User:Alec Bertsch/sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The primary function of the L5 protein is to anchor the peptide-linked tRNA to the P-site for the transfer of the peptide to the growing chain.<ref>PMID:11497428</ref> | The primary function of the L5 protein is to anchor the peptide-linked tRNA to the P-site for the transfer of the peptide to the growing chain.<ref>PMID:11497428</ref> | ||
The L5 protein is also responsible for the assembly of the ribosome. In ribosomes that fail to synthesize the L5 protein, the ribosome is unable to connect the large and small units together. Without this protein, the cell would only be able to divide a select few times. <ref>doi:10.1093/nar/gks676</ref> | The L5 protein is also responsible for the assembly of the ribosome. In ribosomes that fail to synthesize the L5 protein, the ribosome is unable to connect the large and small units together. Without this protein, the cell would only be able to divide a select few times. <ref>doi:10.1093/nar/gks676</ref> | ||
| - | The 5S rRNA is responsible for enhancing protein synthesis. This is done by stabilizing the structure of the ribosome.<ref>PMID:11440169</ref> 5S rRNA has also been noted to be a major component in tumor suppression.<ref> It is not completely known the extent of its role in ribosomal function, but there have been studies to suggest that the 5S rRNA helps with the binding of the tRNA within the P-site.<ref>PMID: | + | The 5S rRNA is responsible for enhancing protein synthesis. This is done by stabilizing the structure of the ribosome.<ref>PMID:11440169</ref> 5S rRNA has also been noted to be a major component in tumor suppression.<ref> It is not completely known the extent of its role in ribosomal function, but there have been studies to suggest that the 5S rRNA helps with the binding of the tRNA within the P-site.<ref>PMID:11440169</ref> |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 10:25, 10 October 2017
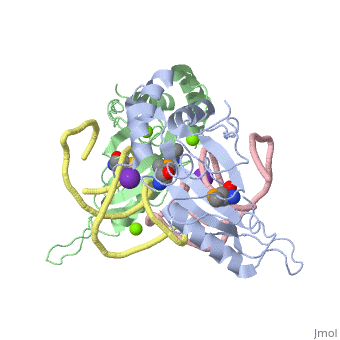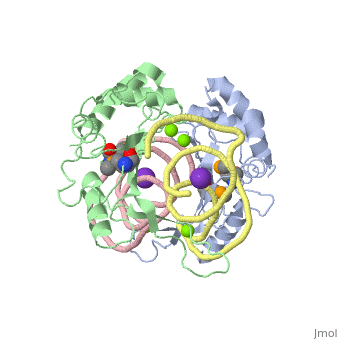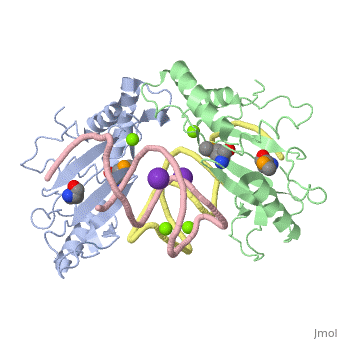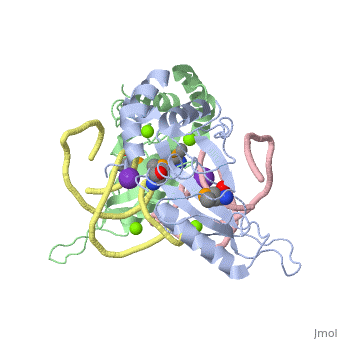
L5/5S rRNA Complex
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wise JP, Leonard JC, Patierno SR. Clastogenicity of lead chromate particles in hamster and human cells. Mutat Res. 1992 Jan;278(1):69-79. PMID:1370121
- ↑ Meskauskas A, Dinman JD. Ribosomal protein L5 helps anchor peptidyl-tRNA to the P-site in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA. 2001 Aug;7(8):1084-96. PMID:11497428
- ↑ Korepanov AP, Korobeinikova AV, Shestakov SA, Garber MB, Gongadze GM. Protein L5 is crucial for in vivo assembly of the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit central protuberance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(18):9153-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks676. Epub 2012 Jul, 20. PMID:22821559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks676
- ↑ Barciszewska MZ, Szymanski M, Erdmann VA, Barciszewski J. Structure and functions of 5S rRNA. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;48(1):191-8. PMID:11440169
- ↑ It is not completely known the extent of its role in ribosomal function, but there have been studies to suggest that the 5S rRNA helps with the binding of the tRNA within the P-site.<ref>PMID:11440169</li> <li id="cite_note-5">[[#cite_ref-5|↑]] Wise JP, Leonard JC, Patierno SR. Clastogenicity of lead chromate particles in hamster and human cells. Mutat Res. 1992 Jan;278(1):69-79. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1370121 1370121] </li> <li id="cite_note-6">[[#cite_ref-6|↑]] Wise JP, Leonard JC, Patierno SR. Clastogenicity of lead chromate particles in hamster and human cells. Mutat Res. 1992 Jan;278(1):69-79. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1370121 1370121] </li> <li id="cite_note-7">[[#cite_ref-7|↑]] doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S1355838202029953</li></ol></ref>