This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Polygalacturonase
From Proteopedia
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
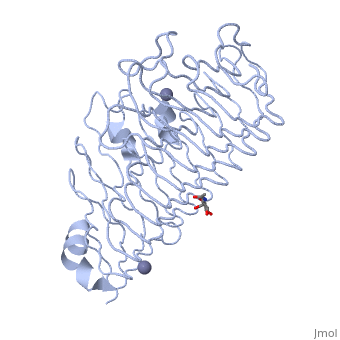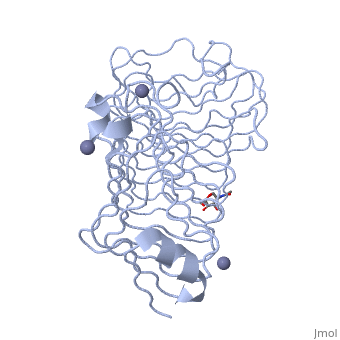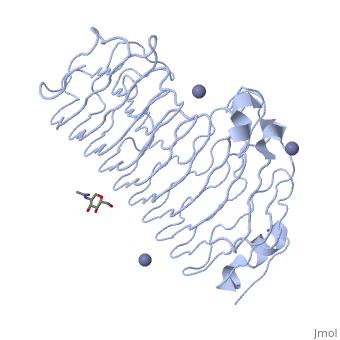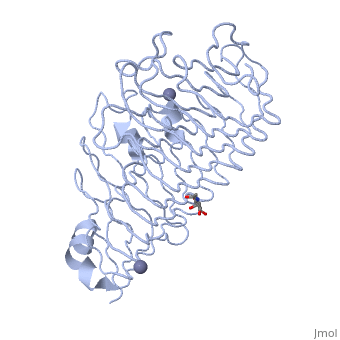
| - | The secondary structure of PGs is comprised of a ten turn right handed beta helix domain along with two loop regions that together form the substrate-binding cleft, which appears to have a tunnel-like shape. The active site of PGs is found between the two looped regions of the protein. Located within the looped regions are two conserved aspartate residues that are predicted to participate in catalytic activity. | + | The secondary structure of PGs is comprised of a ten turn right handed beta helix domain along with two loop regions that together form the substrate-binding cleft, which appears to have a tunnel-like shape. The active site of PGs is found between the two looped regions of the protein. Located within the looped regions are two conserved aspartate residues that are predicted to participate in catalytic activity (crystal structure). |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 19:28, 12 July 2017
|
Contents |
Function
Polygalacturonases hydrolyze α-(1-4) – glycosidic bonds between consecutive galacturonic acid residues in polygalacturonic acids. Structural variation has been identified among differing PGs depending on organismal origins and catalytic functions. For example, endo-polygalacturonases produced from Erwinia carotovora demonstrate functional similarity to pectate lyases in that they cleave polygalacturonic acids in a calcium-depended manner via β-elimination (crystal structure).
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
The secondary structure of PGs is comprised of a ten turn right handed beta helix domain along with two loop regions that together form the substrate-binding cleft, which appears to have a tunnel-like shape. The active site of PGs is found between the two looped regions of the protein. Located within the looped regions are two conserved aspartate residues that are predicted to participate in catalytic activity (crystal structure).
References
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Krishna Amin, Michal Harel, Marilyn Yoder, OCA, Jaime Prilusky