User:Brittany Allen/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
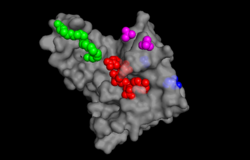
[[Image: pymol ligand pic.png |250px|left|thumb| Image 1. The binding sites of TIP30 as identified using PYMOL.]] | [[Image: pymol ligand pic.png |250px|left|thumb| Image 1. The binding sites of TIP30 as identified using PYMOL.]] | ||
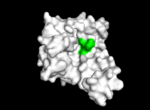
TIP30 is an evolutionary conserved gene located on human chromosome 11<ref>1</ref> . TIP30 has a molecular mass of 30 kd<ref>6</ref> and is composed of 242 amino acids<ref> 1 </ref>. TIP30 is composed of alpha helices, beta sheets, and loops. Through sequence analysis studies, it is thought that TIP30 may be a member of the SDR (substrate determining residue) family which contain a characteristic motif at their catalytic start sites<ref> 1 </ref>. The carboxyl terminus of TIP30 binds to the SDR substrate, while the amino terminus of TIP30 is the nucleotide cofactor-binding domain which has a characteristic Gly-X-X-Gly- X-X-Gly motif (where X can be any amino acid)<ref> 1 </ref>. Since SDR families have binding specificity for NADPH<ref> 8 </ref> and TIP30 contains a dehydrogenase reductase fold that contains binding specificity for NADPH<ref> 1 </ref>., the binding of NADPH may be important for the biological activity of TIP30 including interactions with importins as well as the c-myc system<ref> 8 </ref>. [[Image: resi19-52 site.png |150px|right|thumb| Image 2. TIP30 displayed showing residues 19-52.]] | TIP30 is an evolutionary conserved gene located on human chromosome 11<ref>1</ref> . TIP30 has a molecular mass of 30 kd<ref>6</ref> and is composed of 242 amino acids<ref> 1 </ref>. TIP30 is composed of alpha helices, beta sheets, and loops. Through sequence analysis studies, it is thought that TIP30 may be a member of the SDR (substrate determining residue) family which contain a characteristic motif at their catalytic start sites<ref> 1 </ref>. The carboxyl terminus of TIP30 binds to the SDR substrate, while the amino terminus of TIP30 is the nucleotide cofactor-binding domain which has a characteristic Gly-X-X-Gly- X-X-Gly motif (where X can be any amino acid)<ref> 1 </ref>. Since SDR families have binding specificity for NADPH<ref> 8 </ref> and TIP30 contains a dehydrogenase reductase fold that contains binding specificity for NADPH<ref> 1 </ref>., the binding of NADPH may be important for the biological activity of TIP30 including interactions with importins as well as the c-myc system<ref> 8 </ref>. [[Image: resi19-52 site.png |150px|right|thumb| Image 2. TIP30 displayed showing residues 19-52.]] | ||
| + | |||
TIP30 is known to bind 4 ligands: NDP (NADPH Dihydro-nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide-phosphate), PE8 (3,6,9,12,15,18,21 heptatricosane-1,2,3-diol), GOL (glycerol), and SO4 (sulfate ion)<ref> 9 </ref>. The location these residues bind can be seen in image 1. According to Uniprot, TIP30 contains a nucleotide binding region between residues 19-52, as shown in image 2. and a binding site at residue 131. When comparing images 1 and 2, it can be observed that the ligands bind in the active regions and interact with the residues. Uniprot also noted that TIP30 can contain a mutagenic site at positions 28-31 (image 3), [[Image: resi 28-31 mutagenesis.png |150px|left|thumb| Image 3. Mutagenesis]]if this site is present there is a loss of proapoptotic and metastasis-inhibiting effects. | TIP30 is known to bind 4 ligands: NDP (NADPH Dihydro-nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide-phosphate), PE8 (3,6,9,12,15,18,21 heptatricosane-1,2,3-diol), GOL (glycerol), and SO4 (sulfate ion)<ref> 9 </ref>. The location these residues bind can be seen in image 1. According to Uniprot, TIP30 contains a nucleotide binding region between residues 19-52, as shown in image 2. and a binding site at residue 131. When comparing images 1 and 2, it can be observed that the ligands bind in the active regions and interact with the residues. Uniprot also noted that TIP30 can contain a mutagenic site at positions 28-31 (image 3), [[Image: resi 28-31 mutagenesis.png |150px|left|thumb| Image 3. Mutagenesis]]if this site is present there is a loss of proapoptotic and metastasis-inhibiting effects. | ||
Revision as of 02:54, 4 December 2017
|
Contents |
General Background Information
TIP30, also known as both CC3[1]. TIP30 acts as a transcription cofactor that can regulate gene expression[2] and has both pro-apoptotic and anti-metastatic properties[3]. When the promoter of TIP30 is methylated, TIP30 becomes downregulated and associated with tumor prognosis[4]. It is thought that the tumor suppressor effect is the result of the inhibition of nuclear transport through binding with importin βs or by regulating transcription through interaction as a complex with a co-activator independent of AF-2 function and the c-myc gene[5]. Several studies have found that TIP30 may be linked to esophageal carcinoma, laryngeal carcinoma, glioma, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, breast cancer, gastric cancer, gallbladder adenocarcinoma, lung cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma[6].
