We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
T-box proteins
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
A T-box protein is typically 50 - 78 kDa, within which the T-box domain is typically 17 - 26 kDa. T-box proteins have folds characteristic of the immunoglobin fold. The T-box domains of most family members bind to the consensus sequence TCACACCT. Some residues are conserved through particular subfamilies, such as Lys149 of the Xbra family, and others throughout the entire T-box family. However, differences lie in the binding topology of multiple recognised sequence motifs. For example, Xbra binds two head-to-head sequence motifs, and cannot bind them tail-to-tail; VegT can bind tail-to-tail and not head-to-head. It has been suggested that other functions may lie within the T-box such as mediating protein-protein interactions. The transcription-mediating domain can either be activating or repressing and bears less to no sequence homology. | A T-box protein is typically 50 - 78 kDa, within which the T-box domain is typically 17 - 26 kDa. T-box proteins have folds characteristic of the immunoglobin fold. The T-box domains of most family members bind to the consensus sequence TCACACCT. Some residues are conserved through particular subfamilies, such as Lys149 of the Xbra family, and others throughout the entire T-box family. However, differences lie in the binding topology of multiple recognised sequence motifs. For example, Xbra binds two head-to-head sequence motifs, and cannot bind them tail-to-tail; VegT can bind tail-to-tail and not head-to-head. It has been suggested that other functions may lie within the T-box such as mediating protein-protein interactions. The transcription-mediating domain can either be activating or repressing and bears less to no sequence homology. | ||
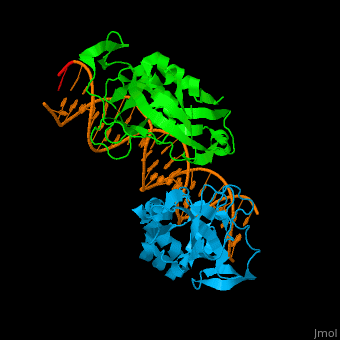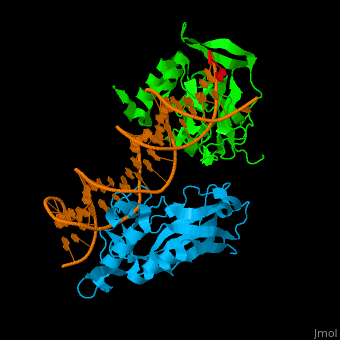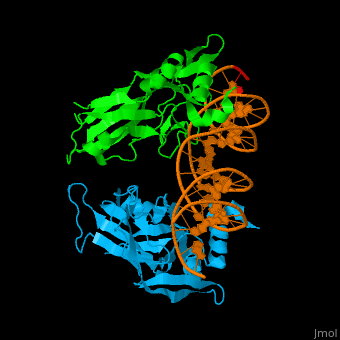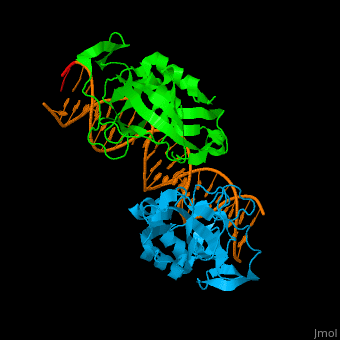
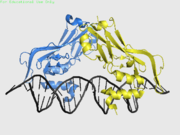
| - | *<scene name='40/408030/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='40/408030/Cv/4'>Human TBX1 dimer complex with DNA</scene> ([[4a04]]). |
=Function and implications in development= | =Function and implications in development= | ||
Revision as of 13:37, 21 June 2017
| |||||||||||
Genes involved in limb bud formation and development are a subset of T-box proteins: T, TBX2, TBX3, TBX5, TBX15 and TBX18.
Contents |
T-box family members in Homo sapiens
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| T | Crystal structure solved | |
| TBX19 |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBX1 | Crystal structure solved (4a04) | DiGeorge syndrome |
| TBX10 | ||
| TBX15 | Cousin syndrome | |
| TBX18 | ||
| TBX20 | ||
| TBX22 | Truncated T-box domain predicted not to bind DNA | Cleft palate with ankyloglossia |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBX2 | Mutation of Arg122 destroys DNA binding. Acts as a repressor. TRP-1 promoter is a possible binding site. | Amplified in certain types of breast cancer. |
| TBX3 | Crystal structure solved | Ulnar-mammary syndrome |
| TBX4 | Small patella syndrome | |
| TBX5 | Crystal structure solved | Holt-Oram syndrome |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBX6 | ||
| MGA | Also contains leucine zipper domain |
| Members | Notes | Linked diseases |
|---|---|---|
| TBR1 | ||
| EOMES | ||
| TBX21 |
3D structures of T-box protein
4a04 – hTBX1 T-box domain + DNA - human
1h6f - hTBX3 T-box domain + DNA
2x6u, 5bqd – hTBX5 T-box domain
2x6v – hTBX5 T-box domain + DNA
4s0h, 5flv - hTBX5 T-box domain + homebox protein + DNA
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Transcription and RNA Processing
References
- Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 1997, 7:474-480;
- Gene 258 (2000) 15–29;
- American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A 140A:1407–1413 (2006);
- Genome Biology 2002, 3(6):reviews3008.1–3008.7;
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Helen Ginn, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman