We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Pyruvate phosphate dikinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
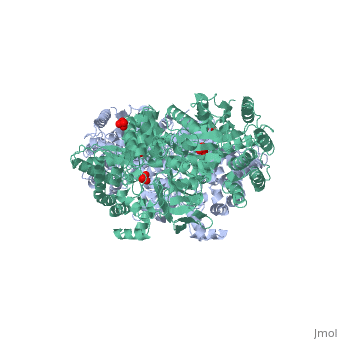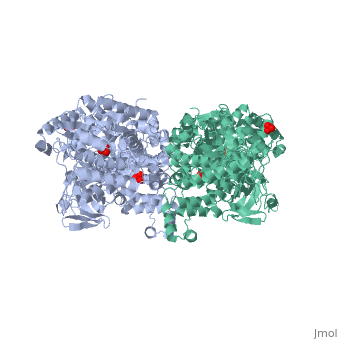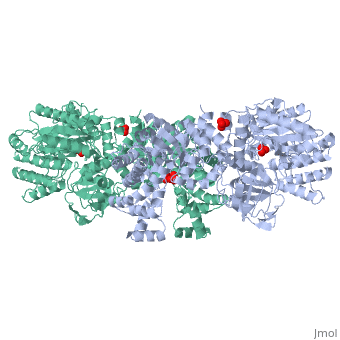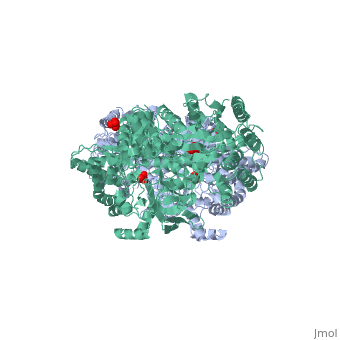
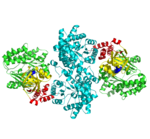
[[Image:1KBL dimer.png|left|150px|''PPDK dimer'']]<br />PPDK assembles into homodimers of ~95 kD subunit molecular mass. The monomer is comprised of three domains and contains two distinct reaction centers located ~45 Å apart; the PEP/pyruvate partial reaction (step 1) takes place at the C-terminal domain (adopting an α/β barrel fold) and the nucleotide and inorganic phosphate partial reactions (steps 2 and 3) take place at the N-terminal domain (adopting the ATP grasp fold with two sub domains). A central domain, tethered to the N- and C-terminal domains by two closely-associated linkers, contains a phosphorylatable histidine residue (His455). To shuttle the phosphoryl group between the two reaction centers, the His-domain undergoes domain motion of ~110° swivel around the two linkers. In addition, upon detachment from the His-domain, the two nucleotide-binding sub domains undergo a ~40° hinge motion that opens the active site cleft. | [[Image:1KBL dimer.png|left|150px|''PPDK dimer'']]<br />PPDK assembles into homodimers of ~95 kD subunit molecular mass. The monomer is comprised of three domains and contains two distinct reaction centers located ~45 Å apart; the PEP/pyruvate partial reaction (step 1) takes place at the C-terminal domain (adopting an α/β barrel fold) and the nucleotide and inorganic phosphate partial reactions (steps 2 and 3) take place at the N-terminal domain (adopting the ATP grasp fold with two sub domains). A central domain, tethered to the N- and C-terminal domains by two closely-associated linkers, contains a phosphorylatable histidine residue (His455). To shuttle the phosphoryl group between the two reaction centers, the His-domain undergoes domain motion of ~110° swivel around the two linkers. In addition, upon detachment from the His-domain, the two nucleotide-binding sub domains undergo a ~40° hinge motion that opens the active site cleft. | ||
<br>PEP-binding domain - cyan; nucleotide binding domain - green; His-domain - yellow; domain linkers -red; phosphorylatable His455 - blue spheres|200px]] | <br>PEP-binding domain - cyan; nucleotide binding domain - green; His-domain - yellow; domain linkers -red; phosphorylatable His455 - blue spheres|200px]] | ||
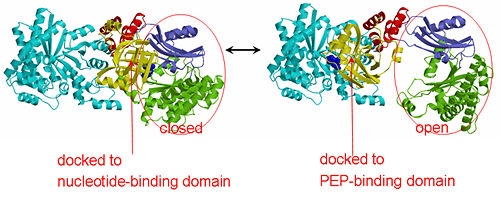
| - | '''The His-domain in the two conformational states of PPDK. His455 is shown in blue spheres:'''[[Image:two_cond.jpg|center|500px]]<br> | + | '''The His-domain in the two conformational states of PPDK. His455 is shown in blue spheres:'''[[Image:two_cond.jpg|center|500px]]<br> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<p align="center"><html5media width="500" height="281" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen>https://www.youtube.com/embed/hxuBouGfs_4</html5media></p> | <p align="center"><html5media width="500" height="281" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen>https://www.youtube.com/embed/hxuBouGfs_4</html5media></p> | ||
'''''The movie''' depicts the catalytic reaction involving 3 in-line phosphotransfers & the accompanied protein conformational transitions. Model based on crystal structures of PPDK from '''Clostridium symbiosum''' in the 2 extreme conformational states shown to the left and of complexes bound to substrate analogs, phosphonopyruvate and 5'-adenylyl-β,γ-imidodiphosphate (AMPPNP). The nucleotide binding subdomains are colored green & blue, PEP binding domain colored cyan, His-domain colored yellow, and linker segments that connect the His-domain to the partner domains colored red. Ligands and the catalytic histidine are depicted in stick models with the atomic color scheme: '''''C''''' – gray, '''''N''''' – blue, '''''O''''' – red, '''''P''''' – green, '''''Mg''''' – magenta. Note that the reaction progresses in the movie in the reverse direction; steps 3 and 2 occur first followed by step 1. The movie was created by Kap Lim and Osnat Herzberg''<br> | '''''The movie''' depicts the catalytic reaction involving 3 in-line phosphotransfers & the accompanied protein conformational transitions. Model based on crystal structures of PPDK from '''Clostridium symbiosum''' in the 2 extreme conformational states shown to the left and of complexes bound to substrate analogs, phosphonopyruvate and 5'-adenylyl-β,γ-imidodiphosphate (AMPPNP). The nucleotide binding subdomains are colored green & blue, PEP binding domain colored cyan, His-domain colored yellow, and linker segments that connect the His-domain to the partner domains colored red. Ligands and the catalytic histidine are depicted in stick models with the atomic color scheme: '''''C''''' – gray, '''''N''''' – blue, '''''O''''' – red, '''''P''''' – green, '''''Mg''''' – magenta. Note that the reaction progresses in the movie in the reverse direction; steps 3 and 2 occur first followed by step 1. The movie was created by Kap Lim and Osnat Herzberg''<br> | ||
Revision as of 16:46, 23 October 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of PPDK
Updated on 23-October-2017
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Osnat Herzberg, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky, Alexander Berchansky, Dan Bolser, Karl Oberholser, David Canner, Eran Hodis