Ribozyme
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
*Hammerhead ribozyme | *Hammerhead ribozyme | ||
| - | **[[1nyi]], [[1q29]], [[379d]], [[359d]], [[299d]], [[300d]], [[301d]], [[1mme]], [[1hmh]] - Hammerhead RZ<BR /> | + | **[[1nyi]], [[1q29]], [[379d]], [[359d]], [[299d]], [[300d]], [[301d]], [[1mme]], [[1hmh]], [[5di2]], [[5di4]], [[5dh6]], [[5dh7]], [[5dh8]], [[5eao]], [[5eaq]] - Hammerhead RZ<BR /> |
**[[1rmn]] - Hammerhead RZ – fluorescence measurements<BR /> | **[[1rmn]] - Hammerhead RZ – fluorescence measurements<BR /> | ||
**[[2ro2]], [[2rpk]] – Hammerhead RZ domain I<BR /> | **[[2ro2]], [[2rpk]] – Hammerhead RZ domain I<BR /> | ||
**[[3czw]], [[3d0m]] - Hammerhead RZ shorter strands<BR /> | **[[3czw]], [[3d0m]] - Hammerhead RZ shorter strands<BR /> | ||
**[[2qus]], [[2quw]] - Hammerhead RZ (mutant) <BR /> | **[[2qus]], [[2quw]] - Hammerhead RZ (mutant) <BR /> | ||
| - | **[[2oeu]] - Hammerhead RZ + RNA<br /> | + | **[[2oeu]], [[5dqk]] - Hammerhead RZ + RNA<br /> |
**[[488d]] – Hammerhead RZ + RNA products<br /> | **[[488d]] – Hammerhead RZ + RNA products<br /> | ||
**[[3zd5]], [[3zp8]] - Hammerhead RZ enzyme+substrate strands<br /> | **[[3zd5]], [[3zp8]] - Hammerhead RZ enzyme+substrate strands<br /> | ||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
**[[1l8v]], [[1gid]] – TtRZ P4-P6 domain<BR /> | **[[1l8v]], [[1gid]] – TtRZ P4-P6 domain<BR /> | ||
**[[1hr2]] - TtRZ P4-P6 domain (mutant) <BR /> | **[[1hr2]] - TtRZ P4-P6 domain (mutant) <BR /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Group II intron ribozymes | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[5j01]], [[5j02]] - RZ - ''Oceanobacillus iheyensis'' <br/> | ||
| Line 101: | Line 105: | ||
**[[2l5z]], [[1e4p]], [[2mis]] – 26-mer of VS RZ – ''Neurospora'' – NMR<BR /> | **[[2l5z]], [[1e4p]], [[2mis]] – 26-mer of VS RZ – ''Neurospora'' – NMR<BR /> | ||
**[[1yn1]], [[1yn2]], [[1tbk]], [[1tjz]], [[1hwq]] - VS RZ stem-loop V – NMR<BR /> | **[[1yn1]], [[1yn2]], [[1tbk]], [[1tjz]], [[1hwq]] - VS RZ stem-loop V – NMR<BR /> | ||
| + | **[[5v3i]] - VS RZ <BR /> | ||
| + | **[[4r4p]], [[4r4v]] - VS RZ (mutant)<BR /> | ||
**[[3hhn]] – Class I ligase RZ + U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A<BR /> | **[[3hhn]] – Class I ligase RZ + U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A<BR /> | ||
**[[3r1h]], [[3r1l]] - Class I ligase RZ (mutant) + U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A+ RNA<br /> | **[[3r1h]], [[3r1l]] - Class I ligase RZ (mutant) + U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A+ RNA<br /> | ||
| Line 112: | Line 118: | ||
