Introduction
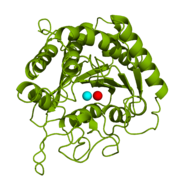
Figure 1: Catalytic and inhibitory Zn
2+ ions in the active site of CPA. The catalytic and inhibitory Zn
2+ ions are shown in cyan and red, respectively. PDB code:
1CPX.
is a metalloexopeptidase whose biological function is to cleave the C-terminal amino acid residue from polypeptide substrates.[1] Specifically, CPA is one member of a large group of Zn2+ metalloenzymes that carries out the hydrolysis of C-terminal polypeptide residues through the deprotonation of a water molecule that is coordinated to the Zn2+ ion in the enzyme's active site.[2] CPA consists of a single polypeptide chain that contains 307 amino acids. Produced in the pancreas, CPA itself must first be modified by trypsin and chymotrypsin in order to achieve an active form that serves its biological function.[1] Although different biologically active forms of CPA are found across different species, including humans, much research has investigated bovine pancreatic zinc carboxypeptidase A. X-ray crystallography has demonstrated that bovine CPA has the ability to bind two Zn2+ ions in its active site, in which the binding of one Zn2+ ion is catalytic (shown in cyan), while the binding of a second Zn2+ ion (shown in red) inhibits the hydrolysis reaction (Figure 1).[1] An example crystal structure for active CPA in which one Zn2+ ion is bound has been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) database as 3CPA. An inhibited CPA in which two Zn2+ ions are bound has been deposited under the label 1CPX.
Structure
Bovine CPA exists as a monomeric unit with C1 symmetry in the pancreatic physiological environment. The single polypeptide chain of CPA contains a mixture of ; the helices are shown in magenta whereas the β-sheets are displayed in yellow. A disulfide bond connects the residues Cys138 and Cys161, which can be seen in yellow in the .
Six different biologically active forms of the CPA monomeric unit exist. are produced following the cleavage of amino acid residue segments from the initial zymogen, or proenzyme, by trypsin and chymotrypsin, which are also found in the pancreas. Cleavage by trypsin generates either the α-form (residues Ala1-Asn307) or the β-form (residues Ser3-Asn307). Chymotrypsin cleavage generates the γ-form (residues Asn8-Asn307). The α-form essentially is the protein without any additional residue cleavages. The Ala and Arg residues, shown in red and white respectively, are cleaved in the β-form. In addition to the red and white residues, the residues displayed in cyan are cleaved to give the γ-form. The of CPA arise from genetic variation in residues located at three separate positions on the polypeptide chain. The differences include the following: Ile/Val179 (red), Ala/Glu228 (cyan), and Val/Leu305 (white). Each of the six biologically active monomeric units carry out the same function of hydrolyzing the C-terminal peptide bond of a polypeptide substrate.
Active Site
The active site of bovine pancreatic CPA is embedded within a (shown in orange); the deep pocket's opening is located on the surface of the protein. Kinetics experiments have indicated that the binding region of the active site is actually capable of extending over five amino acids of the substrate.[2] When no polypeptide substrate is bound in the active site, the pocket is open. However, the pocket is (see section titled "Important Tyr248 Residue") when a substrate or inhibitor molecule binds.[2] In this view, the Tyr248 is shown in magenta. The active site contains two separate subsites, labeled S1' and S1, each of which contain several pertinent residues that serve important roles during the catalyzed hydrolysis reaction.
