Paxillin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
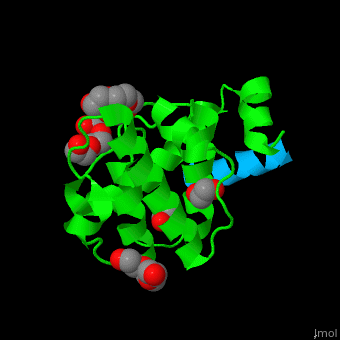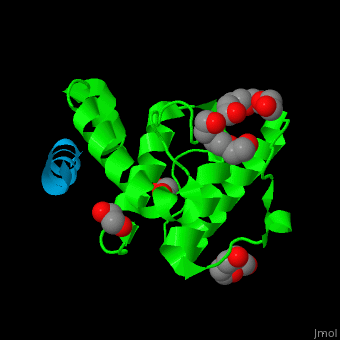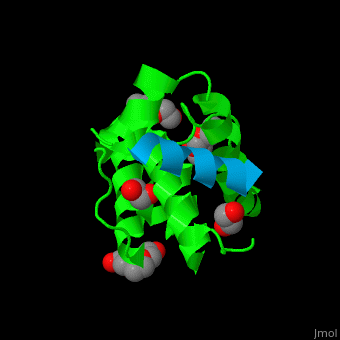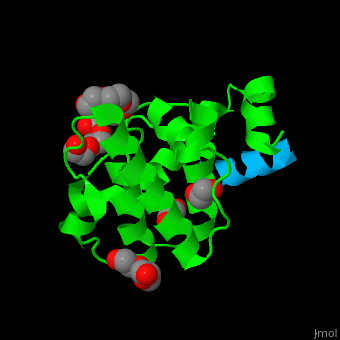
| - | <StructureSection load='2vzi' size='400' side='right' caption='Human paxillin LD4 domain complex with α-parvin (green), tetraethylene glycol, triethylene glycol and etylene glycol (PDB code [[2vzi]])' scene='71/715908/Cv/1' pspeed='8'> | + | <StructureSection load='2vzi' size='400' side='right' caption='Human paxillin LD4 domain complex (sky blue) with α-parvin (green), tetraethylene glycol, triethylene glycol and etylene glycol (PDB code [[2vzi]])' scene='71/715908/Cv/1' pspeed='8'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Paxillin''' (PXN) is involved in actin membrane attachment at sites of cell adhesion to focal adhesion domains. PXN contains a number of domains which are involved in protein-protein interactions: LD, LIM, SH2 and SH3 binding sites. LD motifs are leucine-rich sequences which begin with leucine (L) and end with aspartate (D)<ref>PMID:11911889</ref>. PXN serves as a docking protein recruiting signaling molecules to focal adhesions. | '''Paxillin''' (PXN) is involved in actin membrane attachment at sites of cell adhesion to focal adhesion domains. PXN contains a number of domains which are involved in protein-protein interactions: LD, LIM, SH2 and SH3 binding sites. LD motifs are leucine-rich sequences which begin with leucine (L) and end with aspartate (D)<ref>PMID:11911889</ref>. PXN serves as a docking protein recruiting signaling molecules to focal adhesions. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
PXN LD motifs are localized on the N-terminal region while the LIM double zinc finger domains are found at the C-terminal. | PXN LD motifs are localized on the N-terminal region while the LIM double zinc finger domains are found at the C-terminal. | ||
| - | + | *<scene name='71/715908/Cv/2'>Human paxillin LD4 domain interactions with α-parvin</scene>. | |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 13:10, 24 August 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of paxillin
Updated on 24-August-2017
References
- ↑ Tumbarello DA, Brown MC, Turner CE. The paxillin LD motifs. FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 20;513(1):114-8. PMID:11911889
- ↑ Jagadeeswaran R, Surawska H, Krishnaswamy S, Janamanchi V, Mackinnon AC, Seiwert TY, Loganathan S, Kanteti R, Reichman T, Nallasura V, Schwartz S, Faoro L, Wang YC, Girard L, Tretiakova MS, Ahmed S, Zumba O, Soulii L, Bindokas VP, Szeto LL, Gordon GJ, Bueno R, Sugarbaker D, Lingen MW, Sattler M, Krausz T, Vigneswaran W, Natarajan V, Minna J, Vokes EE, Ferguson MK, Husain AN, Salgia R. Paxillin is a target for somatic mutations in lung cancer: implications for cell growth and invasion. Cancer Res. 2008 Jan 1;68(1):132-42. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1998. PMID:18172305 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1998