We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Siderocalin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
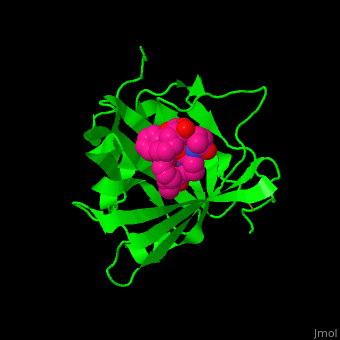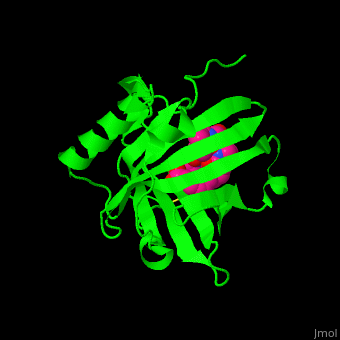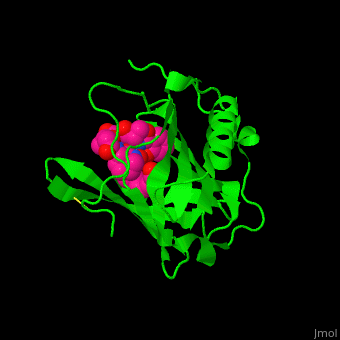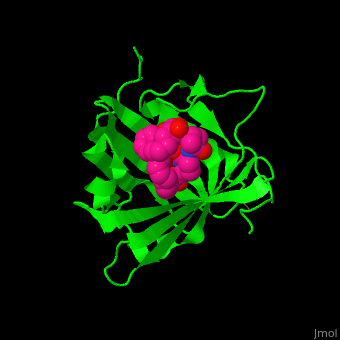
<StructureSection load='1x89' size='450' side='right' caption='Human siderocalin complex with the siderophore carboxymycobactin (PDB code [[1x89]])' scene='48/488406/Cv/1' > | <StructureSection load='1x89' size='450' side='right' caption='Human siderocalin complex with the siderophore carboxymycobactin (PDB code [[1x89]])' scene='48/488406/Cv/1' > | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Siderocalin''' (Scn) binds ferric siderophores in order to intercept delivery of iron to bacteria which require it thus impeding their virulence<ref>PMID:19053425</ref>. | + | '''Siderocalin''' (Scn) or '''neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin''' binds ferric siderophores in order to intercept delivery of iron to bacteria which require it thus impeding their virulence<ref>PMID:19053425</ref>. |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*Siderocalin or lipocalin-2 | *Siderocalin or lipocalin-2 | ||
| - | **[[5jr8]], [[3bx8]] – hScn NGAL - human<br /> | + | **[[5jr8]], [[3bx8]], [[5khp]], [[5kid]], [[5kic]] – hScn NGAL - human<br /> |
**[[3s26]] – mScn NGAL - mouse<br /> | **[[3s26]] – mScn NGAL - mouse<br /> | ||
**[[2kt4]] – qScn Q83 – quail<br /> | **[[2kt4]] – qScn Q83 – quail<br /> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
*Siderocalin complex | *Siderocalin complex | ||
| - | **[[4mvi]], [[4mvk]], [[4mvl]] – hScn NGAL (mutant) + | + | **[[4mvi]], [[4mvk]], [[4mvl]] – hScn NGAL (mutant) + β-amyloid protein 40 peptide<br /> |
**[[3bx7]] – hScn NGAL + CTLA-4<br /> | **[[3bx7]] – hScn NGAL + CTLA-4<br /> | ||
**[[3tzs]] – hScn NGAL (mutant) + phenylurea<br /> | **[[3tzs]] – hScn NGAL (mutant) + phenylurea<br /> | ||
Revision as of 22:49, 3 October 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of siderocalin
Updated on 03-October-2017
>
References
- ↑ Hoette TM, Abergel RJ, Xu J, Strong RK, Raymond KN. The role of electrostatics in siderophore recognition by the immunoprotein Siderocalin. J Am Chem Soc. 2008 Dec 24;130(51):17584-92. doi: 10.1021/ja8074665. PMID:19053425 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja8074665
- ↑ Paragas N, Qiu A, Hollmen M, Nickolas TL, Devarajan P, Barasch J. NGAL-Siderocalin in kidney disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep;1823(9):1451-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.06.014., Epub 2012 Jun 19. PMID:22728330 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.06.014
- ↑ Holmes MA, Paulsene W, Jide X, Ratledge C, Strong RK. Siderocalin (Lcn 2) also binds carboxymycobactins, potentially defending against mycobacterial infections through iron sequestration. Structure. 2005 Jan;13(1):29-41. PMID:15642259 doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.10.009