The Hydrophobic Binding Pocket: S1' Subsite
The (spacefill view, subsite in green) contains multiple hydrophobic residues that interact by van der Walls forces with C-terminal hydrophobic side chains of polypeptide substrates. For this reason, the S1' subsite is referred to as the (pseudo-mesh view, subsite in green). It should be of note that the S1' subsite, despite being named as a hydrophobic pocket, is not another pocket in addition to the deep pocket active site. Rather, it is simply a particular region of the deep pocket. Specifically, the hydrophobic pocket includes the residues . The hydrophobic nature of the S1' subsite assists in establishing some degree of specificity for CPA. Because the hydrophobic pocket anchors the polypeptide substrate in the active site, the larger and more hydrophobic the side chain of the C-terminal substrate residue, the stronger the van der Walls interactions between the subsite and the substrate. Therefore, the stability of substrate binding is increased when residues like phenylalanine are present at the C-terminus. Essentially, the S1' subsite serves as a recognition site for the C-terminal side chain of the substrate.[1]
S1 Subsite
In the same way that the S1' subsite is involved in anchoring the polypeptide substrate in place, the (spacefill view, subsite in magenta) contains several residues that help hold the substrate in the active site, but the S1 subsite also contains the residues that are involved in the catalytic chemical mechanism. In general, the residues of the (pseudo-mesh view, subsite in magenta) have polar or charged side chains that either allow for hydrogen bonding to stabilize negatively charged intermediates of the hydrolysis reaction or position particular atoms appropriately to allow for chemistry to occur. Three residues () aid in the recognition of the C-terminal residue of a polypeptide substrate.[1] The Asn144 and Tyr248 residues each engage in hydrogen bonding and ion-dipole interactions with the carboxyl group at the C-terminus, while Arg145 provides additional stability by participating in ion-ion interactions with the carboxyl group (see Figure 3 in the section titled "Mechanism of Action"). helps stabilize the substrate in the active site by engaging in ion-dipole interactions with the carbonyl oxygen of the penultimate substrate residue (Figure 3). Three residues () are liganded to a catalytic Zn2+ ion that is complexed to a water molecule positioned one bond distance away from the C-terminal peptide bond carbonyl carbon (Figure 3). This gives the Zn2+ ion a tetrahedral binding configuration.[2] deprotonates this water molecule and acts as a base catalyst in the hydrolysis mechanism (Figure 3). and the positively charged Zn2+ ion help stabilize the negatively charged intermediate generated in the addition-elimination step of the hydrolysis reaction (Figure 3).[2]
Putting It All Together
For a 3D manipulative applet displaying the essential amino acid residues and their interactions with a bound ligand, . The hydrophobic binding pocket (shown in yellow) can be seen interacting with a phenylalanine side chain of the C-terminal amino acid. The Zn2+ ion (shown in cyan) is held in place by the three side chains mentioned previously (shown in green). The Tyr248 side chain is explicitly shown in magenta and is "capping" the pocket since a substrate is bound. The base catalyst, Glu270, is explicitly shown in orange. The other side chains in the darker blue color are part of the stabilizing side chains of the S1 subsite. Manipulate the scene manually, and zoom in and out to see the interactions between CPA's side chains and the bound substrate. This crystal structure with the bound ligand, which is actually a phosphonate, has been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) with code 6CPA.
Important Tyr248 Residue
CPA from
B. taurus has been co-crystallized with two Zn
2+ ions (Figure 1). This structure has been deposited in the PDB database under the label
1CPX, which is a β-form of CPA. 1CPX has an interesting distinction from some other crystallized CPA proteins in that its crystallographic data has revealed a different conformation of the Tyr248 residue.
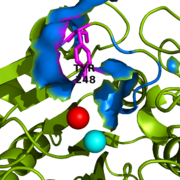
Figure 2: Important Tyr248 residue (shown in magenta) of 1CPX is capping the hydrophobic binding pocket (shown in blue) when liganded to a second inhibitory zinc ion (shown in red).
Previous literature has suggested that the conserved tyrosine residue among CPA proteins has been involved in an
induced fit mechanism, as Tyr248 has typically been found toward solution when a substrate is not bound in the active site.
[1] However, crystallographic data for 1CPX shows Tyr248 (Figure 2) without a polypeptide substrate bound. Therefore, this contradicts the previously proposed induced fit mechanism for CPA proteins, and suggests that Tyr248 is liganded to the catalytic Zn
2+ ion in 1CPX.
[1] Not only does Tyr248 point toward the active site, but in doing so, Tyr248 (shown in blue) through its and a hydrogen bond (see Figure 3 for Tyr248 hydrogen bonding interactions).
[1] This point of view demonstrates how Tyr248 is thought to be a ligand with the catalytic Zn
2+ ion.
Mechanism of Action
Two chemical mechanisms have been proposed for the hydrolysis reaction catalyzed by CPA. One mechanism, referred to as the nucleophilic pathway, involves a covalent acyl enzyme intermediate (an anhydride intermediate) containing Glu270, the active site base.[2] Although there is some chemical and kinetic support for the nucleophilic pathway, the evidence is mixed and ambiguous. In one set of experiments conducted by Suh and his colleagues in 1985, accumulation of an intermediate (assumed to be the acyl enzyme) was obtained; however, the intermediate was isolated without confirmation by trapping experiments. Therefore, the conclusions of the study only provide marginal evidence for the mixed anhydride intermediate.[3]
The second mechanism, which has been coined as the promoted water pathway, is better supported by chemical and structural data. The mechanism of the reaction (Figure 3) is as follows:
- Three S1 subsite residues () and the recognize the C-terminus of the polypeptide substrate.
- After aiding in the recognition of the substrate, .
- The engage in ion-dipole interactions with the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group of the C-terminal peptide bond, further polarizing the carbon to oxygen double bond (see Figure 3).
- A water molecule, which has been deprotonated by (base catalyst) and is being held in place one bond distance away from the partially positive carbon of the C-terminal carbonyl, acts as a nucleophile and attacks this carbon to generate a tetrahedral intermediate stabilized by both the Zn2+ ion and surrounding positive charges of S1 subsite residues. A water molecule was not crystallized in the active site of 3CPA. It has been displayed, however, in Figure 3 for reference.
- The peptide bond is cleaved through an addition-elimination step.
- The Glu270 base catalyst is regenerated through a final proton transfer with the nitrogen atom of the former C-terminal peptide bond.
- Product release is facilitated, in part, by unfavorable electrostatic interactions between the regenerated Glu270 base catalyst and the deprotonated carboxylic acid at the new C-terminus.
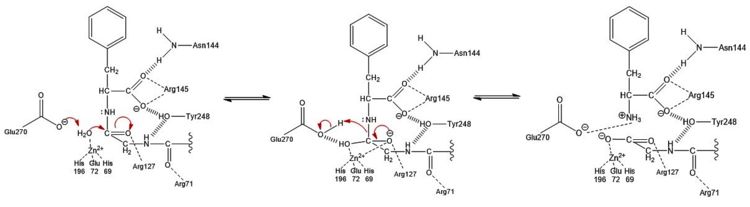
Figure 3: Hydrolysis of C-terminal polypeptide substrate residue by CPA using the promoted water pathway. Residues of the S1 subsite stabilize the negatively charged intermediate once the water molecule complexed with the Zn
2+ ion is deprotonated by the base catalyst, Glu270, and attacks the carbonyl. This figure is derived from Figure 10 in "Carboxypeptidase A" by Christianson and Lipscomb (
Acc. Chem. Res., 1989).
[2] Catalytic and Inhibitory Zinc Binding
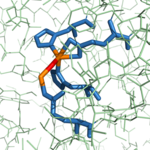
Figure 4: Hydroxy-bridge between catalytic and inhibitory zinc ions. The catalytic Zn
2+ ion (shown in orange on the right) is bridged to the inhibitory Zn
2+ ion (shown in orange on the left) by a OH
- (shown in red).
As previously stated, from B. taurus has the ability to bind two Zn2+ ions in its active site. The binding of only one Zn2+ ion is catalytic, while the binding of a second is inhibitory. These Zn2+ ions are connected to each other via a hydroxy-bridge (Figure 4) with a distance of 3.48 Å.[1] The catalytic Zn2+ ion maintains its tetrahedral binding configuration just as if the inhibitory Zn2+ ion was not bound. In the CPA structure containing only the catalytic Zn2+ ion (3CPA), a water molecule complexed to the zinc is able to be deprotonated by , allowing normal initiation of hydrolysis. Again, this water molecule was not crystallized in the structure of 3CPA, but it is shown in Figure 3. However, when is also present (1CPX), it occupies the physical space that would normally be occupied by the water molecule. Thus, the inhibitory Zn2+ ion interacts with the carboxylate group of Glu270. The Glu270 (shown in yellow) now simply stabilizes the second Zn2+ ion and is unable to perform its usual base catalyst role; the catalytic Zn2+ ion (shown in cyan) is still being stabilized in place by His69, Glu72, and His196 (shown in orange).
Carboxypeptidase A has been chemically modified and kinetically assayed to determine its Zn2+ ion kinetic binding constants. Literature shows the Kd value of the catalytic Zn2+ ion to be two orders of magnitude less than the Kd value of the inhibitory Zn2+ ion (Kd = 2.6x10-6M for the catalytic Zn2+ ion and 5.5x10-4M for inhibitory Zn2+ ion; pH = 8.2). This signifies that the catalytic Zn2+ ion is approximately one hundred times more likely to bind to CPA compared to the inhibitory Zn2+ ion.[4]
Other Inhibitors
In addition to the inhibitory Zn2+ ion, CPA can be inhibited by other ions and molecules. Some of these inhibitors include, but are not limited to, other metal ions and anions,[5] phosphonates,[6] cysteine, sulfides, and cyanide, the chelating agent 1,10-pentathroline,[7] Ochratoxin A,[8] and Latexin.[9]
Further detailed studies of anions have indicated that the nature of anion inhibition in the binding site is partly competitive.[1] In particular, the sulfate anion (SO42-) has been of interest to researchers. In a crystallized structure of carboxypeptidase T (PDB code: 1ORD), a SO42- anion was found occupying a portion of a region that corresponds to the amino acid residues Arg127, Asn144, Arg145, and Tyr248 of the S1 subsite of carboxypeptidase A.[1] In this case, it is understood that the SO42- anion prevents the recognition of the carboxylate group at the C-terminus of the polypeptide substrate.




