Succinyl-CoA synthetase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
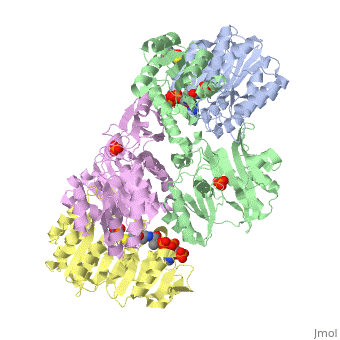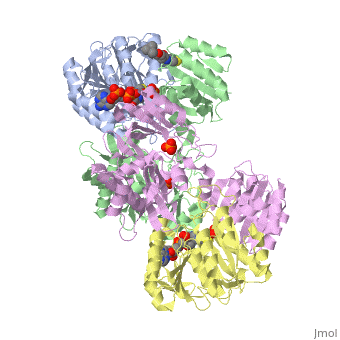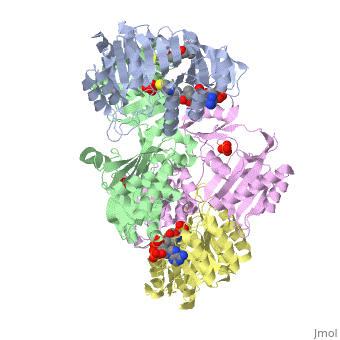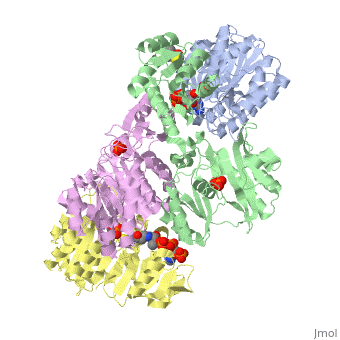
<StructureSection load='1cqj' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='E. coli succinyl-CoA synthetase α subunit (grey, yellow) and β subunit (green, magenta) complex with CoA and phosphate (PDB code [[1cqj]])'> | <StructureSection load='1cqj' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='E. coli succinyl-CoA synthetase α subunit (grey, yellow) and β subunit (green, magenta) complex with CoA and phosphate (PDB code [[1cqj]])'> | ||
| - | '''Succinyl- | + | '''Succinyl-CoA synthetase''' catalyzes the reversible reaction of succinyl-CoA + NDP + Pi <-> succinate + CoA + NTP (where N is either adenosine or guanosine. It can be found in Escherichia coli and is the fifth step in the [[Citric Acid Cycle|citric acid cycle]]. Due to its involvement in the citric acid cycle it is very important in all living cells that use oxygen as a part of cellular respiration. This entire process (Citric acid cycle) is necessary in producing one GTP or ATP, three NADHs, and two carbon dioxides. See also:<br /> |
*[[Krebs cycle carbons]] | *[[Krebs cycle carbons]] | ||
*[[Krebs cycle importance]] | *[[Krebs cycle importance]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| - | '''Succinyl-CoA synthetase''' is a tetramer with an active site on each subunit. This can be seen in the Jmol representation (the PDB code is 1CQJ). The two subunits are denoted alpha and beta. A phosphorylated histidine intermediate <scene name='Lucas_Hamlow_sandbox_1/Active_histidine_residue/1'>(HIS 246 alpha)</scene> is responsible for the dephosphorylation of ATP and it is suspected that there is another active site on the beta subunit that is responsible for the continued catalysis of the reaction. There is a suspected nucleotide binding site on the N-terminal of the beta subunit which would imply that there are two active sites roughly 35 A apart from each other and that the HIS 246 alpha loop moves between them during catalysis.<ref>PMID:10353839</ref> | + | '''Succinyl-CoA synthetase''' or '''Succinyl-CoA ligase''' is a tetramer with an active site on each subunit. This can be seen in the Jmol representation (the PDB code is 1CQJ). The two subunits are denoted alpha and beta. A phosphorylated histidine intermediate <scene name='Lucas_Hamlow_sandbox_1/Active_histidine_residue/1'>(HIS 246 alpha)</scene> is responsible for the dephosphorylation of ATP and it is suspected that there is another active site on the beta subunit that is responsible for the continued catalysis of the reaction. There is a suspected nucleotide binding site on the N-terminal of the beta subunit which would imply that there are two active sites roughly 35 A apart from each other and that the HIS 246 alpha loop moves between them during catalysis.<ref>PMID:10353839</ref> |