**[[1ykq]] – Diels-Alder RZ<BR /> | **[[1ykq]] – Diels-Alder RZ<BR /> | ||
**[[1ykv]], [[1yls]] - Diels-Alder RZ + reaction products<br /> | **[[1ykv]], [[1yls]] - Diels-Alder RZ + reaction products<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4qjh]] – twister RZ – synthetic<br /> | + | **[[4qjh]], [[5dun]] – twister RZ – synthetic<br /> |
**[[4rge]], [[4rgf]] – twister RZ env22 – synthetic<br /> | **[[4rge]], [[4rgf]] – twister RZ env22 – synthetic<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5k7c]],[[5k7d]],[[5k7e]] - pistol RZ - synthetic <br/> | + | **[[5t5a]] – twister sister RZ – Metagenome<br /> |
| + | **[[5k7c]],[[5k7d]],[[5k7e]], [[5ktj]] - pistol RZ - synthetic <br/> | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 22:48, 29 September 2017
|
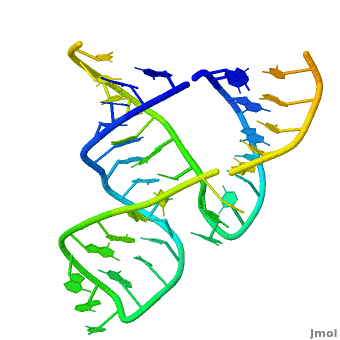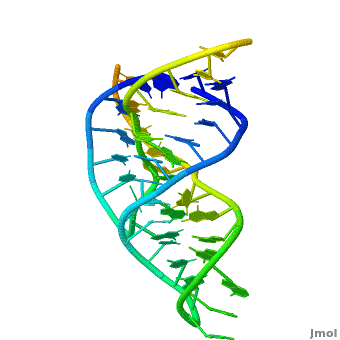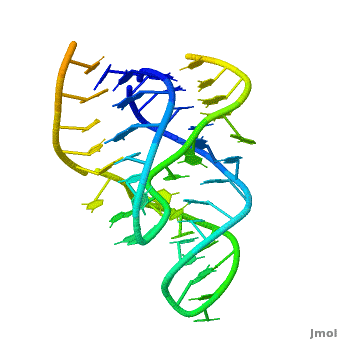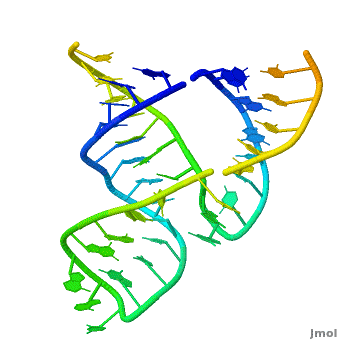
Ribozyme (RZ) is an RNA molecule which catalyzes a chemical reaction[1].
- Glucosamine-6-phosphate activated RZ (glmS RZ) is a RZ and a riboswitch which regulates genes in response to metabolites.
- Leadzyme is a small, artificially-made RZ which can cleave RNA in the presence of lead. For more details on leadzyme see Student Projects for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2012-10.
- Hairpin RZ and hammerhead RZ are named based on their shape[2].
- Group I intron catalyzes its own selfish splicing[3].
- Comparative genomic analysis revealed Twister, Twister sister, Hatchet, and Pistol [4][5].
Articles in Proteopedia concerning ribozymes include:
- Azoarcus group I intron
- Kink-turn motif
- Ribosome
- The Large Ribosomal Subunit
- Hairpin Ribozyme
- Human CPEB3 ribozyme's P4 domain
To view automatically seeded indices concerning ribozymes, see:
- Ribozyme
- Catalytic RNA
- GlmS
- Hammerhead
- Hairpin
- Hepatitis delta virus
- Twister
- Twister sister
- Hatchet
- Pistol
- Group I intron
- Varkud satellite
3D Structures of Ribozymes
Updated on 29-September-2017
References
- ↑ Tang J, Breaker RR. Rational design of allosteric ribozymes. Chem Biol. 1997 Jun;4(6):453-9. PMID:9224568
- ↑ Amarzguioui M, Prydz H. Hammerhead ribozyme design and application. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998 Nov;54(11):1175-202. PMID:9849614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s000180050247
- ↑ Cech TR. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543-68. PMID:2197983 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551
- ↑ Roth A, Weinberg Z, Chen AG, Kim PB, Ames TD, Breaker RR. A widespread self-cleaving ribozyme class is revealed by bioinformatics. Nat Chem Biol. 2014 Jan;10(1):56-60. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1386. Epub 2013 Nov, 17. PMID:24240507 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1386
- ↑ Weinberg Z, Kim PB, Chen TH, Li S, Harris KA, Lunse CE, Breaker RR. New classes of self-cleaving ribozymes revealed by comparative genomics analysis. Nat Chem Biol. 2015 Aug;11(8):606-10. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1846. Epub 2015 Jul, 13. PMID:26167874 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1846
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Wayne Decatur, Joel L. Sussman, Alexander Berchansky