This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
ModG
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | {{STRUCTURE_1atg| PDB=1atg | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right| CAPTION=Molybdate-binding protein complex with tungstate, ethylene glycol, acetate and sulfate, [[1atg]] } | + | {{STRUCTURE_1atg| PDB=1atg | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right| CAPTION=Molybdate-binding protein complex with tungstate, ethylene glycol, acetate and sulfate, [[1atg]] } |
| - | + | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='1atg' size='350' side='right' caption='Molybdate-binding protein complex with tungstate, ethylene glycol, acetate and sulfate (PDB entry [[1atg]])' scene=''> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
=Fate= | =Fate= | ||
ModG is eventually degraded and incorporated into molybdopterin, a cofactor of molybdenum enzymes, or the iron-molybdenum cofactor of a nitrogenase enzyme.<ref name="MODGR1"/><ref name="MODGR2"/> Currently there is little known about cofactor biosynthesis involving the ModG protein.<ref name="MODGR1"/> | ModG is eventually degraded and incorporated into molybdopterin, a cofactor of molybdenum enzymes, or the iron-molybdenum cofactor of a nitrogenase enzyme.<ref name="MODGR1"/><ref name="MODGR2"/> Currently there is little known about cofactor biosynthesis involving the ModG protein.<ref name="MODGR1"/> | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
=3D structures of ModG= | =3D structures of ModG= | ||
Revision as of 06:49, 24 July 2017
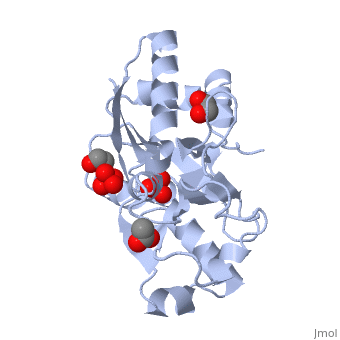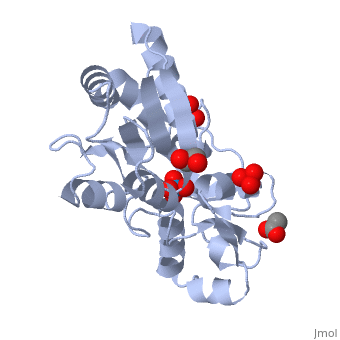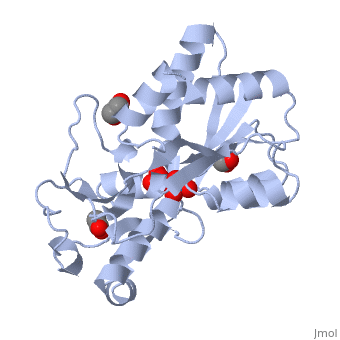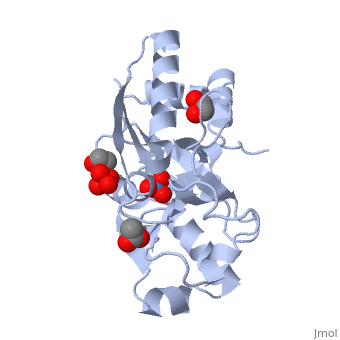
{{STRUCTURE_1atg| PDB=1atg | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right| CAPTION=Molybdate-binding protein complex with tungstate, ethylene glycol, acetate and sulfate, 1atg }
| |||||||||||
3D structures of ModG
1h9j – AvModG + phosphate + molybdate – Azotobacter vinelandii
1atg – AvModG + tungstate + sulfate + acetate
1h9k - AvModG + tungstate + phosphate
1h9m - AvModG + molybdate
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 Delarbre L, Stevenson CE, White DJ, Mitchenall LA, Pau RN, Lawson DM. Two crystal structures of the cytoplasmic molybdate-binding protein ModG suggest a novel cooperative binding mechanism and provide insights into ligand-binding specificity. J Mol Biol. 2001 May 18;308(5):1063-79. PMID:11352591 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4636
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Yang ZY, Dean DR, Seefeldt LC. Molybdenum nitrogenase catalyzes the reduction and coupling of CO to form hydrocarbons. J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 28. PMID:21454640 doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.229344
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Lawson DM, Williams CE, Mitchenall LA, Pau RN. Ligand size is a major determinant of specificity in periplasmic oxyanion-binding proteins: the 1.2 A resolution crystal structure of Azotobacter vinelandii ModA. Structure. 1998 Dec 15;6(12):1529-39. PMID:9862806
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Mouncey NJ, Mitchenall LA, Pau RN. Mutational analysis of genes of the mod locus involved in molybdenum transport, homeostasis, and processing in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1995 Sep;177(18):5294-302. PMID:7665518
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Williams CE, White DJ, Delarbre L, Mitchenall LA, Pau RN, Lawson DM. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray studies on the molbindin ModG from Azotobacter vinelandii. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1999 Jul;55(Pt 7):1356-8. PMID:10393312
See also
This page originally authored by Corbin Black