Polyneuridine Aldehyde Esterase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='37/373631/Cv/1' caption='Polyneuridine aldehyde esterase complex with vellosimine [[3gzj]]'> |
Plant species that contain alkaloids have been used in traditional medicines for many centuries. Since the identification of the first alkaloid, morphine from Papaver somniferum in 1806, about 20000 alkaloids have been isolated and their structures elucidated. Among these compounds the indole alkaloids are of particular interest due to their rich biological active constitutents which are used as therapeutic agents in various medicines, for example quinine, vincristine and '''ajmaline'''. The latter can be isolated from the Indian medicinal plant ''Rauwolfia serpentina'' (L.) Benth ex Kurz. | Plant species that contain alkaloids have been used in traditional medicines for many centuries. Since the identification of the first alkaloid, morphine from Papaver somniferum in 1806, about 20000 alkaloids have been isolated and their structures elucidated. Among these compounds the indole alkaloids are of particular interest due to their rich biological active constitutents which are used as therapeutic agents in various medicines, for example quinine, vincristine and '''ajmaline'''. The latter can be isolated from the Indian medicinal plant ''Rauwolfia serpentina'' (L.) Benth ex Kurz. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
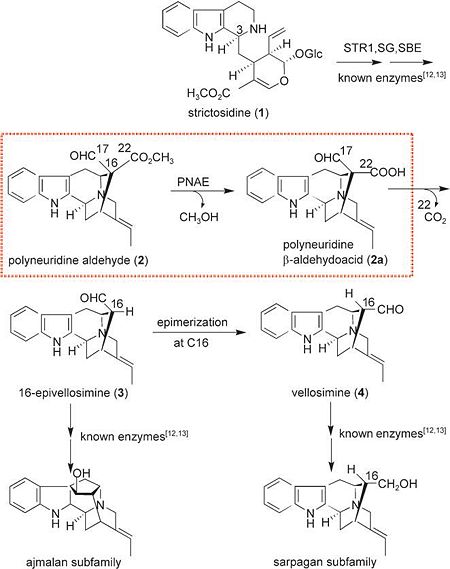
Sequence analysis led to the preliminary classification of '''PNAE''' as a new candidate of the large α/β hydrolase superfamily. This classification is based in particular on the catalytic triad Ser87, Asp216, and His244, which was previously verified by single mutations and homology modeling. | Sequence analysis led to the preliminary classification of '''PNAE''' as a new candidate of the large α/β hydrolase superfamily. This classification is based in particular on the catalytic triad Ser87, Asp216, and His244, which was previously verified by single mutations and homology modeling. | ||
| - | [[Image:F1-1.jpg|left| | + | [[Image:F1-1.jpg|left|350px|thumb]] |
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
The structural data now available for '''PNAE''' support the overall mechanism, which undoubtedly represents the key reaction for the biosynthesis of C9-monoterpenoid ''Rauvolfia'' alkaloids. The data will also allow a rational, structure-based redesign of '''PNAE''', similar what we have recently demonstrated for the Pictet-Spenglerase, strictosidine synthase, which is now applied for chemoenzymatic synthesis of novel alkaloid libraries. | The structural data now available for '''PNAE''' support the overall mechanism, which undoubtedly represents the key reaction for the biosynthesis of C9-monoterpenoid ''Rauvolfia'' alkaloids. The data will also allow a rational, structure-based redesign of '''PNAE''', similar what we have recently demonstrated for the Pictet-Spenglerase, strictosidine synthase, which is now applied for chemoenzymatic synthesis of novel alkaloid libraries. | ||
Revision as of 16:33, 23 October 2017
| |||||||||||
3D structures of polyneuridine aldehyde esterase
2wfm – SePAE (mutant) – Serpentwood
2wfl – SePAE
3gzj – SePAE + 16-epi-vellosimine
References
- ↑ Mattern-Dogru E, Ma X, Hartmann J, Decker H, Stockigt J. Potential active-site residues in polyneuridine aldehyde esterase, a central enzyme of indole alkaloid biosynthesis, by modelling and site-directed mutagenesis. Eur J Biochem. 2002 Jun;269(12):2889-96. PMID:12071952
- ↑ Yang L, Hill M, Wang M, Panjikar S, Stockigt J. Structural basis and enzymatic mechanism of the biosynthesis of C9- from C10-monoterpenoid indole alkaloids. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009;48(28):5211-3. PMID:19496101 doi:10.1002/anie.200900150
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Alexander Berchansky, Michal Harel, Liuqing Yang, Joel L. Sussman