On the alpha subunit it has been shown that <scene name='Lucas_Hamlow_sandbox_1/Active_his_with_glu_208/1'>GLU 208 alpha</scene> interacts in some way with the active HIS 246 alpha residue in the phosphorylated and dephosphorylated enzyme and it is supposed that GLU 197 beta serves a similar purpose on the beta subunit.<ref>PMID:11781092</ref> | On the alpha subunit it has been shown that <scene name='Lucas_Hamlow_sandbox_1/Active_his_with_glu_208/1'>GLU 208 alpha</scene> interacts in some way with the active HIS 246 alpha residue in the phosphorylated and dephosphorylated enzyme and it is supposed that GLU 197 beta serves a similar purpose on the beta subunit.<ref>PMID:11781092</ref> | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
**[[1euc]] – pSCS α+β (mutant) subunits + PO4<br /> | **[[1euc]] – pSCS α+β (mutant) subunits + PO4<br /> | ||
**[[2fpg]] – pSCS α+β subunits + PO4 + GDP<br /> | **[[2fpg]] – pSCS α+β subunits + PO4 + GDP<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4xx0]] - pSCS α+β subunit | + | **[[4xx0]] - pSCS α+β subunit + PO4 + CoA <br /> |
**[[5cae]] - pSCS α+β subunit + PO4 + CoA + succinate<br /> | **[[5cae]] - pSCS α+β subunit + PO4 + CoA + succinate<br /> | ||
**[[1oi7]] – SCS α subunit (mutant) – ''Thermos thermophilus''<br /> | **[[1oi7]] – SCS α subunit (mutant) – ''Thermos thermophilus''<br /> | ||
Revision as of 22:37, 5 October 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of succinyl-CoA synthetase
Updated on 05-October-2017
Additional Resources
References
- ↑ Joyce MA, Fraser ME, Brownie ER, James MN, Bridger WA, Wolodko WT. Probing the nucleotide-binding site of Escherichia coli succinyl-CoA synthetase. Biochemistry. 1999 Jun 1;38(22):7273-83. PMID:10353839 doi:10.1021/bi990527s
- ↑ Fraser ME, Joyce MA, Ryan DG, Wolodko WT. Two glutamate residues, Glu 208 alpha and Glu 197 beta, are crucial for phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the active-site histidine residue in succinyl-CoA synthetase. Biochemistry. 2002 Jan 15;41(2):537-46. PMID:11781092
- ↑ Bild GS, Janson CA, Boyer PD. Subunit interaction during catalysis. ATP modulation of catalytic steps in the succinyl-CoA synthetase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8109-15. PMID:6997289
- ↑ Mikeladze DG, Matveeva LN, Severin SE. [Reaction mechanism of succinyl CoA synthetase from pigeon thoracic muscle] Biokhimiia. 1978 Aug;43(8):1458-67. PMID:570066
- ↑ Joyce MA, Fraser ME, James MN, Bridger WA, Wolodko WT. ADP-binding site of Escherichia coli succinyl-CoA synthetase revealed by x-ray crystallography. Biochemistry. 2000 Jan 11;39(1):17-25. PMID:10625475
- ↑ Frank J. Moffet and W. A. Bridger. The Kinetics of Succinyl Coenzyme A Synthetase from Escherichia coli : A REACTION WITH A COVALENT ENZYME-SUBSTRATE INTERMEDIATE NOT EXHIBITING "PING-PONG" KINETICS J. Biol. Chem. 1970 245: 2758-2762.[1]
- ↑ Um, H.-D., and C. Klein. 1993. Evidence for allosteric regulation of succinyl-CoA synthetase. Biochem. J. 295:821–826.[2]
Content Donators
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Lucas Hamlow, J.D. McClintic, Wayne Decatur, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky