactivate conformation. The GGEEF domains are catalytic, containing the active sites for cyclizing GTP into c-di-GMP. The CZB domains are used for ligand-mediated regulation of c-di-GMP production and have an important role in signal transduction of bacteria. CZB and GGEEF domains are found in proteins from many bacterial lineages, including DgcZ homologs<sup>[5]</sup>. | DgcZ is a dimeric protein with <scene name='69/694239/Dgcz_ggeef_dom_and_czb_dom/3'>two domains</scene> per monomer<sup>[4]</sup>. The DgcZ protein has <scene name='69/694239/C2_symmetry/6'>C2</scene> symmetry down its central axis. The catalytic glycine-glycine-glutamate-glutamate-phenylalanine (GGEEF) domains are responsible for synthesizing c-di-GMP. The regulatory chemoreceptor Zinc binding (CZB) domains house the two zinc binding sites, one site located on each monomer. DgcZ binds Zinc in the CZB domains with sub-femtomolar (10<sup>-16</sup>M) affinity. When Zinc is bound, the CZB and GGEEF domains adopt conformations that inhibit DgcZ function, as illustrated in Figure 3<sup>[3]</sup>. Enzyme DgcZ was co-crystallized with Zinc, fixing the structure in its inactivate conformation. The GGEEF domains are catalytic, containing the active sites for cyclizing GTP into c-di-GMP. The CZB domains are used for ligand-mediated regulation of c-di-GMP production and have an important role in signal transduction of bacteria. CZB and GGEEF domains are found in proteins from many bacterial lineages, including DgcZ homologs<sup>[5]</sup>. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
===Mechanism of Action=== | ===Mechanism of Action=== | ||
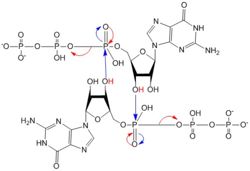
| - | [[Image:C-di-GMP arrows.jpg|250 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 5: Mechanism of c-di-GMP synthesis.''' Addition arrows are shown in blue and elimination arrows are shown in red.]] | + | [[Image:C-di-GMP arrows.jpg|250 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 5: Mechanism of c-di-GMP synthesis.''' Addition arrows are shown in blue and elimination arrows are shown in red.]] Diguanylate cyclases only function efficiently when the two half-sites of the GGEEF domain are in close enough proximity to bind the substrates. The presence of Zinc disrupts the ability of the two domains to overlap. |
| - | Diguanylate cyclases only function efficiently | + | |
1. The enzyme coordinates the substrate <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_alone/5'>GTP</scene> in a conformation to allow deprotonation of the C3 alcohol groups of the ribose. The negatively charged Oxygens on the phosphate groups of GTP are stabilized by Mg<sup>2+</sup> ions. | 1. The enzyme coordinates the substrate <scene name='69/694239/Gtp_alone/5'>GTP</scene> in a conformation to allow deprotonation of the C3 alcohol groups of the ribose. The negatively charged Oxygens on the phosphate groups of GTP are stabilized by Mg<sup>2+</sup> ions. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 26: | ||
3. The β and γ phosphates of GTP are kicked off as leaving groups. | 3. The β and γ phosphates of GTP are kicked off as leaving groups. | ||
| - | 4. The result of this reaction is the C3 alcohol group of each ribose covalently bonded to an α-phosphate forming c-di-GMP | + | 4. The result of this reaction is the C3 alcohol group of each ribose covalently bonded to an α-phosphate forming c-di-GMP<sup>[7]</sup>. |
| - | ==CZB | + | ==CZB Domains and Zinc Binding Site== |
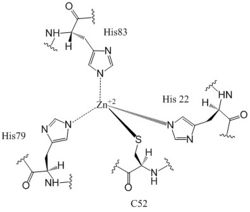
The <scene name='69/694239/Zb_domain_residues_19-90/7'>CZB domain</scene>, residues 19-90, is responsible for regulating the function of DgcZ due to the presence of two zinc binding sites. The domain contains the <scene name='69/694239/Zinc_binding_domain_zmout/2'>allosteric binding sites</scene> of the enzyme which exhibits cooperative binding (Figure 4). Four residues bind zinc with a high affinity even at 10<sup>-16</sup>M concentrations of Zinc in solution. Due to the tightness of Zinc binding, the complete enzyme has not yet been crystallized in its active conformation without the presence of Zinc metal inhibitor. When zinc is bound, DgcZ activity is limited<sup>[3]</sup>. Two Zinc binding sites are located on the CZB domain. | The <scene name='69/694239/Zb_domain_residues_19-90/7'>CZB domain</scene>, residues 19-90, is responsible for regulating the function of DgcZ due to the presence of two zinc binding sites. The domain contains the <scene name='69/694239/Zinc_binding_domain_zmout/2'>allosteric binding sites</scene> of the enzyme which exhibits cooperative binding (Figure 4). Four residues bind zinc with a high affinity even at 10<sup>-16</sup>M concentrations of Zinc in solution. Due to the tightness of Zinc binding, the complete enzyme has not yet been crystallized in its active conformation without the presence of Zinc metal inhibitor. When zinc is bound, DgcZ activity is limited<sup>[3]</sup>. Two Zinc binding sites are located on the CZB domain. | ||
[[Image:Zinc binding site labels.jpg|250 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 6: Zn<sup>+2</sup> Coordination to amino acid residues.''' Three of the four 𝝰 helices of the CZB domain of DgcZ coordinate to the Zn<sup>+2</sup> ion for binding.]] | [[Image:Zinc binding site labels.jpg|250 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 6: Zn<sup>+2</sup> Coordination to amino acid residues.''' Three of the four 𝝰 helices of the CZB domain of DgcZ coordinate to the Zn<sup>+2</sup> ion for binding.]] | ||
Revision as of 23:08, 21 April 2017
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Diguanylate Cyclase DgcZ from Escherichia coli
| |||||||||||
![Figure 3: Diagram of DgcZ. DgcZ is shown in its active (left) and inactive (right) conformations. The boxes represent the GGEEF domains of the enzyme, while the cylinders represent the alpha helices of the CZB domains, where the Zinc binding sites are located[3]. Binding Zn+2 inactivates the enzyme, by disrupting the active conformation of the GGEEF domain. The red and blue sections represent the two monomers of the symmetric homodimer.](/wiki/images/thumb/1/10/Conformation_change_2_bold.png/250px-Conformation_change_2_bold.png)