User:Brittany Allen/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <Structure load='2bka' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
==General Background Information== | ==General Background Information== | ||
TIP30, also known as both CC3<ref>1</ref>. and HTATIP<ref>2</ref> is a tat-interacting protein that functions as a tumor suppressor involved in cell growth, apoptosis, metastasis, DNA repair, metabolism and angiogenesis of tumor cells<ref>3,4,5</ref>. TIP30 acts as a transcription cofactor that can regulate gene expression<ref> 6</ref> and has both pro-apoptotic and anti-metastatic properties<ref>7</ref>. When the promoter of TIP30 is methylated, TIP30 becomes downregulated and associated with tumor prognosis<ref>2</ref>. It is thought that the tumor suppressor effect is the result of the inhibition of nuclear transport through binding with importin βs or by regulating transcription through interaction as a complex with a co-activator independent of AF-2 function and the c-myc gene<ref>8</ref>. Several studies have found that TIP30 may be linked to esophageal carcinoma, laryngeal carcinoma, glioma, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, breast cancer, gastric cancer, gallbladder adenocarcinoma, lung cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma<ref>1</ref>. | TIP30, also known as both CC3<ref>1</ref>. and HTATIP<ref>2</ref> is a tat-interacting protein that functions as a tumor suppressor involved in cell growth, apoptosis, metastasis, DNA repair, metabolism and angiogenesis of tumor cells<ref>3,4,5</ref>. TIP30 acts as a transcription cofactor that can regulate gene expression<ref> 6</ref> and has both pro-apoptotic and anti-metastatic properties<ref>7</ref>. When the promoter of TIP30 is methylated, TIP30 becomes downregulated and associated with tumor prognosis<ref>2</ref>. It is thought that the tumor suppressor effect is the result of the inhibition of nuclear transport through binding with importin βs or by regulating transcription through interaction as a complex with a co-activator independent of AF-2 function and the c-myc gene<ref>8</ref>. Several studies have found that TIP30 may be linked to esophageal carcinoma, laryngeal carcinoma, glioma, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, breast cancer, gastric cancer, gallbladder adenocarcinoma, lung cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma<ref>1</ref>. | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | [[Image: pymol spin shape |300px|right|thumb| Image 1. ]] | ||
| - | |||
TIP30 is an evolutionary conserved gene located on human chromosome 11<ref>1</ref> . TIP30 has a molecular mass of 30 kd<ref>6</ref> and is composed of 242 amino acids<ref> 1 </ref>. TIP30 is composed of alpha helices, beta sheets, and loops (Movie). Through sequence analysis studies, it is thought that TIP30 may be a member of the SDR (substrate determining residue) family which contain a characteristic motif at their catalytic start sites<ref> 1 </ref>. The carboxyl terminus of TIP30 binds to the SDR substrate, while the amino terminus of TIP30 is the nucleotide cofactor-binding domain which has a characteristic Gly-X-X-Gly- X-X-Gly motif (where X can be any amino acid)<ref> 1 </ref>. Since SDR families have binding specificity for NADPH<ref> 8 </ref> and TIP30 contains a dehydrogenase reductase fold that contains binding specificity for NADPH<ref> 1 </ref>., the binding of NADPH may be important for the biological activity of TIP30 including interactions with importins as well as the c-myc system<ref> 8 </ref>. | TIP30 is an evolutionary conserved gene located on human chromosome 11<ref>1</ref> . TIP30 has a molecular mass of 30 kd<ref>6</ref> and is composed of 242 amino acids<ref> 1 </ref>. TIP30 is composed of alpha helices, beta sheets, and loops (Movie). Through sequence analysis studies, it is thought that TIP30 may be a member of the SDR (substrate determining residue) family which contain a characteristic motif at their catalytic start sites<ref> 1 </ref>. The carboxyl terminus of TIP30 binds to the SDR substrate, while the amino terminus of TIP30 is the nucleotide cofactor-binding domain which has a characteristic Gly-X-X-Gly- X-X-Gly motif (where X can be any amino acid)<ref> 1 </ref>. Since SDR families have binding specificity for NADPH<ref> 8 </ref> and TIP30 contains a dehydrogenase reductase fold that contains binding specificity for NADPH<ref> 1 </ref>., the binding of NADPH may be important for the biological activity of TIP30 including interactions with importins as well as the c-myc system<ref> 8 </ref>. | ||
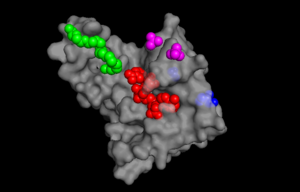
[[Image: pymol ligand pic.png |300px|left|thumb| Figure 1. The binding sites of TIP30 as identified using PYMOL.]] | [[Image: pymol ligand pic.png |300px|left|thumb| Figure 1. The binding sites of TIP30 as identified using PYMOL.]] | ||
Revision as of 02:14, 4 December 2017
|
Contents |
General Background Information
TIP30, also known as both CC3[1]. and HTATIP[2] is a tat-interacting protein that functions as a tumor suppressor involved in cell growth, apoptosis, metastasis, DNA repair, metabolism and angiogenesis of tumor cells[3]. TIP30 acts as a transcription cofactor that can regulate gene expression[4] and has both pro-apoptotic and anti-metastatic properties[5]. When the promoter of TIP30 is methylated, TIP30 becomes downregulated and associated with tumor prognosis[6]. It is thought that the tumor suppressor effect is the result of the inhibition of nuclear transport through binding with importin βs or by regulating transcription through interaction as a complex with a co-activator independent of AF-2 function and the c-myc gene[7]. Several studies have found that TIP30 may be linked to esophageal carcinoma, laryngeal carcinoma, glioma, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, breast cancer, gastric cancer, gallbladder adenocarcinoma, lung cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma[8].
Structure
TIP30 is an evolutionary conserved gene located on human chromosome 11[9] . TIP30 has a molecular mass of 30 kd[10] and is composed of 242 amino acids[11]. TIP30 is composed of alpha helices, beta sheets, and loops (Movie). Through sequence analysis studies, it is thought that TIP30 may be a member of the SDR (substrate determining residue) family which contain a characteristic motif at their catalytic start sites[12]. The carboxyl terminus of TIP30 binds to the SDR substrate, while the amino terminus of TIP30 is the nucleotide cofactor-binding domain which has a characteristic Gly-X-X-Gly- X-X-Gly motif (where X can be any amino acid)[13]. Since SDR families have binding specificity for NADPH[14] and TIP30 contains a dehydrogenase reductase fold that contains binding specificity for NADPH[15]., the binding of NADPH may be important for the biological activity of TIP30 including interactions with importins as well as the c-myc system[16].
TIP30 is known to bind 4 ligands: NDP (NADPH Dihydro-nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide-phosphate), PE8 (3,6,9,12,15,18,21 heptatricosane-1,2,3-diol), GOL (glycerol), and SO4 (sulfate ion)[17]. The location these residues bind can be seen in ________. According to uniprot, TIP30 contains a nucleotide binding region between residues 19-52, as shown in ________, and a binding site at residue 131, as shown in______. When comparing _____ and ________, it can be observed that the ligands bind in the active regions and interact with the residues. Uniprot also noted that TIP30 can contain a mutagenic site at positions 28-31 (______), if this site is present there is a loss of proapoptotic and metastasis-inhibiting effects.
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
</StructureSection>