Structure
TIP30 is an evolutionary conserved gene located on human chromosome 11[7] . TIP30 has a molecular mass of 30 kd[8] and is composed of 242 amino acids[9]. TIP30 is composed of alpha helices, beta sheets, and loops. Through sequence analysis studies, it is thought that TIP30 may be a member of the SDR (substrate determining residue) family which contain a characteristic motif at their catalytic start sites[10]. The carboxyl terminus of TIP30 binds to the SDR substrate, while the amino terminus of TIP30 is the nucleotide cofactor-binding domain which has a characteristic Gly-X-X-Gly- X-X-Gly motif (where X can be any amino acid)[11]. Since SDR families have binding specificity for NADPH[12] and TIP30 contains a dehydrogenase reductase fold that contains binding specificity for NADPH[13]., the binding of NADPH may be important for the biological activity of TIP30 including interactions with importins as well as the c-myc system[14].
Function
TIP30 is found in both the cell nucleus and cytoplasm[16] and functions in a variety of cellular processes including apoptosis, proliferation, metastasis, angiogenesis, DNA damage repair, and metabolic adaptation.[17] In normal cell growth, TIP30 regulates DNA replication and repair. Stress activates TIP30 to regulate cell proliferation through cell cycle arrest, senescence, and apoptosis to prevent tumor formation. In this manner, TIP30 can act as a tumor-suppressor gene of Type I (caretaker) or a Type 2 (gatekeeper) to prevent mutagenesis.[18] Type I tumor-suppressor genes work by repairing damaged DNA while Type 2 halt the cell cycle to allow time to fix the DNA.[19]
TIP30 Tumor Suppressive Functions
TIP30 regulates apoptosis
TIP30 has proapoptotic activity. In certain types of cancer, TIP30 will be overexpressed and cause the cells to undergo apoptosis.1 TIP30 can also enhance the expression of p53, another tumor suppressor that can inhibit cell growth.[20]
TIP30 regulates proliferation
In a study done with HCC cells, when TIP30 is expressed with increased levels of p53, and decreased levels of Bcl-2, and combined with cytotoxic drug 5-fluorouracil treatment, tumor growth was suppressed, implicating TIP30 to play a role in suppressing tumor proliferation.[21]
TIP30 regulates metastasis
TIP30 can inhibit metastasis through two mechanisms: one is through an apoptosis-inducing effect, and second through an angiogenesis-inhibiting effect.[22]
TIP30 regulates angiogenesis
In vitro experiments have demonstrated that TIP30 can induce changes in RNA levels of angiogenic-modulating factors that reduce angiogenesis.[23] In an in vitro experiment using both macro and microvascular origin tumor cells, angiogenic stimulator angiopoietin I was reduced while angiogenic inhibitors had increased expression, indicating that TIP30 uses angiogenic modulators to inhibit angiogenesis.[24]
TIP30 controls gene expression
TIP30 is a gene transcription factor that uses tat proteins and RNA polymerase II.[25] TIP30 can mediate tumor suppressive regulation by directly affecting the transcription of genes in the nucleus or by indirectly changing the signal transduction pathways in the cytoplasm or inhibiting nuclear import of proteins.[26] TIP30 also plays a role in the regulation of EGFR, a protein that plays a role in the pathogenesis of human cancers.[27]
TIP30 regulates tumor cell metabolism
In an experiment with silenced TIP30 in HeLa cells, the researchers were able to demonstrate that in the silence of TIP30, tumor cells can thrive in a low glucose setting.[28] When TIP30 is absent, mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation of glucose is low.[29] The silencing of TIP30 in tumor cells is dependent on glycolysis to give the cells flexibility to use both OXPHOS and glycolysis for metabolism.[30]