We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Fibrinogen binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
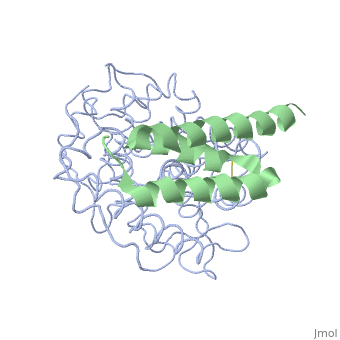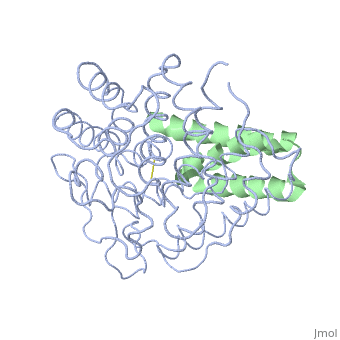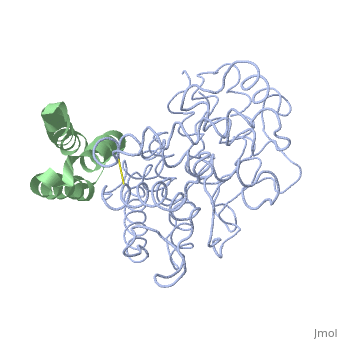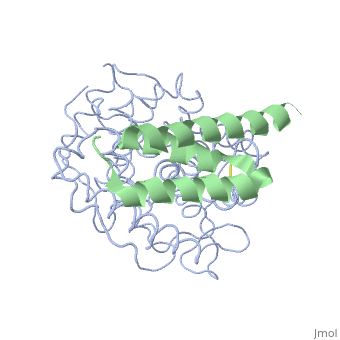
| - | <StructureSection load='2gox' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Efb (green | + | <StructureSection load='2gox' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Efb (green) complex with complement C3 α chain fragment (grey) (PDB entry [[2gox]])' scene=''> |
== Extra cellular fibrinogen binding protein- Efb == | == Extra cellular fibrinogen binding protein- Efb == | ||
'''''Staphylococcous Aureus''''' is a bacterium that is commonly found on human skin and respiratory tracts; however, when it becomes pathogenic it can cause many diseases: skin infections, respiratory diseases(pneumonia), food poisoning. It is a Gram +, cluster forming coccus, non-motile, facultative Anaerobe and a leading cause of nosocomial infection. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Staphylococcus_aureus More about Staph Aureus] | '''''Staphylococcous Aureus''''' is a bacterium that is commonly found on human skin and respiratory tracts; however, when it becomes pathogenic it can cause many diseases: skin infections, respiratory diseases(pneumonia), food poisoning. It is a Gram +, cluster forming coccus, non-motile, facultative Anaerobe and a leading cause of nosocomial infection. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Staphylococcus_aureus More about Staph Aureus] | ||
Revision as of 19:01, 19 October 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of fibrinogen binding protein
Updated on 19-October-2017
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Hammel M, Sfyroera G, Ricklin D, Magotti P, Lambris JD, Geisbrecht BV. A structural basis for complement inhibition by Staphylococcus aureus. Nat Immunol. 2007 Apr;8(4):430-7. Epub 2007 Mar 11. PMID:17351618 doi:10.1038/ni1450
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Rahul Gunasekera, Alexander Berchansky, Jaime Prilusky