We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Villin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
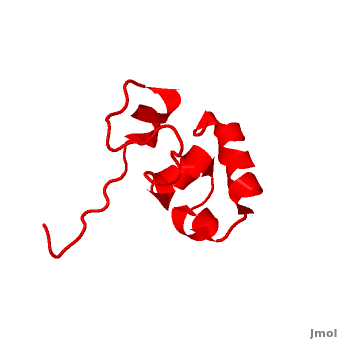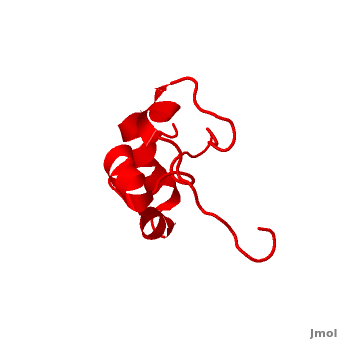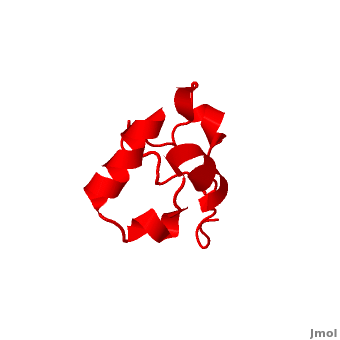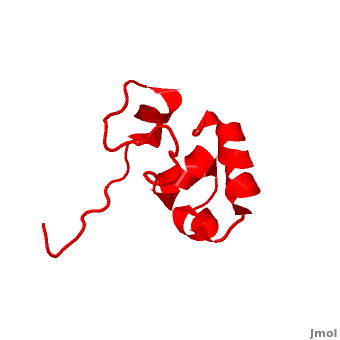
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='340' side='right' caption='Human supervillin headpiece, [[2k6n]]' scene='Villin/Cv/1' > |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
* [[Villin]] (VIL) is an actin-binding protein. It contains gelsolin-like domains in its N-terminal and a helical headpiece which binds actin<ref>PMID:10480879</ref>.<br /> | * [[Villin]] (VIL) is an actin-binding protein. It contains gelsolin-like domains in its N-terminal and a helical headpiece which binds actin<ref>PMID:10480879</ref>.<br /> | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 16 October 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Villin
Updated on 16-October-2017
References
- ↑ Friederich E, Vancompernolle K, Louvard D, Vandekerckhove J. Villin function in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Correlation of in vivo effects to its biochemical activities in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 17;274(38):26751-60. PMID:10480879
- ↑ Shillingford NM, Calicchio ML, Teot LA, Boyd T, Kurek KC, Goldsmith JD, Bousvaros A, Perez-Atayde AR, Kozakewich HP. Villin immunohistochemistry is a reliable method for diagnosing microvillus inclusion disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015 Feb;39(2):245-50. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000355. PMID:25517957 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000000355
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky, Joel L. Sussman