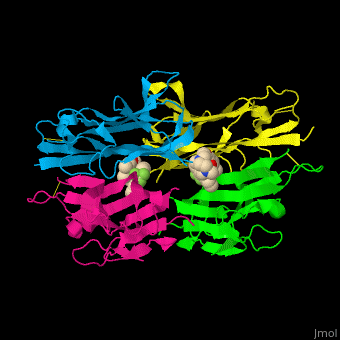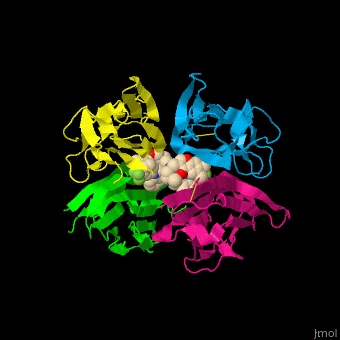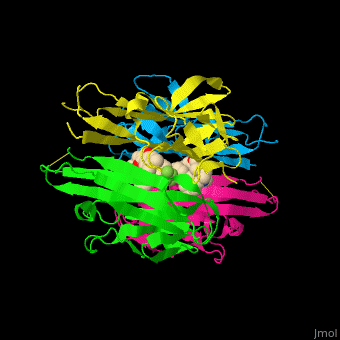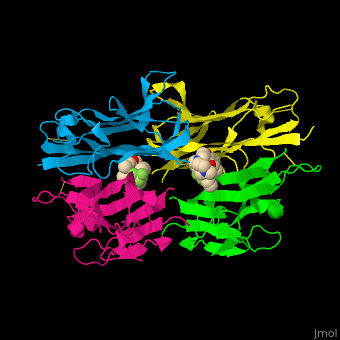We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Tumor necrosis factor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='400' side='right' caption='Structure of human tumor necrosis factor tetramer complex with inhibitor (PDB entry [[2az5]])' scene='55/551212/Cv/1'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Tumor necrosis factor''' (TNF) is a cytokine which can cause apoptosis. '''TNFα''' is implicated in tumor regression, septic shock, inflammation and cachexia (wasting syndrome). It is involved in the regulation of the immune cells<ref>PMID:11514191</ref>. '''TNFβ''' is inhibited by interleukin 10. TNF is a transmembrane homotrimer. The soluble TNF is produced by cleavage by the metalloprotease TNFα-converting enzyme (TACE or ADAM17 see [[A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase]]). | '''Tumor necrosis factor''' (TNF) is a cytokine which can cause apoptosis. '''TNFα''' is implicated in tumor regression, septic shock, inflammation and cachexia (wasting syndrome). It is involved in the regulation of the immune cells<ref>PMID:11514191</ref>. '''TNFβ''' is inhibited by interleukin 10. TNF is a transmembrane homotrimer. The soluble TNF is produced by cleavage by the metalloprotease TNFα-converting enzyme (TACE or ADAM17 see [[A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase]]). | ||
Revision as of 04:01, 16 October 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of tumor necrosis factor
Updated on 16-October-2017
References
- ↑ Baud V, Karin M. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;11(9):372-7. PMID:11514191
- ↑ Balkwill F. Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009 May;9(5):361-71. doi: 10.1038/nrc2628. Epub 2009 Apr 3. PMID:19343034 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc2628