Sphingomyelinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
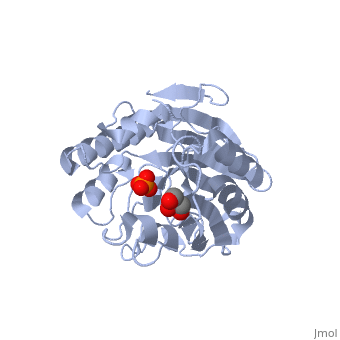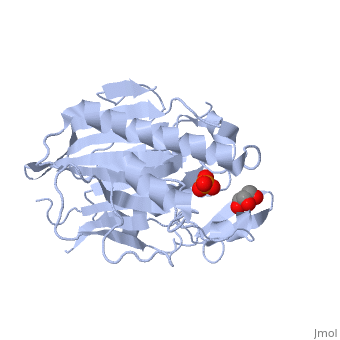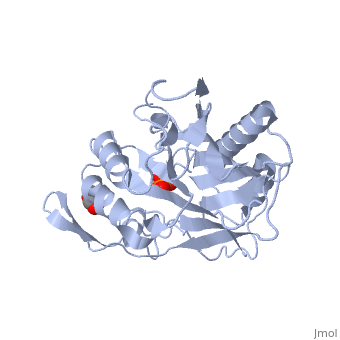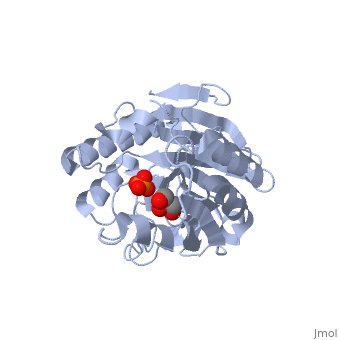
| - | {{STRUCTURE_1zwx| PDB=1zwx | SIZE=400| SCENE= |right|CAPTION=Sphingomyelinase complex with glycerol and phosphate ion [[1zwx]] }} | ||
| + | <StructureSection load='1zwx' size='350' side='right' caption='Sphingomyelinase complex with glycerol and phosphate ion (PDB entry [[21zwx])' scene=''> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Sphingomyelinase''' (SMase) or '''sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase''' is a hydrolase involved in sphingolipid metabolism. It catalyzes the breakdown of sphingomyelin (SM) to phosphocholine and ceramide<ref>PMID:11001563</ref>. The SMase is classified into 5 types according to their pH dependence and cation dependence. | '''Sphingomyelinase''' (SMase) or '''sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase''' is a hydrolase involved in sphingolipid metabolism. It catalyzes the breakdown of sphingomyelin (SM) to phosphocholine and ceramide<ref>PMID:11001563</ref>. The SMase is classified into 5 types according to their pH dependence and cation dependence. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Mutations in acid SMase are found in patients with Niemann-Pick disease<ref>PMID:17011332</ref>. | Mutations in acid SMase are found in patients with Niemann-Pick disease<ref>PMID:17011332</ref>. | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
==3D structures of sphingomyelinase== | ==3D structures of sphingomyelinase== | ||
Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
Revision as of 09:58, 3 September 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of sphingomyelinase
Updated on 03-September-2017
References
- ↑ Chatterjee S. Neutral sphingomyelinase: past, present and future. Chem Phys Lipids. 1999 Nov;102(1-2):79-96. PMID:11001563
- ↑ Wasserstein MP, Aron A, Brodie SE, Simonaro C, Desnick RJ, McGovern MM. Acid sphingomyelinase deficiency: prevalence and characterization of an intermediate phenotype of Niemann-Pick disease. J Pediatr. 2006 Oct;149(4):554-9. PMID:17011332 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2006.06.034