This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Pal
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | ||
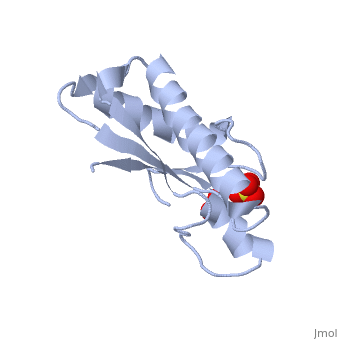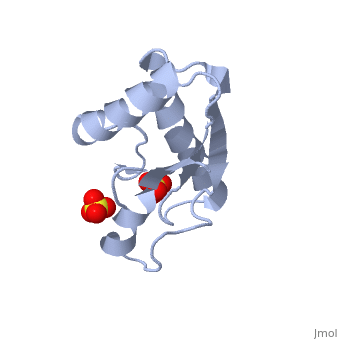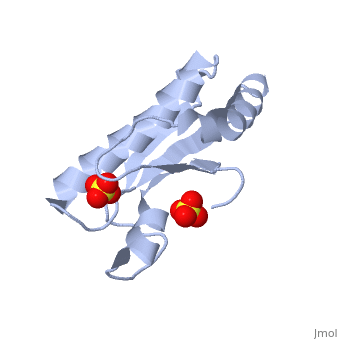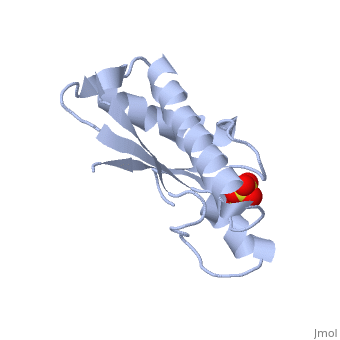
| + | <StructureSection load='1oap' size='350' side='right' caption='E. coli pal protein periplasmic domain complex with sulfate (PDB entry [[1oap]])' scene=''> | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
'''Pal (peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein)''' is a lipoprotein which is anchored in the outer membrane with an approximate length of 173 amino acids in the precursor form. It contains a signal sequence including an LVAC motif, with the flexible, hydrophobic N-terminal tail binding to the inner leaflet of the outer membrane and anchoring it. During translocation, signal peptidase II cleaves the LVAC motif, and the localisation of Pal is dependent on the Lol protein system. Serine, the amino acid at #2 position in the mature protein is a localisation determinant for the position of Pal in the outer membrane<ref name='Godlewska'>PMID: 19519769</ref>. The periplasmic domain of Pal can be seen in the 3D structure 1OAP. | '''Pal (peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein)''' is a lipoprotein which is anchored in the outer membrane with an approximate length of 173 amino acids in the precursor form. It contains a signal sequence including an LVAC motif, with the flexible, hydrophobic N-terminal tail binding to the inner leaflet of the outer membrane and anchoring it. During translocation, signal peptidase II cleaves the LVAC motif, and the localisation of Pal is dependent on the Lol protein system. Serine, the amino acid at #2 position in the mature protein is a localisation determinant for the position of Pal in the outer membrane<ref name='Godlewska'>PMID: 19519769</ref>. The periplasmic domain of Pal can be seen in the 3D structure 1OAP. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
#'''Pal and TolB''' - ''see'' [[TolB]] | #'''Pal and TolB''' - ''see'' [[TolB]] | ||
#'''Pal and TolA''' - Pal may play a role in the stabilisation of [[TolA]], and that this interaction is essential if the cell integrity is to be maintained. | #'''Pal and TolA''' - Pal may play a role in the stabilisation of [[TolA]], and that this interaction is essential if the cell integrity is to be maintained. | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
==3D structures of Pal== | ==3D structures of Pal== | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
Revision as of 09:30, 29 August 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Pal
Updated on 29-August-2017
2w8b – EcPal periplasmic domain + TolB - Escherichia coli
2hqs – EcPal + TolB
1oap - EcPal periplasmic domain
1n3o – PaPal + methyl-glucose – Pterocarpus angolensis
1n3p – PaPal + sucrose
1n3q – PaPal + turanose
1q8o, 1q8p, 1q8q, 1q8s, 1qmv, 1ukg, 2ar6, 2arb, 2are, 2arx, 2gn3, 2phr, 2phw, 2phx – PaPal + oligosaccharide
2gnm, 2gnt - PaPal
4pwt – YpPal – Yersinia pestis
4r40 – YpPal + TolB
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Godlewska R, Wisniewska K, Pietras Z, Jagusztyn-Krynicka EK. Peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein (Pal) of Gram-negative bacteria: function, structure, role in pathogenesis and potential application in immunoprophylaxis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009 Sep;298(1):1-11. Epub 2009 May 21. PMID:19519769 doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01659.x
- ↑ Parsons LM, Orban J. NMR assignment of the periplasmic domain of peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein (Pal) from Haemophilus influenzae. J Biomol NMR. 2005 May;32(1):93. PMID:16041489 doi:10.1007/s10858-005-3676-x
- ↑ Cascales E, Lloubes R. Deletion analyses of the peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein Pal reveals three independent binding sequences including a TolA box. Mol Microbiol. 2004 Feb;51(3):873-85. PMID:14731286