Ribosome recycling factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
RRF splits the ribosome into its small and large subunits. RRF is used together with elongation factor G in achieving this separation<ref>PMID:16043510</ref>. RRF is a structural mimic of tRNA but binds to the ribosome differently than the A-site, P-site or E-site tRNA. | RRF splits the ribosome into its small and large subunits. RRF is used together with elongation factor G in achieving this separation<ref>PMID:16043510</ref>. RRF is a structural mimic of tRNA but binds to the ribosome differently than the A-site, P-site or E-site tRNA. | ||
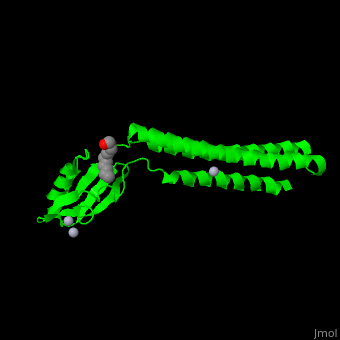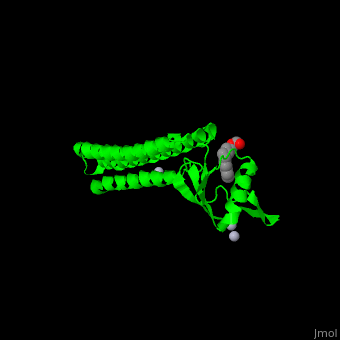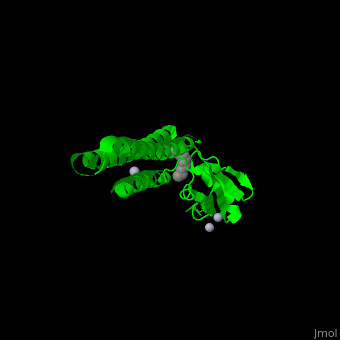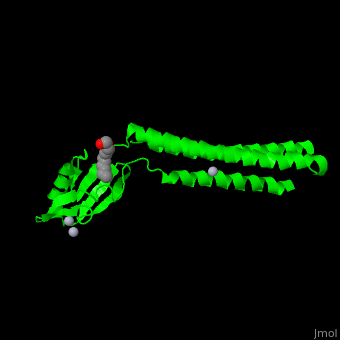
*<scene name='70/706271/Cv/2'>1st Hg coordination site</scene>. | *<scene name='70/706271/Cv/2'>1st Hg coordination site</scene>. | ||
| - | *<scene name='70/706271/Cv/3'>2nd and 3rd Hg coordination sites</scene>. | + | *<scene name='70/706271/Cv/3'>2nd and 3rd Hg coordination sites</scene>. Water molecule shown as red sphere. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 09:52, 17 May 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of ribosome recycling factor
Updated on 17-May-2017
References
- ↑ Hirokawa G, Nijman RM, Raj VS, Kaji H, Igarashi K, Kaji A. The role of ribosome recycling factor in dissociation of 70S ribosomes into subunits. RNA. 2005 Aug;11(8):1317-28. PMID:16043510 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1261/rna.2520405